Ch 12 Notes
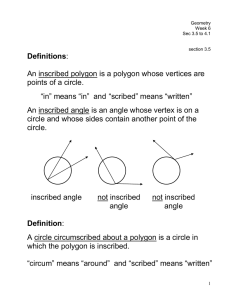
... Corollary to 12.11: Two inscribed angles that intercept the same arc are congruent. Corollary to 12.11: An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle. Corollary to 12.11: The opposite angles of an inscribed quadrilateral are supplementary (ADD TO 180) Examples: Find the value of each variable. ...
... Corollary to 12.11: Two inscribed angles that intercept the same arc are congruent. Corollary to 12.11: An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle. Corollary to 12.11: The opposite angles of an inscribed quadrilateral are supplementary (ADD TO 180) Examples: Find the value of each variable. ...
week6
... eyelashes on the paper. These marks represent lines that have no width, so make the representations believable. Make light marks that can be erased if necessary. 3. Be neat. Carefully align your arcs and lines to pass through the correct points. Also, do not use dots for points. The marks of the com ...
... eyelashes on the paper. These marks represent lines that have no width, so make the representations believable. Make light marks that can be erased if necessary. 3. Be neat. Carefully align your arcs and lines to pass through the correct points. Also, do not use dots for points. The marks of the com ...
Euler - Abdulla Eid
... The letter “i” to denote the imaginary unit. The use of the Greek letter to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. ...
... The letter “i” to denote the imaginary unit. The use of the Greek letter to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. ...
Things start to get complicated when the single point separates into
... Pi is amazing by itself as a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. It is an "irrational number," as its decimal representation never ends or settles into a permanent repeating pattern. Pi is also a "transcendental number" (not the root of any nonzero polynomial having rational coeffi ...
... Pi is amazing by itself as a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. It is an "irrational number," as its decimal representation never ends or settles into a permanent repeating pattern. Pi is also a "transcendental number" (not the root of any nonzero polynomial having rational coeffi ...
14.3 Converting Between Degrees and Radians and Inverse
... An is determined by rotating a ray about its vertex. side initial The of an angle is the ray extending from the vertex before rotation. The resulting ray, after the rotation, is called the terminal side ...
... An is determined by rotating a ray about its vertex. side initial The of an angle is the ray extending from the vertex before rotation. The resulting ray, after the rotation, is called the terminal side ...
Basic Geometry - Area Perimeter Volume Surface Area
... VOLUME: simply, the calculation of the area combined with the height, or thickness. Here are some other important definitions in understanding basic geometry. PLANES: the area defined by two-dimensional, flat surfaces. INTERSECT: to cross. PARALLEL: nonintersecting lines and/or planes. (The distance ...
... VOLUME: simply, the calculation of the area combined with the height, or thickness. Here are some other important definitions in understanding basic geometry. PLANES: the area defined by two-dimensional, flat surfaces. INTERSECT: to cross. PARALLEL: nonintersecting lines and/or planes. (The distance ...