Cell Structure: From an Information Processing View
... he possessed a well-balanced mind, and was looked upon by those who knew him as a shrewd, smart businessman, very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation. In this regard his mind was radically changed, so decidedly that his friends and acquaintances said he was 'no longer Ga ...
... he possessed a well-balanced mind, and was looked upon by those who knew him as a shrewd, smart businessman, very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation. In this regard his mind was radically changed, so decidedly that his friends and acquaintances said he was 'no longer Ga ...
Tehnici de optimizare – Programare Genetica
... Obviously this presents a number of disadvantages too, because they are not easily trained, require a large number of "training" hours for the network to be able to act for what it was designed for, cannot detect singular elements other than those for which it has been accustomed (3), it's hard to d ...
... Obviously this presents a number of disadvantages too, because they are not easily trained, require a large number of "training" hours for the network to be able to act for what it was designed for, cannot detect singular elements other than those for which it has been accustomed (3), it's hard to d ...
Notes Module #1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... Removal of brain tissue or structures leads to an understanding of those cells/structures. (tumors/elective) ...
... Removal of brain tissue or structures leads to an understanding of those cells/structures. (tumors/elective) ...
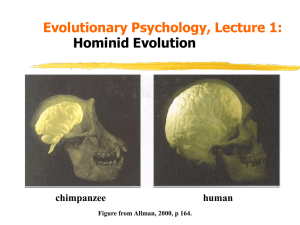
Introduction
... expected from a primate of their size but hominid brain size steadily expanded. Modern human brains are around 7 times larger than expected for a primate of our size. ...
... expected from a primate of their size but hominid brain size steadily expanded. Modern human brains are around 7 times larger than expected for a primate of our size. ...
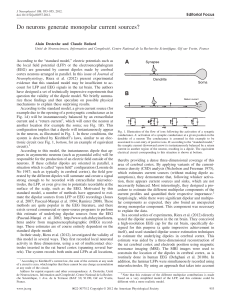
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... sources, if uniquely based on dipoles, can be flawed because the monopolar components are erroneously “absorbed” in the dipoles. If confirmed, this finding has potentially devastating consequences for the estimates of dipolar sources from the EEG or MEG. Indeed, there is evidence that the dipolar mo ...
... sources, if uniquely based on dipoles, can be flawed because the monopolar components are erroneously “absorbed” in the dipoles. If confirmed, this finding has potentially devastating consequences for the estimates of dipolar sources from the EEG or MEG. Indeed, there is evidence that the dipolar mo ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... muscles or glands (effectors). * A motor neuron makes something move. ...
... muscles or glands (effectors). * A motor neuron makes something move. ...
Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
... • Gray Matter: The neurons or cells which have specialized neurologic functions (motor or sensory) • White Matter: Axons which form pathways for conducting different types of information. ...
... • Gray Matter: The neurons or cells which have specialized neurologic functions (motor or sensory) • White Matter: Axons which form pathways for conducting different types of information. ...
BRAIN FACTS
... * Your brain uses 20% oxygen and 20% of the blood circulating in your body * While awake, your brain generates between 10 and 23 watts of power-or enough energy to power a light bulb * Children who learn two languages before the age of five alters the brain structure and adults have a much denser gr ...
... * Your brain uses 20% oxygen and 20% of the blood circulating in your body * While awake, your brain generates between 10 and 23 watts of power-or enough energy to power a light bulb * Children who learn two languages before the age of five alters the brain structure and adults have a much denser gr ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ...
... Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ...
Document
... Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ...
... Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ...
Chapter2 - cfhssocialstudies
... Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ...
... Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ...
The Human brain
... The cerebrum has sensory, motor, and association functions: • Sensory functions: receives info from sense receptors and interprets these messages • Motor functions: motor areas of the cerebrum are responsible for all voluntary movement and for some involuntary movement • Association functions: lear ...
... The cerebrum has sensory, motor, and association functions: • Sensory functions: receives info from sense receptors and interprets these messages • Motor functions: motor areas of the cerebrum are responsible for all voluntary movement and for some involuntary movement • Association functions: lear ...
The Brain - PSYCHOUT
... connections to other brain areas. For example, motor neurons in the spinal cord receive signals from neurons in the cortex that generate basic movement commands. In turn, these spinal cord neurons send signals to the muscles, causing them to contract. If scientists electrically stimulate only the ...
... connections to other brain areas. For example, motor neurons in the spinal cord receive signals from neurons in the cortex that generate basic movement commands. In turn, these spinal cord neurons send signals to the muscles, causing them to contract. If scientists electrically stimulate only the ...
Congenital Malformation & Hydrocephalus
... formation of the neural tube, the inside of which will become the ventricular system and the wall of which will become the brain and spinal cord Failure of a portion of the neural tube to close, or reopening after successful closure, may lead to one of several malformations. All are characterized by ...
... formation of the neural tube, the inside of which will become the ventricular system and the wall of which will become the brain and spinal cord Failure of a portion of the neural tube to close, or reopening after successful closure, may lead to one of several malformations. All are characterized by ...
November 1 CNS INTRO
... information is exchanged between brainstem and spinal cord, or deep brain nucleand cortical ribbon. What two major anatomical areas of gray matter in the brain account for each respectively? ...
... information is exchanged between brainstem and spinal cord, or deep brain nucleand cortical ribbon. What two major anatomical areas of gray matter in the brain account for each respectively? ...
Central Nervous System Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... dendrite or cell body of another – Neurotransmitters: • Chemicals that are released in the synaptic cleft • They cause electrical activity in the second neuron ...
... dendrite or cell body of another – Neurotransmitters: • Chemicals that are released in the synaptic cleft • They cause electrical activity in the second neuron ...
Quiz 10
... b. Happiness; tone of voice c. Fear; tone of voice d. Happiness; body posture e. Anger; tone of voice 9. People with volitional paresis are unable to a. Cry b. Comprehend other people’s emotions c. Voluntarily move their facial muscles d. Move their facial muscles when having a natural emotional res ...
... b. Happiness; tone of voice c. Fear; tone of voice d. Happiness; body posture e. Anger; tone of voice 9. People with volitional paresis are unable to a. Cry b. Comprehend other people’s emotions c. Voluntarily move their facial muscles d. Move their facial muscles when having a natural emotional res ...
File - Hardman`s AP Biology
... Transmission Across a Synapse • A synapse is a region where neurons nearly touch • Small gap between neurons is the synaptic cleft • Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters – Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron – Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presy ...
... Transmission Across a Synapse • A synapse is a region where neurons nearly touch • Small gap between neurons is the synaptic cleft • Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters – Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron – Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presy ...