Field 3Ce Final MS Ch04
... always have opportunity costs; they could have been used to produce something else. Furthermore, firms will try to find ways of reducing costs when the relative prices of inputs change. However, in many production operations there is another type of cost that represents a true cost to society but do ...
... always have opportunity costs; they could have been used to produce something else. Furthermore, firms will try to find ways of reducing costs when the relative prices of inputs change. However, in many production operations there is another type of cost that represents a true cost to society but do ...
Where Do Cities Develop? - Pomona College Economics
... Ubiquitous inputs Cost of delivery included in price of product Choose location that minimizes delivery costs - midpoint • More generally, median location is where 1/2 sales on one side and 1/2 on other ...
... Ubiquitous inputs Cost of delivery included in price of product Choose location that minimizes delivery costs - midpoint • More generally, median location is where 1/2 sales on one side and 1/2 on other ...
HW 4 - Part II Cost and PC Markets-1
... 1) A firm has revenues of $1,000,000 and pays $500,000 in salaries and materials costs. It also has a factory in which it produces. If it did not use the factory, it could rent it to another manufacturer for $350,000 per year. What is the economic profit of this firm? A) -$350,000 B) -$150,000 C) $5 ...
... 1) A firm has revenues of $1,000,000 and pays $500,000 in salaries and materials costs. It also has a factory in which it produces. If it did not use the factory, it could rent it to another manufacturer for $350,000 per year. What is the economic profit of this firm? A) -$350,000 B) -$150,000 C) $5 ...
basic market equation
... What about information? Many ecological economists are trying to price non-market goods and services (e.g. ecosystem services). If we could do this, would it lead to their optimal allocation? ...
... What about information? Many ecological economists are trying to price non-market goods and services (e.g. ecosystem services). If we could do this, would it lead to their optimal allocation? ...
Autumn Examinations 2007/2008
... impossible for a monopolist to differentiate between types of customers by sight, how is it possible for the monopolist to practice price discrimination? Give examples of this in practice. ...
... impossible for a monopolist to differentiate between types of customers by sight, how is it possible for the monopolist to practice price discrimination? Give examples of this in practice. ...
Exam Name___________________________________ You may
... You may not discuss this test in any way shape or form with anyone before 1500 Thursday, February 24, 2011. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The price elasticity of demand is a measure of the extent to which the quantity demand ...
... You may not discuss this test in any way shape or form with anyone before 1500 Thursday, February 24, 2011. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The price elasticity of demand is a measure of the extent to which the quantity demand ...
ECOLE DES HAUTES ETUDES COMMERCIALES
... Julia take the new job? c) Suppose that Julia takes the new job, and suppose that there is insurance available that would continue to pay her 30 if she loses the job. What is the maximum amount ...
... Julia take the new job? c) Suppose that Julia takes the new job, and suppose that there is insurance available that would continue to pay her 30 if she loses the job. What is the maximum amount ...
Why does a Firm Maximize its Profit where Marginal
... If a firm is operating in a competitive industry, then its total revenue is simply equal to the market price times the quantity it produces, so we can depict Total Revenue as a linear function of output (a straight line) in the graph on the next page (i.e. TR pQ ). In the graph, I’ve assumed that th ...
... If a firm is operating in a competitive industry, then its total revenue is simply equal to the market price times the quantity it produces, so we can depict Total Revenue as a linear function of output (a straight line) in the graph on the next page (i.e. TR pQ ). In the graph, I’ve assumed that th ...
No Slide Title
... • Long run market adjustment: when capital variable • Transfers of resources between ...
... • Long run market adjustment: when capital variable • Transfers of resources between ...
A Public Good
... market price is $4 and the quantity demanded in an unregulated market is QMKT. But the efficient level of consumption is QOPT, the quantity demanded when the price is zero. The efficient quantity, QOPT, exceeds the quantity demanded in an unregulated market, QMKT. The shaded area represents the loss ...
... market price is $4 and the quantity demanded in an unregulated market is QMKT. But the efficient level of consumption is QOPT, the quantity demanded when the price is zero. The efficient quantity, QOPT, exceeds the quantity demanded in an unregulated market, QMKT. The shaded area represents the loss ...
Econ 101A — Midterm 2 Th 10 April 2014. You have approximately
... 3. Maximize the expected utility with respect to and derive the first-order conditions. Interpret the first order conditions in terms of marginal cost of effort and marginal benefit of effort Do not worry about the corner solutions (that is, the constraint that 0 ≤ ≤ 1) (5 points) 4. Write d ...
... 3. Maximize the expected utility with respect to and derive the first-order conditions. Interpret the first order conditions in terms of marginal cost of effort and marginal benefit of effort Do not worry about the corner solutions (that is, the constraint that 0 ≤ ≤ 1) (5 points) 4. Write d ...
Economics of Labor Econ 355
... • Information failures – ignorance of the “true” costs and benefits of a transaction. (e.g. hearing protection) • Transaction barriers – institutional restrictions or ability to pay considerations that prevent mutually beneficial transactions from occurring (worker mobility, laws restricting workers ...
... • Information failures – ignorance of the “true” costs and benefits of a transaction. (e.g. hearing protection) • Transaction barriers – institutional restrictions or ability to pay considerations that prevent mutually beneficial transactions from occurring (worker mobility, laws restricting workers ...
AP Microeconomics Review #4
... • Circle Test: use to find dom. strategy: circle your opponents best move based on your move; if player gets two circles in same decision, then it is a dominant strategy ...
... • Circle Test: use to find dom. strategy: circle your opponents best move based on your move; if player gets two circles in same decision, then it is a dominant strategy ...
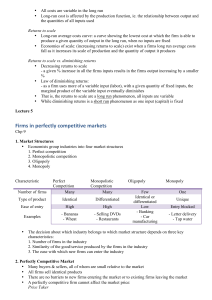
Chapter 6: The Role of Profit
... How businesses in each market structure maximize profits The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
... How businesses in each market structure maximize profits The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
Presentation
... There would be less of an impact on the sales from a change in the price than she predicted Based on our analysis in part b, we determined that the ...
... There would be less of an impact on the sales from a change in the price than she predicted Based on our analysis in part b, we determined that the ...
Review Questions 2 – 23.11.2016 Question 1 Suppose a perfectly
... a) An increase in marginal costs at all levels of output. b) An increase in marginal revenue at all levels of output. c) A reduction in telecommunication costs. d) An increase in tastes and preferences for the good or service being made. e) An increase in transport costs following an increase in oil ...
... a) An increase in marginal costs at all levels of output. b) An increase in marginal revenue at all levels of output. c) A reduction in telecommunication costs. d) An increase in tastes and preferences for the good or service being made. e) An increase in transport costs following an increase in oil ...
Midterm 2
... One. Show graphically and identify the non-price determinant for the change in the market (8 Show the impact on the market for SUVs of an increase in gas prices. Show the impact on the market for automobiles owing to the development of mass transit systems. Show the impact on the market for sushi ow ...
... One. Show graphically and identify the non-price determinant for the change in the market (8 Show the impact on the market for SUVs of an increase in gas prices. Show the impact on the market for automobiles owing to the development of mass transit systems. Show the impact on the market for sushi ow ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.