Mr. Maurer Name: AP Economics 2004 Free Response Question
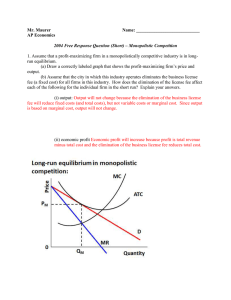
... (c) Assume now that the demand for cleaning products increases and that the company is now earning short-run economic profits. Relative to this short-run situation, how does each of the following change in the long run? (i) The number of firms The number of firms will increase. ...
... (c) Assume now that the demand for cleaning products increases and that the company is now earning short-run economic profits. Relative to this short-run situation, how does each of the following change in the long run? (i) The number of firms The number of firms will increase. ...
Homework Quiz 8
... b. Decrease production to increase profits. c. Increase production to increase profits. d. Shut down immediately, it is losing money. 5. Suppose there is a permanent increase in the demand for beer. In the perfectly competitive market, the most likely result would be: a. higher price in the short ru ...
... b. Decrease production to increase profits. c. Increase production to increase profits. d. Shut down immediately, it is losing money. 5. Suppose there is a permanent increase in the demand for beer. In the perfectly competitive market, the most likely result would be: a. higher price in the short ru ...
Lecture 3 Non-renewable resource exploitation: externalities, exploration, scarcity and rents
... (with perfect information). Assuming that d ( ) does not a¤ect the …rm directly, however, a pro…t-maximising …rm clearly has an incentive to set (a) = 0. How can we force the …rm to incur abatement costs? We could use a pollution tax set at an appropriate level, we could impose standards to control ...
... (with perfect information). Assuming that d ( ) does not a¤ect the …rm directly, however, a pro…t-maximising …rm clearly has an incentive to set (a) = 0. How can we force the …rm to incur abatement costs? We could use a pollution tax set at an appropriate level, we could impose standards to control ...
Economic Analysis of Environmental Issues
... Just as it is in society’s interest to internalize the social costs of pollution, it is also socially beneficial to internalize the social benefits of activities that generate positive externalities. For example, many suburban and rural towns have instituted open land preservation programs. Using ta ...
... Just as it is in society’s interest to internalize the social costs of pollution, it is also socially beneficial to internalize the social benefits of activities that generate positive externalities. For example, many suburban and rural towns have instituted open land preservation programs. Using ta ...
CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY
... like to know is how much a 5-percent increase in price is likely to reduce sales. What would you need to know to help the company with this problem? Explain why these facts are important. As a large producer of farm equipment, Caterpillar Tractor has some market power and should consider the entire ...
... like to know is how much a 5-percent increase in price is likely to reduce sales. What would you need to know to help the company with this problem? Explain why these facts are important. As a large producer of farm equipment, Caterpillar Tractor has some market power and should consider the entire ...
Document
... Perfectly competitive markets are efficient and lead to the best possible outcomes, if: – There are no production and consumption externalities (neither positive nor negative) – There are no public goods – All cost and effects are captured in this static model (i.e., there are no effects spread out ...
... Perfectly competitive markets are efficient and lead to the best possible outcomes, if: – There are no production and consumption externalities (neither positive nor negative) – There are no public goods – All cost and effects are captured in this static model (i.e., there are no effects spread out ...
- Catalyst - University of Washington
... insensitive to changes in relative factor prices. (b) If capital and labor a perfect substitutes, changing relative factor prices can cause dramatic shifts from exclusive use of one factor of production to the other. ...
... insensitive to changes in relative factor prices. (b) If capital and labor a perfect substitutes, changing relative factor prices can cause dramatic shifts from exclusive use of one factor of production to the other. ...
JEOPARDY
... You own a company that makes wire. The price of copper has recently gone up. What characteristic is it and what happens to supply? ...
... You own a company that makes wire. The price of copper has recently gone up. What characteristic is it and what happens to supply? ...
Quiz 9
... A firm will hire additional units of any input up to the point where a. the marginal productivity of the input is maximized. b. the marginal cost of employing the input is minimized. c. the expense of employing the last unit is equal to the revenue brought in by the last unit. d. the revenue brought ...
... A firm will hire additional units of any input up to the point where a. the marginal productivity of the input is maximized. b. the marginal cost of employing the input is minimized. c. the expense of employing the last unit is equal to the revenue brought in by the last unit. d. the revenue brought ...
Econ 102 Midterm 1 – List of topics
... Macroeconomics – the study of the aggregate behavior of individual economic agents Positive Economics – the study of how the economy behaves Normative Economics – the benchmarking of how the economy should be Reasons for market failure Externalities – a situation when the market fails to fully accou ...
... Macroeconomics – the study of the aggregate behavior of individual economic agents Positive Economics – the study of how the economy behaves Normative Economics – the benchmarking of how the economy should be Reasons for market failure Externalities – a situation when the market fails to fully accou ...
What is Demand?
... deals with behaviors and decisions made by individuals or small firms Demand schedule- Chart showing prices and quantity demanded (page 90) Demand Curve- Same info shown in graph form ...
... deals with behaviors and decisions made by individuals or small firms Demand schedule- Chart showing prices and quantity demanded (page 90) Demand Curve- Same info shown in graph form ...
Price elasticity of supply - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... 2. Describe how the firm employs fixed and variable inputs to produce output 3. Determine why price equals marginal cost at the profit-maximizing output level 4. Construct the industry supply curve from the supply curves of individual firms 5. Define and calculate price elasticity of supply 6. Defin ...
... 2. Describe how the firm employs fixed and variable inputs to produce output 3. Determine why price equals marginal cost at the profit-maximizing output level 4. Construct the industry supply curve from the supply curves of individual firms 5. Define and calculate price elasticity of supply 6. Defin ...
Lec08.pdf
... These relationships work via incentives, monitoring, explicit and implicit contracts, career concerns ... Some principal-agent issues later; more in ECO 307 Old view still useful in characterizing firm’s relationships with rest of economy (output supply and input demand functions) ...
... These relationships work via incentives, monitoring, explicit and implicit contracts, career concerns ... Some principal-agent issues later; more in ECO 307 Old view still useful in characterizing firm’s relationships with rest of economy (output supply and input demand functions) ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.