C2 - The Biological Perspective
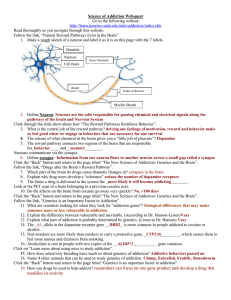
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Nervous System Notes
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal but ...
... Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal but ...
Chapter 3
... Once the threshold is reached, the neuron will fire at full strength. If the threshold is not reached, the neuron will not fire. ...
... Once the threshold is reached, the neuron will fire at full strength. If the threshold is not reached, the neuron will not fire. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Messages are gathered by the dendrites & cell body Transmitted along the axon in the form of a short electrical impulse called Action Potential ...
... Messages are gathered by the dendrites & cell body Transmitted along the axon in the form of a short electrical impulse called Action Potential ...
Document
... • A neuron which carries signals from tissue to brain is a sensory neuron or afferent neuron. • A neuron which carries signals from the brain to tissue is a motor neuron or efferent neuron. ...
... • A neuron which carries signals from tissue to brain is a sensory neuron or afferent neuron. • A neuron which carries signals from the brain to tissue is a motor neuron or efferent neuron. ...
Nerve Pathways Practice Sheet
... The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) _____________________ connect differen ...
... The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) _____________________ connect differen ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 55. What is a cerebrovascular accident? What is it also called? What causes it? A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), also called a stroke, is a form of brain damage caused when blood circulation to the brain is blocked due to a blood clot or ruptured blood vessel and part of the brain tissue dies. ...
... 55. What is a cerebrovascular accident? What is it also called? What causes it? A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), also called a stroke, is a form of brain damage caused when blood circulation to the brain is blocked due to a blood clot or ruptured blood vessel and part of the brain tissue dies. ...
The nervous system
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
Neurons, Hormones, and the Brain
... Spinal reflexes cont… • Neural circuits linked to neural pathways that run up and down the spinal cord= 2 and from the brain, As a result reflexes effected by thoughts and emotions • For example erection in men • However you can control your knee from jerking when it is tapped; and most men can lea ...
... Spinal reflexes cont… • Neural circuits linked to neural pathways that run up and down the spinal cord= 2 and from the brain, As a result reflexes effected by thoughts and emotions • For example erection in men • However you can control your knee from jerking when it is tapped; and most men can lea ...
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... Neurons communicate via the synapse 6. Define synapse: Information from one neuron flows to another neuron across a small gap called a synapse Click the “Back” button and return to the page titled “The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain”. Follow the link, “Drugs alter the Brain’s Rewar ...
... Neurons communicate via the synapse 6. Define synapse: Information from one neuron flows to another neuron across a small gap called a synapse Click the “Back” button and return to the page titled “The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain”. Follow the link, “Drugs alter the Brain’s Rewar ...
Chapter 14 - FacultyWeb
... Which of these is NOT usually a characteristic function associated with the left cerebral hemisphere? 1. Performing mathematical calculations 2. Analyzing emotional context of a conversation 3. Containing the general interpretive and speech centers 4. Processing associated with reading, writing, an ...
... Which of these is NOT usually a characteristic function associated with the left cerebral hemisphere? 1. Performing mathematical calculations 2. Analyzing emotional context of a conversation 3. Containing the general interpretive and speech centers 4. Processing associated with reading, writing, an ...
ES145 - Systems Analysis & Physiology
... responds to the change in their activity by increasing the blood in the vessels that are near these neurons. ...
... responds to the change in their activity by increasing the blood in the vessels that are near these neurons. ...
doc - Shoreline Community College
... using only hindsight to explain why events have occurred? 10. How does your text book author define “critical thinking?” (note: there are 4 parts to this definition) 11. What are four common scientific attitudes (a fourth was added in lecture)? 12. What is a theory? 13. What is a hypothesis? 14. Wha ...
... using only hindsight to explain why events have occurred? 10. How does your text book author define “critical thinking?” (note: there are 4 parts to this definition) 11. What are four common scientific attitudes (a fourth was added in lecture)? 12. What is a theory? 13. What is a hypothesis? 14. Wha ...
RNI_Introduction - Cognitive and Linguistic Sciences
... Few believe that nodes in a semantic network correspond in any sense to single neurons or groups of neurons. Physiology (fMRI) suggests that any complex cognitive structure – a word, for instance – gives rise to widely distributed cortical activation. Therefore a node in a language-based network lik ...
... Few believe that nodes in a semantic network correspond in any sense to single neurons or groups of neurons. Physiology (fMRI) suggests that any complex cognitive structure – a word, for instance – gives rise to widely distributed cortical activation. Therefore a node in a language-based network lik ...
Neuroanatomy - Kelley Kline
... medulla. Both pons & medulla form reticular formation & raphe system. ...
... medulla. Both pons & medulla form reticular formation & raphe system. ...
Organization of the nervous system
... A Neuron is a very special cell: You have about 100 billion of them! •Cell body: Keeps the neuron alive and determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
... A Neuron is a very special cell: You have about 100 billion of them! •Cell body: Keeps the neuron alive and determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
psych mod 4 terms
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
Ch 2 Cognition & the Brain
... different characteristics of stimuli • E.g., color, shapes, brightness, faces, artifacts, so on. • There are a bunch of neurons that respond to specific physical characteristics of stimuli. • Q: the reason why we can communicate, think, solve problems, get angry, sing, walk, so on is because neurons ...
... different characteristics of stimuli • E.g., color, shapes, brightness, faces, artifacts, so on. • There are a bunch of neurons that respond to specific physical characteristics of stimuli. • Q: the reason why we can communicate, think, solve problems, get angry, sing, walk, so on is because neurons ...
The Brain
... The brainstem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Some texts include the diencephalon as a brain stem structure, but others include it in the forebrain. The brain stem acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord and performs many of the body’s au ...
... The brainstem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Some texts include the diencephalon as a brain stem structure, but others include it in the forebrain. The brain stem acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord and performs many of the body’s au ...
Brain Scan Lie Detec..
... of individual subjects) with great accuracy." He goes on to point out a major flaw in what little research there is on lie detection: "Reports of finding brain patterns of activation corresponding to 'deception' almost always use subjects (often university students) who are told to lie about someth ...
... of individual subjects) with great accuracy." He goes on to point out a major flaw in what little research there is on lie detection: "Reports of finding brain patterns of activation corresponding to 'deception' almost always use subjects (often university students) who are told to lie about someth ...
11.3: The Central Nervous System The nervous system consists of
... The Brain is the major centre that receives, integrates, stores, and retrieves information. The Brain and its network of interneurons provide the basis for our voluntary movements, consciousness, behaviour, emotions, learning, reasoning, language and memory. The brain contains grey and white matter, ...
... The Brain is the major centre that receives, integrates, stores, and retrieves information. The Brain and its network of interneurons provide the basis for our voluntary movements, consciousness, behaviour, emotions, learning, reasoning, language and memory. The brain contains grey and white matter, ...