Chapter 7. Dynamics of Systems of Particles
... We now work out two examples dealing the motion of rockets. The first one concerns a rocket in free space, whereas the second deals with vertical ascent under gravity. 7.5.1 Rocket Motion in Free Space We consider the case where a rocket is moving under the influence of no external forces. We also c ...
... We now work out two examples dealing the motion of rockets. The first one concerns a rocket in free space, whereas the second deals with vertical ascent under gravity. 7.5.1 Rocket Motion in Free Space We consider the case where a rocket is moving under the influence of no external forces. We also c ...
Ch 8 Momentum
... from an initial speed of 4.00 m/s. (a) What is the average force exerted on the leg, taking the effective mass of the hand and forearm to be 1.50 kg? (b) Would the force be any different ...
... from an initial speed of 4.00 m/s. (a) What is the average force exerted on the leg, taking the effective mass of the hand and forearm to be 1.50 kg? (b) Would the force be any different ...
Forces and Motion Commotion 2012
... Part A: Motion and Speed of Objects 1. Describe and measure motion using the concept of a reference point. 2. Describe and measure speed and be able to calculate speed. (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time ...
... Part A: Motion and Speed of Objects 1. Describe and measure motion using the concept of a reference point. 2. Describe and measure speed and be able to calculate speed. (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time ...
Academic Vocabulary Words #10
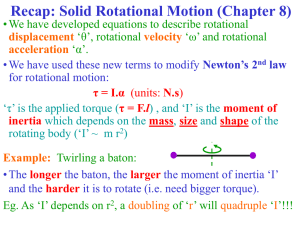
... 9. Newton’s Third Law of Motion • If one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object exerts a force of equal strength and opposite direction on the first object. ...
... 9. Newton’s Third Law of Motion • If one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object exerts a force of equal strength and opposite direction on the first object. ...
3 Types of Chemical Reactions
... For example, if someone holds down the darker ball in the collision shown above, it will not move. In that case, the momentum of the lighter ball would be transferred to the person holding the ball. The person is exerting an outside force. The law of conservation of momentum is true for objects that ...
... For example, if someone holds down the darker ball in the collision shown above, it will not move. In that case, the momentum of the lighter ball would be transferred to the person holding the ball. The person is exerting an outside force. The law of conservation of momentum is true for objects that ...
CHAPTER 7 IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
... energies of the objects, however, are scalar quantities that are always positive; thus, the total kinetic energy of the system of objects would necessarily be nonzero. Therefore, it is possible for a system of two or more objects to have a total kinetic energy that is not zero but a total momentum t ...
... energies of the objects, however, are scalar quantities that are always positive; thus, the total kinetic energy of the system of objects would necessarily be nonzero. Therefore, it is possible for a system of two or more objects to have a total kinetic energy that is not zero but a total momentum t ...
Momentum Class Notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... Since both ice skaters experience the same force for the same amount of time, they experience equal and opposite impulses, or change in momentum. So the total change in momentum for both ice skaters is 0. ...
... Since both ice skaters experience the same force for the same amount of time, they experience equal and opposite impulses, or change in momentum. So the total change in momentum for both ice skaters is 0. ...
Physics 2170
... Conservation of momentum So the relativistic momentum is: p u mu Note the addition of a subscript on . Our previous use of was to relate between two different frames with a relative velocity of v. In contrast, u is associated with a particle. If we measure p=umu in one inertial frame we ca ...
... Conservation of momentum So the relativistic momentum is: p u mu Note the addition of a subscript on . Our previous use of was to relate between two different frames with a relative velocity of v. In contrast, u is associated with a particle. If we measure p=umu in one inertial frame we ca ...