ECON 2010-400 Principles of Microeconomics
... Study Guide: Martin, L.W., (1993), Study Guide for Principles of Microeconomics . New York: Norton. ...
... Study Guide: Martin, L.W., (1993), Study Guide for Principles of Microeconomics . New York: Norton. ...
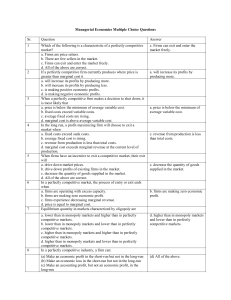
Managerial Economics Multiple Choice Questions Sr. Question
... Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market? a. Firms are price setters. b. There are few sellers in the market. c. Firms can exit and enter the market freely. d. All of the above are correct. If a perfectly competitive firm currently produces where price is greater ...
... Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market? a. Firms are price setters. b. There are few sellers in the market. c. Firms can exit and enter the market freely. d. All of the above are correct. If a perfectly competitive firm currently produces where price is greater ...
Which of the following statement is most closely associated with
... b. Determining the best level of immigration into a country. c. Determining whether too many luxury goods being produced. d. Determining whether or not the government should reduce poverty. ...
... b. Determining the best level of immigration into a country. c. Determining whether too many luxury goods being produced. d. Determining whether or not the government should reduce poverty. ...
e301t2qx
... For the following, please answer "True" or "False" and explain why. 12) If firms in a competitive market are identical, the long-run market supply curve is horizontal. 6) If entry is limited due to a limited input, firms in that market earn long run economic profit. Provide an example of a limited i ...
... For the following, please answer "True" or "False" and explain why. 12) If firms in a competitive market are identical, the long-run market supply curve is horizontal. 6) If entry is limited due to a limited input, firms in that market earn long run economic profit. Provide an example of a limited i ...
Quiz 4
... Note: You have to write down the formula and calculation steps for all the problems. Answers without supporting formula and steps or curves will not get any marks. (1) A city is considering increasing its airport capacity. Two mutually exclusive alternatives are being considered. Alternative A is to ...
... Note: You have to write down the formula and calculation steps for all the problems. Answers without supporting formula and steps or curves will not get any marks. (1) A city is considering increasing its airport capacity. Two mutually exclusive alternatives are being considered. Alternative A is to ...
1.3 Choosing to spend
... need to be paid to cover their costs. • Eventually, the price will settle at a point where supply equals demand, known as the market price • Prices change when there are changes in demand or supply. ...
... need to be paid to cover their costs. • Eventually, the price will settle at a point where supply equals demand, known as the market price • Prices change when there are changes in demand or supply. ...
AP_MICRO_EXAM_REVIEW_SHEET
... Definition of Diminishing Marginal Returns and the point at which it occurs. ...
... Definition of Diminishing Marginal Returns and the point at which it occurs. ...
ECON 3070-100 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... This course is divided into three sections. The first deals with the theories of consumer behavior and demand. The second treats theories of production, cost, supply, and the firm under various types of market structure, including perfect competition, monopoly, and structures intermediate between th ...
... This course is divided into three sections. The first deals with the theories of consumer behavior and demand. The second treats theories of production, cost, supply, and the firm under various types of market structure, including perfect competition, monopoly, and structures intermediate between th ...
CHAPTER 4: Valuing Benefits and Costs in Primary Markets
... Therefore, if the government adds a quantity q' to the market, the supply curve again shifts to the right, but this time the price of the good falls to P1. The gain in consumer surplus corresponds to an area bounded by the demand curve and the change in price (area P0abP1 from Figure 4.3). The priva ...
... Therefore, if the government adds a quantity q' to the market, the supply curve again shifts to the right, but this time the price of the good falls to P1. The gain in consumer surplus corresponds to an area bounded by the demand curve and the change in price (area P0abP1 from Figure 4.3). The priva ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.

![Lecture Notes : MS-Word File [Chapter 8.]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/021776319_1-e5e5d7dcdd0726608b5b8a17ee7fe081-300x300.png)