Chapter 3
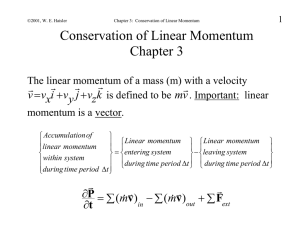
... Chapter 3 The linear momentum of a mass (m) with a velocity v vxi v y j vzk is defined to be mv . Important: linear momentum is a vector. ...
... Chapter 3 The linear momentum of a mass (m) with a velocity v vxi v y j vzk is defined to be mv . Important: linear momentum is a vector. ...
Motion, Newtons` laws, Impulse Mechanics Kinetics, kinematics
... All of the bodies are in resting state or consistently move on linear way, until an other body change it. F=0 Mass: is the quantity of disability. Kinetics studies the interaction of bodies. The reference is the inertionsystem. ...
... All of the bodies are in resting state or consistently move on linear way, until an other body change it. F=0 Mass: is the quantity of disability. Kinetics studies the interaction of bodies. The reference is the inertionsystem. ...
P2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... The forces which cause the change in speed do so by doing work. The momentum of an object is produced by the object’s mass and velocity. The kinetic energy of an object depends on its mass and speed Kinetic energy (J) = ½ x mass (kg) x speed2 (m/s)2 Elastic potential energy (the energy stored in an ...
... The forces which cause the change in speed do so by doing work. The momentum of an object is produced by the object’s mass and velocity. The kinetic energy of an object depends on its mass and speed Kinetic energy (J) = ½ x mass (kg) x speed2 (m/s)2 Elastic potential energy (the energy stored in an ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... motion unless acted upon by an external force. Inertia is a tendency for a body to resist change in its state of motion, whether that be at rest or moving with a constant velocity. It is harder to move or change the state of motion of an object if it has a greater amount of inertia which is directly ...
... motion unless acted upon by an external force. Inertia is a tendency for a body to resist change in its state of motion, whether that be at rest or moving with a constant velocity. It is harder to move or change the state of motion of an object if it has a greater amount of inertia which is directly ...
P4: Explaining Motion
... If we increase the time over which the force acts then the resultant force will be smaller (the change in momentum is unchanged!) • This is the principle used in crash helmets, air bags, seat belts, climbing ropes and crumple zones on cars ...
... If we increase the time over which the force acts then the resultant force will be smaller (the change in momentum is unchanged!) • This is the principle used in crash helmets, air bags, seat belts, climbing ropes and crumple zones on cars ...
KEY - Mrs. Wendorf
... The time of impact will be greater because the pillow causes the plate to slow down over a distance equal to the thickness of the pillow. b) Hopefully for part a, you answered that the time would be greater. It will be greater because the pillow causes a gradual slowing of the plate instead of a sud ...
... The time of impact will be greater because the pillow causes the plate to slow down over a distance equal to the thickness of the pillow. b) Hopefully for part a, you answered that the time would be greater. It will be greater because the pillow causes a gradual slowing of the plate instead of a sud ...
momentum
... m1 = m2 – the particles exchange velocities When a very heavy particle collides head-on with a very light one initially at rest, the heavy particle continues in motion unaltered and the light particle rebounds with a speed of about twice the initial speed of the heavy particle. When a very lig ...
... m1 = m2 – the particles exchange velocities When a very heavy particle collides head-on with a very light one initially at rest, the heavy particle continues in motion unaltered and the light particle rebounds with a speed of about twice the initial speed of the heavy particle. When a very lig ...