THE PELOPONNESIAN WAR
... THE PELOPONNESIAN WAR CAUSES OF THE WAR Greek city-states began to fear Athens attempt at power and prestige. Athens had grown into a naval empire under the rule of Pericles. Athenian settlers began moving into other Greek territories. City-states that wanted to break away from the Delian Le ...
... THE PELOPONNESIAN WAR CAUSES OF THE WAR Greek city-states began to fear Athens attempt at power and prestige. Athens had grown into a naval empire under the rule of Pericles. Athenian settlers began moving into other Greek territories. City-states that wanted to break away from the Delian Le ...
What mattered to the Ancient Athenians?
... and offered a horse. • Athena offered an olive tree. • The men chose Poseidon, the women Athena and as there was one more woman, Athena became the protector and the city is named after her. ...
... and offered a horse. • Athena offered an olive tree. • The men chose Poseidon, the women Athena and as there was one more woman, Athena became the protector and the city is named after her. ...
World History I Unit 5: Ancient Greece
... Please keep the following question in mind: Is America more or less democratic than Ancient Athens? ...
... Please keep the following question in mind: Is America more or less democratic than Ancient Athens? ...
Glory that was Greece Wk9
... 1. What geo-politico-economic factors led to the Trojan War? 2. The period after the fall of Mycenae has seemed “dark.” Examine 2 reasons. How has this period emerged more clearly to historians? 3. Why did ancient Greece develop into many small, self-governing city-states and why did they conquer or ...
... 1. What geo-politico-economic factors led to the Trojan War? 2. The period after the fall of Mycenae has seemed “dark.” Examine 2 reasons. How has this period emerged more clearly to historians? 3. Why did ancient Greece develop into many small, self-governing city-states and why did they conquer or ...
The Abnormal States: Sparta and Athens
... respect of one thing but of everything that equality and free speech are clearly a good; take the case of Athens, which under the rule of tyrants proved no better in war than any of its neighbors but, once rid of those tyrants, was far the first of all. What this makes clear is that when held in sub ...
... respect of one thing but of everything that equality and free speech are clearly a good; take the case of Athens, which under the rule of tyrants proved no better in war than any of its neighbors but, once rid of those tyrants, was far the first of all. What this makes clear is that when held in sub ...
CA_NTSG_007 - Mira Costa High School
... individual included submitting to the laws of the state. His student Plato rejected democracy and, instead, argued that the state should regulate every aspect of its citizens’ lives to provide for their best interests. Plato’s most famous student, Aristotle, favored a constitutional government and t ...
... individual included submitting to the laws of the state. His student Plato rejected democracy and, instead, argued that the state should regulate every aspect of its citizens’ lives to provide for their best interests. Plato’s most famous student, Aristotle, favored a constitutional government and t ...
Greek City-States Politics and Society Characteristics of City
... • Governed by landowning families ...
... • Governed by landowning families ...
Pre-Socratics
... father Aegeus, he became king of Athens. He is responsible for the synoecism or unifying of the villages in Attica to join the city-state of Athens. Alcamaeonidae: family-line in Athens that became “cursed” after murdering suppliants of Athena. This family would continue to stir up trouble and be e ...
... father Aegeus, he became king of Athens. He is responsible for the synoecism or unifying of the villages in Attica to join the city-state of Athens. Alcamaeonidae: family-line in Athens that became “cursed” after murdering suppliants of Athena. This family would continue to stir up trouble and be e ...
AncientGreeceSummary
... Athenian Society • 3 class groups – Citizens: extended to all those born in Athens, only the men had political rights – Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land – Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of ...
... Athenian Society • 3 class groups – Citizens: extended to all those born in Athens, only the men had political rights – Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land – Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of ...
Ancient Greece
... Were responsible for household affairs Lived in separate quarters Did not eat or socialize with men Could not appear in public alone ...
... Were responsible for household affairs Lived in separate quarters Did not eat or socialize with men Could not appear in public alone ...
Ancient Greece: Day 2
... • Draco: legal code w/equality under law • Solon: outlawed debt slavery & all citizens allowed to participate in Athenian assembly • Cleisthenes: Council of 500 created with random membership & all citizens could submit laws to Athenian assembly ...
... • Draco: legal code w/equality under law • Solon: outlawed debt slavery & all citizens allowed to participate in Athenian assembly • Cleisthenes: Council of 500 created with random membership & all citizens could submit laws to Athenian assembly ...
CHW 3M1 – Government in Ancient Greece Open Book Quiz Name
... aristocrats and ordinary people who had a share in Spartan land and could benefit from the work of enslaved helots. _____ The name given to the 5 Ephors who were elected annually to the Spartan government. They acted as magistrates and judges and presided over the Council and Assembly and supervised ...
... aristocrats and ordinary people who had a share in Spartan land and could benefit from the work of enslaved helots. _____ The name given to the 5 Ephors who were elected annually to the Spartan government. They acted as magistrates and judges and presided over the Council and Assembly and supervised ...
Sparta v Athens Focus On Culture
... very different in the education of their children and preparation of their citizens for public service within society, as well as the rights and privileges they afforded to their citizens. In this article we will focus on two groups of ancient Greeks, the Spartans and the Athenians, and will share t ...
... very different in the education of their children and preparation of their citizens for public service within society, as well as the rights and privileges they afforded to their citizens. In this article we will focus on two groups of ancient Greeks, the Spartans and the Athenians, and will share t ...
Chapter 4
... refused. At home slaves and women had no vote, which prompted the comic playwright Aristophanes to allow his women to express that exasperation with the system, but if you were an Athenian citizen you took part in a direct democracy. The world has not seen the like of it since. Everyone could turn o ...
... refused. At home slaves and women had no vote, which prompted the comic playwright Aristophanes to allow his women to express that exasperation with the system, but if you were an Athenian citizen you took part in a direct democracy. The world has not seen the like of it since. Everyone could turn o ...
Sparta vs. Athens
... public office. Farming on state-owned plots is the only available occupation for all but the wealthy. Citizens are always on call for military service. Women can own land (only those from wealthy families do). Many run their own households. Mothers of boys (future soldiers) are respected. ...
... public office. Farming on state-owned plots is the only available occupation for all but the wealthy. Citizens are always on call for military service. Women can own land (only those from wealthy families do). Many run their own households. Mothers of boys (future soldiers) are respected. ...
North American Colonization
... • Citizens: extended to all those born in Athens, only the men had political rights • Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land • Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of Athenian society ...
... • Citizens: extended to all those born in Athens, only the men had political rights • Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land • Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of Athenian society ...
Assignment 1 - Walsingham Academy
... 1. What geo-politico-economic factors led to the Trojan War? 2. The period after the fall of Mycenae has seemed “dark.” Examine 2 reasons. How has this period emerged more clearly to historians? 3. Why did ancient Greece develop into many small, self-governing city-states and why did they conquer or ...
... 1. What geo-politico-economic factors led to the Trojan War? 2. The period after the fall of Mycenae has seemed “dark.” Examine 2 reasons. How has this period emerged more clearly to historians? 3. Why did ancient Greece develop into many small, self-governing city-states and why did they conquer or ...
Blank Jeopardy
... The persons responsible for leading the military into battle, as well as having a limited role in religion and as a judge ...
... The persons responsible for leading the military into battle, as well as having a limited role in religion and as a judge ...
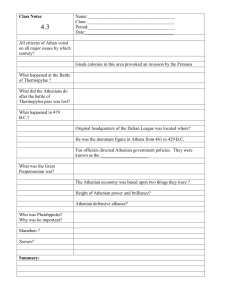
Class Notes:
... All citizens of Athan voted on all major issues by which century? Greek colonies in this area provoked an invasion by the Persians What happened at the Battle of Thermopylae ? What did the Athenians do after the battle of Thermopylea pass was lost? What happened in 479 B.C.? Original headquarters of ...
... All citizens of Athan voted on all major issues by which century? Greek colonies in this area provoked an invasion by the Persians What happened at the Battle of Thermopylae ? What did the Athenians do after the battle of Thermopylea pass was lost? What happened in 479 B.C.? Original headquarters of ...
The Peloponnesian War Purple
... population gathered inside the city's walls for protection. It was then that a terrible plague struck Athens, spreading quickly through the overcrowded city. Before it was over, one of every four Athenians had died. The war continued for 26 more years, with both sides winning and losing many battles ...
... population gathered inside the city's walls for protection. It was then that a terrible plague struck Athens, spreading quickly through the overcrowded city. Before it was over, one of every four Athenians had died. The war continued for 26 more years, with both sides winning and losing many battles ...
satraps
... strait- a narrow body of water with land on both sides ephors- enforced laws and collected taxes in Sparta philosophers- thinkers who ponder questions about life upper class women- could not leave home without a male relative people ...
... strait- a narrow body of water with land on both sides ephors- enforced laws and collected taxes in Sparta philosophers- thinkers who ponder questions about life upper class women- could not leave home without a male relative people ...
Epikleros

An epikleros (ἐπίκληρος; plural epikleroi) was an heiress in ancient Athens and other ancient Greek city states, specifically a daughter of a man who had no male heirs. In Sparta, they were called patrouchoi (πατροῦχοι), as they were in Gortyn. Athenian women were not allowed to hold property in their own name; in order to keep her father's property in the family, an epikleros was required to marry her father's nearest male relative. Even if a woman was already married, evidence suggests that she was required to divorce her spouse to marry that relative. Spartan women were allowed to hold property in their own right, and so Spartan heiresses were subject to less restrictive rules. Evidence from other city-states is more fragmentary, mainly coming from the city-states of Gortyn and Rhegium.Plato wrote about epikleroi in his Laws, offering idealized laws to govern their marriages. In mythology and history, a number of Greek women appear to have been epikleroi, including Agariste of Sicyon and Agiatis, the widow of the Spartan king Agis IV. The status of epikleroi has often been used to explain the numbers of sons-in-law who inherited from their fathers-in-law in Greek mythology. The Third Sacred War originated in a dispute over epikleroi.