Lecture 20
... – Loss of efficiency can raise a potential competitor's value enough to overcome market entry barriers, or provide incentive for research and investment into new alternatives. – The theory of contestable markets argues that in some circumstances (private) monopolies are forced to behave as if there ...
... – Loss of efficiency can raise a potential competitor's value enough to overcome market entry barriers, or provide incentive for research and investment into new alternatives. – The theory of contestable markets argues that in some circumstances (private) monopolies are forced to behave as if there ...
Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics Fall 2012
... or sell it; the costs for the firms selling monopolies are entirely opportunity cost, which is: the profit they could make from running the monopolies themselves. Since in the long run all firms in a perfectly competitive market make zero economic profit, the firms will sell the monopolies at a pric ...
... or sell it; the costs for the firms selling monopolies are entirely opportunity cost, which is: the profit they could make from running the monopolies themselves. Since in the long run all firms in a perfectly competitive market make zero economic profit, the firms will sell the monopolies at a pric ...
Problem Setsz
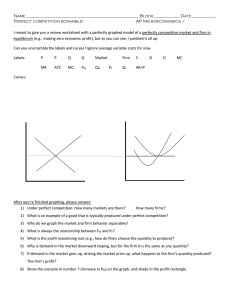
... 8. Use the chart regarding a perfectly competitive Yo-Yo factory to complete the following: (5/12) a. Fully explain why the number of yo-yos produced increases at a decreasing rate as more workers are hired. Identify and explain the three stages of returns. ( ____/5) b. Explain how a firm decides ho ...
... 8. Use the chart regarding a perfectly competitive Yo-Yo factory to complete the following: (5/12) a. Fully explain why the number of yo-yos produced increases at a decreasing rate as more workers are hired. Identify and explain the three stages of returns. ( ____/5) b. Explain how a firm decides ho ...
CHAPTER 7
... manufacturers. At the end of the century, there are only three large ones. Suppose that this situation is not the result of lax federal enforcement of antimonopoly laws. How do you explain the decrease in the number of manufacturers? (Hint: What is the inherent cost structure of the automobile indus ...
... manufacturers. At the end of the century, there are only three large ones. Suppose that this situation is not the result of lax federal enforcement of antimonopoly laws. How do you explain the decrease in the number of manufacturers? (Hint: What is the inherent cost structure of the automobile indus ...
Assignment -The Sherman and Clayton Acts Solution
... tannery's economic profit by $2,100-$1,300=$800 per week. Therefore, the tannery should be willing to use the recycling method if it is compensated with at least $800 per week. Suppose the hiking lodge has the property rights to the lake. That is, the hiking lodge has the right to a clean (unpollut ...
... tannery's economic profit by $2,100-$1,300=$800 per week. Therefore, the tannery should be willing to use the recycling method if it is compensated with at least $800 per week. Suppose the hiking lodge has the property rights to the lake. That is, the hiking lodge has the right to a clean (unpollut ...
Lecture 01.2
... • Look at how to compute (and why it’s important): – Marginal Cost of production for a firm • Derived from total costs of production – Total costs only determine whether or not firm enters an industry, not how much to produce/supply ...
... • Look at how to compute (and why it’s important): – Marginal Cost of production for a firm • Derived from total costs of production – Total costs only determine whether or not firm enters an industry, not how much to produce/supply ...
In-Class Slate Review Problems
... marginal social cost of producing a good is greater than its marginal private cost, and that the marginal social benefit associated with production of the good is equal to its marginal private benefit. Which of the following government actions would most likely increase efficiency? A.Taxing the prod ...
... marginal social cost of producing a good is greater than its marginal private cost, and that the marginal social benefit associated with production of the good is equal to its marginal private benefit. Which of the following government actions would most likely increase efficiency? A.Taxing the prod ...
ECON 2010-100 Principles of Microeconomics
... Course description: Microeconomics is about what goods get produced and sold at what prices. The individual must decide what goods to buy, how much to save and how hard to work. The firm must decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coord ...
... Course description: Microeconomics is about what goods get produced and sold at what prices. The individual must decide what goods to buy, how much to save and how hard to work. The firm must decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coord ...
solution
... AC F/X c , where F represents fixed costs of production, X represents the level of sales by each firm, and c represents marginal costs. We also know that P c (1/bn), where P and b represent price and the demand parameter. Also, if all firms follow the same pricing rule, then X S/n where S ...
... AC F/X c , where F represents fixed costs of production, X represents the level of sales by each firm, and c represents marginal costs. We also know that P c (1/bn), where P and b represent price and the demand parameter. Also, if all firms follow the same pricing rule, then X S/n where S ...
Econ Mid-Term Review Jeopardy
... to replace a costly item with a less costly item is an example of this ...
... to replace a costly item with a less costly item is an example of this ...
Example 12.1 Minimizing Costs for a Cobb
... residual that’s left over after labor and capital expenses have been paid. Economists tend to view entrepreneurial return as something over and above what they might have earned for their services in an alternative employment. 4. Economic Costs. We summarize these observations in the following defin ...
... residual that’s left over after labor and capital expenses have been paid. Economists tend to view entrepreneurial return as something over and above what they might have earned for their services in an alternative employment. 4. Economic Costs. We summarize these observations in the following defin ...
New Material
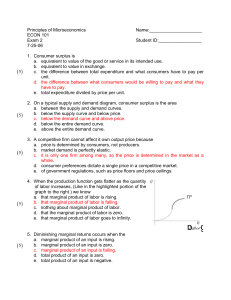
... 14. What is the value of fixed costs for this firm? 15. What is the value of marginal cost for output level 3? 16. What is the value of TVC for output level 4? 17. What is the value of AFC for output level 2? 18) Vipsana's Gyros House sells gyros. The cost of ingredients (pita, meat, spices, etc.) t ...
... 14. What is the value of fixed costs for this firm? 15. What is the value of marginal cost for output level 3? 16. What is the value of TVC for output level 4? 17. What is the value of AFC for output level 2? 18) Vipsana's Gyros House sells gyros. The cost of ingredients (pita, meat, spices, etc.) t ...
Solution
... a. economic profit of the firm to be positive. b. economic profit of the firm to be zero (i.e,, it breaks even). c. economic profit of the firm to be negative (i.e., economic losses). d. approximately half of the firms to have significant economic profit while the other half endure significant econo ...
... a. economic profit of the firm to be positive. b. economic profit of the firm to be zero (i.e,, it breaks even). c. economic profit of the firm to be negative (i.e., economic losses). d. approximately half of the firms to have significant economic profit while the other half endure significant econo ...
basic market equation
... Resources flow to those who value them most Leads to ‘optimal’ allocation of resources ...
... Resources flow to those who value them most Leads to ‘optimal’ allocation of resources ...
Assignment 2
... Now suppose two firms in the same industry sell their product at P=20 per unit, but in one firm the total fixed cost is $40 and average variable cost is $10. In the other firm the total fixed cost is $90 and average variable cost is $9. Determine the breakeven output of each firm. Why is the break e ...
... Now suppose two firms in the same industry sell their product at P=20 per unit, but in one firm the total fixed cost is $40 and average variable cost is $10. In the other firm the total fixed cost is $90 and average variable cost is $9. Determine the breakeven output of each firm. Why is the break e ...
Auxiliary Problems for Chapter 24
... a) What is the price that this profit-maximizing monopolist will charge? b) What is the profit-maximizing output? c) What is the total revenue at this optimum output and price? d) What is the total cost at this optimum output? e) What is the profit at this optimum output? f) If this monopolist were ...
... a) What is the price that this profit-maximizing monopolist will charge? b) What is the profit-maximizing output? c) What is the total revenue at this optimum output and price? d) What is the total cost at this optimum output? e) What is the profit at this optimum output? f) If this monopolist were ...
Course Content
... Supplemental Workbooks (STRONGLY recommended that you buy one of these): - 5 Steps to a 5 – AP Microeconomics - Barron’s AP Microeconomics - Kaplan AP Microeconomics Course Objective: AP Microeconomics is for the exceptionally studious high school student who wishes to earn college credit in high sc ...
... Supplemental Workbooks (STRONGLY recommended that you buy one of these): - 5 Steps to a 5 – AP Microeconomics - Barron’s AP Microeconomics - Kaplan AP Microeconomics Course Objective: AP Microeconomics is for the exceptionally studious high school student who wishes to earn college credit in high sc ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.