Nervous System
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
Nervous System
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
Slide ()
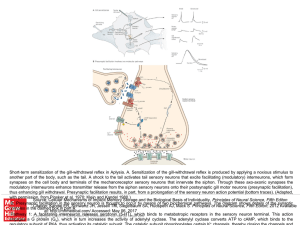
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Lecture 3 Review
... of depolarization is called an excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP), because it brings the membrane potential of the cell closer to the threshold for initiating an action potential. If the receptor is linked to an ion channel that allows Cl- ions to enter the postsynaptic cell, then the cell me ...
... of depolarization is called an excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP), because it brings the membrane potential of the cell closer to the threshold for initiating an action potential. If the receptor is linked to an ion channel that allows Cl- ions to enter the postsynaptic cell, then the cell me ...
Nervous System Function
... Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and ca ...
... Action Potentials and Myelinated Neurons Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and ca ...
Notes – Neurons and the nervous system
... strong the signal was. No matter how excitatory a signal is, the neuron will always fire with the same intensity. ...
... strong the signal was. No matter how excitatory a signal is, the neuron will always fire with the same intensity. ...
Addiction, Drugs, and the Endocrine System
... • With GABA, it is more widely present that all other chemicals combined. * Found in 90% of all synapses!! • Because it’s so widely present, it’s the reason why there are so many side effects to drugs. • Effects “neural plasticity”…strengthen the connection between neurons (memory) • Neural plastici ...
... • With GABA, it is more widely present that all other chemicals combined. * Found in 90% of all synapses!! • Because it’s so widely present, it’s the reason why there are so many side effects to drugs. • Effects “neural plasticity”…strengthen the connection between neurons (memory) • Neural plastici ...
Nervous System Function
... Nerve – collection of axons in PNS Ganglia – collection of cell bodies & dendrites Tract – collection of axons in CNS (White Matter) Nuclei – collection of cell bodies (Grey Matter) ...
... Nerve – collection of axons in PNS Ganglia – collection of cell bodies & dendrites Tract – collection of axons in CNS (White Matter) Nuclei – collection of cell bodies (Grey Matter) ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... 5.Receptor 6.Calcium Channel 7.Releases neurotransmitter 8.Re-uptake ...
... 5.Receptor 6.Calcium Channel 7.Releases neurotransmitter 8.Re-uptake ...
3 Basic Nerve Cells
... take p ride in your job , p ay the rent and feed your kids. It allows you to control your b ehavior when you exp erience a craving, an urge, or a drive. It is p art of what makes you human, and not just an animal. It is closely associated with the p leasure center in your b rain. C ocaine is neuroto ...
... take p ride in your job , p ay the rent and feed your kids. It allows you to control your b ehavior when you exp erience a craving, an urge, or a drive. It is p art of what makes you human, and not just an animal. It is closely associated with the p leasure center in your b rain. C ocaine is neuroto ...
Electrical Signaling-2
... • Amines – Derived from single amino acid tyrosine – Function as neurohormones: 1. Dopamine produced in the brain (substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area [VTA] & hypothalamus (where it inhibits release of prolactin) – Binds to dopamine receptors (at least 5) – GPCR – Targets the CNS » In the subst ...
... • Amines – Derived from single amino acid tyrosine – Function as neurohormones: 1. Dopamine produced in the brain (substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area [VTA] & hypothalamus (where it inhibits release of prolactin) – Binds to dopamine receptors (at least 5) – GPCR – Targets the CNS » In the subst ...
The Nervous System
... Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensity ...
... Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensity ...
neuron and nervous system
... Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensity Neural Communication Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morp ...
... Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensity Neural Communication Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morp ...
Synapses - JNCASR Desktop
... • These receptors are ion channels that allow certain types of ions (charged atoms) to pass through a pore within their structure. • The pore is opened following interaction with the neurotransmitter allowing an influx of ions into the post-synaptic terminal, which is propagated along the dendrite t ...
... • These receptors are ion channels that allow certain types of ions (charged atoms) to pass through a pore within their structure. • The pore is opened following interaction with the neurotransmitter allowing an influx of ions into the post-synaptic terminal, which is propagated along the dendrite t ...
introduction
... • Temporal summation: If a second EPSP from a single neuron is elicited before the first EPSP decays, the two potentials summate and their additive effects are sufficient to induce an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane. • Time constant of the postsynaptic neuron affects the amplitude of t ...
... • Temporal summation: If a second EPSP from a single neuron is elicited before the first EPSP decays, the two potentials summate and their additive effects are sufficient to induce an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane. • Time constant of the postsynaptic neuron affects the amplitude of t ...
Neurotransmitters - Motivational Interviewing Network of Trainers
... positive moods. Dopamine encourages a persistent, goal-centered state of mind and impulse control. Positive thinking can trigger dopamine release. So not surprisingly, anything that raises dopamine levels can boost your powers of concentration. Pleasurable activities (physical activities, eating cho ...
... positive moods. Dopamine encourages a persistent, goal-centered state of mind and impulse control. Positive thinking can trigger dopamine release. So not surprisingly, anything that raises dopamine levels can boost your powers of concentration. Pleasurable activities (physical activities, eating cho ...
Central nervous system
... • Acts through 2nd messenger systems (cAMP) • Receptor is an integral membrane protein associated with a G protein, which activates adenylate cyclase, which converts ATP to cAMP • cAMP has multiple effects ...
... • Acts through 2nd messenger systems (cAMP) • Receptor is an integral membrane protein associated with a G protein, which activates adenylate cyclase, which converts ATP to cAMP • cAMP has multiple effects ...
The Review
... 13. What is a split brain operation? Why would it be performed? Why is it that a split brain person can not describe what they are holding in their left hand? 14. What is and EEG, CAT, MRI, and PET? 15. What is the difference between a neurotransmitter and hormone? 16. Know your glands! ...
... 13. What is a split brain operation? Why would it be performed? Why is it that a split brain person can not describe what they are holding in their left hand? 14. What is and EEG, CAT, MRI, and PET? 15. What is the difference between a neurotransmitter and hormone? 16. Know your glands! ...
EQ2.3 - nerve cells communicate-
... Nerve cells communicate by impulses in a region called the synapse. They send impulses along the membrane due to two phenomenas: electrical and chemical movement. Next, special proteins move ions back and forth across the membrane. Nerves tend to be interconnected by forming electrical activities. T ...
... Nerve cells communicate by impulses in a region called the synapse. They send impulses along the membrane due to two phenomenas: electrical and chemical movement. Next, special proteins move ions back and forth across the membrane. Nerves tend to be interconnected by forming electrical activities. T ...
neurotransmitters 101
... The brain’s 100 billion neurons connect the various organs and brain regions into a complex network of circuits that control specific functions within the body. Simply speaking, these circuits serve as on/off switches for the millions of messages and processes carried out on a daily basis. For examp ...
... The brain’s 100 billion neurons connect the various organs and brain regions into a complex network of circuits that control specific functions within the body. Simply speaking, these circuits serve as on/off switches for the millions of messages and processes carried out on a daily basis. For examp ...
NEUROTRANSMITTER TEST KIT (13 vials) - Life
... ornithine, arginine and polyamines; a stimulatory neurotransmitter; can be converted by the body into GABA; the most common neurotransmitter in the brain; always excitatory; nearly all excitatory neurons in the CNS and possibly half of the synapses in the brain communicate via glutamate; involved in ...
... ornithine, arginine and polyamines; a stimulatory neurotransmitter; can be converted by the body into GABA; the most common neurotransmitter in the brain; always excitatory; nearly all excitatory neurons in the CNS and possibly half of the synapses in the brain communicate via glutamate; involved in ...
VII. The Nervous System
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...