EE Exam 1_Winter 2013
... Your buddies at the bar, Todd and Sarah, don’t understand why this is happening. Sarah says, “wouldn’t the profit incentive cause firms to harvest fish at a sustainable rate? The competitive marketplace should fix this problem!” Use your economics knowledge to explain to them why ocean species tend ...
... Your buddies at the bar, Todd and Sarah, don’t understand why this is happening. Sarah says, “wouldn’t the profit incentive cause firms to harvest fish at a sustainable rate? The competitive marketplace should fix this problem!” Use your economics knowledge to explain to them why ocean species tend ...
Fall 2000
... 30. Dr. Harvey and Dr. Klopfenstein's decide to work together on a paper. The paper is successfully published under their names. Each benefits from the other’s actions. This is an example of: 30. This question was thrown out. I intended for the correct answer to be a. a negative externality (externa ...
... 30. Dr. Harvey and Dr. Klopfenstein's decide to work together on a paper. The paper is successfully published under their names. Each benefits from the other’s actions. This is an example of: 30. This question was thrown out. I intended for the correct answer to be a. a negative externality (externa ...
Chapter 6 Part 2
... to cut prices. Falling prices will cause quantity demanded to rise and quantity supplied to fall until they are equal. ...
... to cut prices. Falling prices will cause quantity demanded to rise and quantity supplied to fall until they are equal. ...
Document
... – Choose largest number – Graphically, find point where distance between TR and TC is largest ...
... – Choose largest number – Graphically, find point where distance between TR and TC is largest ...
File
... C) market value of all resources used to produce a good. D) change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output. ...
... C) market value of all resources used to produce a good. D) change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output. ...
Economics and Entrepreneurship Test – II
... Economics and Entrepreneurship Test – II For questions 1 – 8, choose one word from the box below that best fits the sentence. You will not use all the words, so don’t worry if you have words left over. ...
... Economics and Entrepreneurship Test – II For questions 1 – 8, choose one word from the box below that best fits the sentence. You will not use all the words, so don’t worry if you have words left over. ...
Assignment 2
... University of Hong Kong 1st semester 2009-10 ECON1001 Introduction to Economics I, Subclasses I Assignment 2 Due time: 5:30pm, November 9 (Monday), 2009 Answer all questions. While you are encouraged to discuss with your classmates, you must write up your own script. (The answer to each question sho ...
... University of Hong Kong 1st semester 2009-10 ECON1001 Introduction to Economics I, Subclasses I Assignment 2 Due time: 5:30pm, November 9 (Monday), 2009 Answer all questions. While you are encouraged to discuss with your classmates, you must write up your own script. (The answer to each question sho ...
EC 220 Microeconomics - College of Micronesia
... 4. State some important reasons for studying economics. 5. Explain how economists use the scientific method to formulate economic principles. 6. Differentiate between microeconomics and macroeconomics. 7. Differentiate between positive and normative economics. 8. Explain and give examples of some hi ...
... 4. State some important reasons for studying economics. 5. Explain how economists use the scientific method to formulate economic principles. 6. Differentiate between microeconomics and macroeconomics. 7. Differentiate between positive and normative economics. 8. Explain and give examples of some hi ...
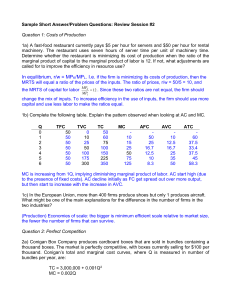
Review Session #2
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
Is the Competitive Market Efficient?
... Explain the connection between demand and marginal benefit and define consumer surplus Explain the connection between supply and marginal cost and define producer surplus Explain the conditions under which markets move resources to their highest-value uses and the sources of inefficiency in our econ ...
... Explain the connection between demand and marginal benefit and define consumer surplus Explain the connection between supply and marginal cost and define producer surplus Explain the conditions under which markets move resources to their highest-value uses and the sources of inefficiency in our econ ...
Markets
... Average Fixed Cost = Total Fixed Cost/Output Average Variable Cost = Total Variable Cost/Output Average Total Cost (ATC) = (AFC) + (AVC) Marginal Costs Cost of producing one more unit of output What is the increase in (Variable) cost for one more unit of output ...
... Average Fixed Cost = Total Fixed Cost/Output Average Variable Cost = Total Variable Cost/Output Average Total Cost (ATC) = (AFC) + (AVC) Marginal Costs Cost of producing one more unit of output What is the increase in (Variable) cost for one more unit of output ...
Jason Majewski
... costs rises if output increases by one unit. For a typical firm, marginal cost rises with the quantity of output. Average total cost first falls as output increases and then rises as output increases further. The marginal cost curve always crosses the average total cost curve at the minimum of avera ...
... costs rises if output increases by one unit. For a typical firm, marginal cost rises with the quantity of output. Average total cost first falls as output increases and then rises as output increases further. The marginal cost curve always crosses the average total cost curve at the minimum of avera ...
Econ 106 * SI review questions for exam 2
... everything you have been taught into a question, and then see if you can write a good answer. If you can, no need to study that concept anymore. If you can’t, re-read your notes on that concept or look it up in the book. 1. For any type of elasticity, there is a change, and a response to that change ...
... everything you have been taught into a question, and then see if you can write a good answer. If you can, no need to study that concept anymore. If you can’t, re-read your notes on that concept or look it up in the book. 1. For any type of elasticity, there is a change, and a response to that change ...
AP Microeconomics - Boise State University
... ____8. The vertical distance between a firm's ATC and AVC curves represents: a. AFC, which increases as output increases. b. AFC, which decreases as output increases. c. marginal costs, which decrease as output decreases. d. marginal costs, which increase as output increases. _____ 9. The law of dim ...
... ____8. The vertical distance between a firm's ATC and AVC curves represents: a. AFC, which increases as output increases. b. AFC, which decreases as output increases. c. marginal costs, which decrease as output decreases. d. marginal costs, which increase as output increases. _____ 9. The law of dim ...
advanced placement microeconomics
... 2. To enable students to use these concepts to analyze current economic problems and issues. 3. To give students practical experience in communicating their understanding of various economic issues through both written and oral means. 4. To develop in students the “economic way of thinking”—the econ ...
... 2. To enable students to use these concepts to analyze current economic problems and issues. 3. To give students practical experience in communicating their understanding of various economic issues through both written and oral means. 4. To develop in students the “economic way of thinking”—the econ ...
1 - Carlos Pitta
... 13. Two firms, A and B, each currently dump 50 tons of chemicals into the local river. The government has decided to reduce the pollution and from now on will require a pollution permit for each ton of pollution dumped into the river. It costs Firm A $100 for each ton of pollution that it eliminates ...
... 13. Two firms, A and B, each currently dump 50 tons of chemicals into the local river. The government has decided to reduce the pollution and from now on will require a pollution permit for each ton of pollution dumped into the river. It costs Firm A $100 for each ton of pollution that it eliminates ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.