Recitation 5 – Lecture Outline
... 2. Market Power a. Optimal supply rule: Keep expanding production as long as MR>MC and stop where MR=MC. Special case is for perfectly comp. firms: MR=P and so rule becomes MR=P=MC. b. Perfect competition: large number of firms producing homogenous products. They have no market power (i.e. no influe ...
... 2. Market Power a. Optimal supply rule: Keep expanding production as long as MR>MC and stop where MR=MC. Special case is for perfectly comp. firms: MR=P and so rule becomes MR=P=MC. b. Perfect competition: large number of firms producing homogenous products. They have no market power (i.e. no influe ...
value for money model
... In order to quantify the benefits, costs and disbenefits the appraisal considers: The benefits to be enjoyed by existing users of buses due to changes in bus service provision and the fares they pay; The benefits to be enjoyed by additional new bus users who start to use the bus because of t ...
... In order to quantify the benefits, costs and disbenefits the appraisal considers: The benefits to be enjoyed by existing users of buses due to changes in bus service provision and the fares they pay; The benefits to be enjoyed by additional new bus users who start to use the bus because of t ...
Economics - Spring Branch ISD
... If we know the total cost at several levels of output, we can determine the marginal cost of production at each level. 35. Profit is defined as total revenue minus total cost. 36. Look at figure 5.10 (page 112) and tell me how many beanbags an hour should this firm make to produce at the lowest poss ...
... If we know the total cost at several levels of output, we can determine the marginal cost of production at each level. 35. Profit is defined as total revenue minus total cost. 36. Look at figure 5.10 (page 112) and tell me how many beanbags an hour should this firm make to produce at the lowest poss ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... _____ On a separate sheet of paper answer the following questions. Restate the question to receive full credit. 1. Think of a good, like gasoline, for which demand can become more elastic over time. What changes can take place in the long term to affect demand? 2. What are three characteristics of a ...
... _____ On a separate sheet of paper answer the following questions. Restate the question to receive full credit. 1. Think of a good, like gasoline, for which demand can become more elastic over time. What changes can take place in the long term to affect demand? 2. What are three characteristics of a ...
chapter 4 demand
... State of the Law of Supply. The tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price What is the relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied? The amount a suppliers willing and able to supply at a certain price What is the difference between a supply schedule and a market supply sche ...
... State of the Law of Supply. The tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price What is the relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied? The amount a suppliers willing and able to supply at a certain price What is the difference between a supply schedule and a market supply sche ...
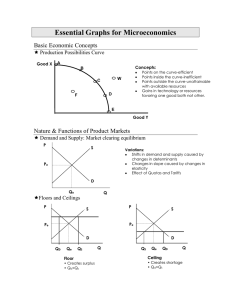
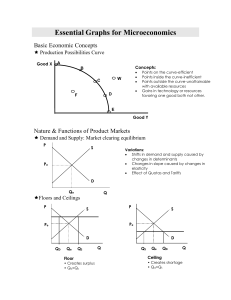
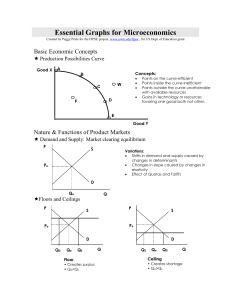
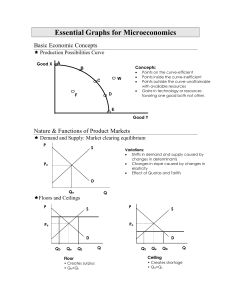
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics - pm
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
review
... Please use an appropriate diagram to further illustrate your answer (required). Question 5 (10%) In a recent publication displayed on a famous news website a journalist argued that in 2000 an average 401k account earned a negative rate of return. Assuming that the typical 401k account earned minus 5 ...
... Please use an appropriate diagram to further illustrate your answer (required). Question 5 (10%) In a recent publication displayed on a famous news website a journalist argued that in 2000 an average 401k account earned a negative rate of return. Assuming that the typical 401k account earned minus 5 ...
Competitive Firm
... can tell the firm which is producing at a higher cost to produce one less unit and the firm producing at a lower cost to produce an additional unit. The level of output is maintained and you save $2 of cost. When every firm produces the last unit at the same marginal cost the total costs are at the ...
... can tell the firm which is producing at a higher cost to produce one less unit and the firm producing at a lower cost to produce an additional unit. The level of output is maintained and you save $2 of cost. When every firm produces the last unit at the same marginal cost the total costs are at the ...
Econ 101 Exam Review Answers: Define: 1. Economics Economics
... 12. Which of the following is the definition of terms of trade? A) the price of one good that is exchanged for one unit of another good. B) the price of many goods that is exchanged for one unit of another good C) the quantity of one good that is exchanged for one unit of another good D) the quantit ...
... 12. Which of the following is the definition of terms of trade? A) the price of one good that is exchanged for one unit of another good. B) the price of many goods that is exchanged for one unit of another good C) the quantity of one good that is exchanged for one unit of another good D) the quantit ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.