answers - Easy Peasy All-in
... What is a synapse and how do nerve impulses pass across a synapse? A synapse is the gap between neurons. Nerve impulses change to a chemical signal when they near the synapse and it triggers an electrical signal when it enters the next neuron. What is a reflex action and how is this a good test of t ...
... What is a synapse and how do nerve impulses pass across a synapse? A synapse is the gap between neurons. Nerve impulses change to a chemical signal when they near the synapse and it triggers an electrical signal when it enters the next neuron. What is a reflex action and how is this a good test of t ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... Positive ions flow back out; the neuron becomes negatively charged again Resting state is restored After firing, the neuron dips below resting level and is less willing to fire ...
... Positive ions flow back out; the neuron becomes negatively charged again Resting state is restored After firing, the neuron dips below resting level and is less willing to fire ...
Correlated neuronal activity and the flow of neural information
... delineated regions within the DMN in terms of their functional roles (Raichle et al., 2001). • PCC appears to serve an important adaptive function and is implicated in broad-based continuous sampling of external and internal environments (Raichle et al., 2001). • Reduced connectivity with anterior D ...
... delineated regions within the DMN in terms of their functional roles (Raichle et al., 2001). • PCC appears to serve an important adaptive function and is implicated in broad-based continuous sampling of external and internal environments (Raichle et al., 2001). • Reduced connectivity with anterior D ...
Document
... In humans, the outermost part of the cerebral cortex forms the neocortex, six parallel layers of neurons arranged tangential to the brain surface. Such a large, highly convoluted neocortex was thought to be required for advanced cognition, the perception and reasoning that form knowledge. Both prima ...
... In humans, the outermost part of the cerebral cortex forms the neocortex, six parallel layers of neurons arranged tangential to the brain surface. Such a large, highly convoluted neocortex was thought to be required for advanced cognition, the perception and reasoning that form knowledge. Both prima ...
Neuron death - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. discuss the mechanisms involved in neuron death. 2. discuss the process and goals of synaptic rearrangement. 3. discuss neurodevelopment in infancy through to adolescence. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. discuss the mechanisms involved in neuron death. 2. discuss the process and goals of synaptic rearrangement. 3. discuss neurodevelopment in infancy through to adolescence. ...
AChE inhibitor
... For further information on brain plasticity in old age and factors which may enhance this plasticity, see the below papers (full texts are available on the course website under “Relevant Articles”): • Merabet LB et al. What blindness can tell us about seeing again: merging neuroplasticity and neuro ...
... For further information on brain plasticity in old age and factors which may enhance this plasticity, see the below papers (full texts are available on the course website under “Relevant Articles”): • Merabet LB et al. What blindness can tell us about seeing again: merging neuroplasticity and neuro ...
Information Processing SG AK
... a) sensory neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse to the central nervous system b) motor neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse away from the central nervous system and towards the muscle or gland that needs to respond c) interneurons—nerve cells found only in the brain and spinal co ...
... a) sensory neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse to the central nervous system b) motor neurons—nerve cells that carry a nerve impulse away from the central nervous system and towards the muscle or gland that needs to respond c) interneurons—nerve cells found only in the brain and spinal co ...
Brain Computer Interface Seminar Report
... interaction. A brain-computer interface, sometimes called a direct neural interface or a brain machine interface, is a direct communication pathway between a human or animal brain(or brain cell culture) and an external device. In one BCIs, computers either accept commands from the brain or send sign ...
... interaction. A brain-computer interface, sometimes called a direct neural interface or a brain machine interface, is a direct communication pathway between a human or animal brain(or brain cell culture) and an external device. In one BCIs, computers either accept commands from the brain or send sign ...
Ling 8700: Lecture Notes 1 A Model of Neural Activation
... We will assume this kind of transition model, with transitions defined by synaptic weights. ...
... We will assume this kind of transition model, with transitions defined by synaptic weights. ...
Possible Solutions from the Cognitive Neuroscience of Emotion
... dynamic versus static emotional expressions. ...
... dynamic versus static emotional expressions. ...
AP Psychology – Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... a. The patient's left arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. b. The patient's right arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. c. The patient's left arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud. d. The patient's right arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud ...
... a. The patient's left arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. b. The patient's right arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. c. The patient's left arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud. d. The patient's right arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud ...
Mind from brain: physics & neuroscience
... and their connections within different layers. • How does depth and the size of the basins of attractors depend on these parameters? How to measure and/or visualize attractors? • How does it depend on the accommodation level? Noise? General arousal? Inhibition strength, local excitations, long-dista ...
... and their connections within different layers. • How does depth and the size of the basins of attractors depend on these parameters? How to measure and/or visualize attractors? • How does it depend on the accommodation level? Noise? General arousal? Inhibition strength, local excitations, long-dista ...
1 - My Blog
... a. The patient's left arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. b. The patient's right arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. c. The patient's left arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud. d. The patient's right arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud ...
... a. The patient's left arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. b. The patient's right arm will fall limp and he will become speechless. c. The patient's left arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud. d. The patient's right arm will fall limp but he will continue counting aloud ...
File
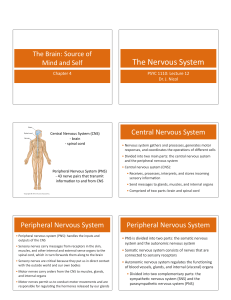
... • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves is the spinal cord. • The brain controls most functions in the body. • The brain is located in the head and is protecte ...
... • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The thick column of nerve tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves is the spinal cord. • The brain controls most functions in the body. • The brain is located in the head and is protecte ...
Neural Crest
... • Homing of peripheral neurons and their supportive cells might be dictated by a delicate equilibrium between the multiple actions of stimulatory and inhibitory molecules, which is modulated further by defined responses of the dispersing cells to these ECM components during their successive phases ...
... • Homing of peripheral neurons and their supportive cells might be dictated by a delicate equilibrium between the multiple actions of stimulatory and inhibitory molecules, which is modulated further by defined responses of the dispersing cells to these ECM components during their successive phases ...
Psychology Chapter 2 Notes CENTRAL – The brain and spinal
... convulsions and possible death. Black widow spider venom is an agonist for acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is also found in the hippocampus, an area of the brain that is responsible for forming new memories, and low levels of acetylcholine have been associated with Alzheimer’s disease, the most common ...
... convulsions and possible death. Black widow spider venom is an agonist for acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is also found in the hippocampus, an area of the brain that is responsible for forming new memories, and low levels of acetylcholine have been associated with Alzheimer’s disease, the most common ...
No Slide Title
... What is the effect of adrenaline's sympathetic action on the digestive system? ...
... What is the effect of adrenaline's sympathetic action on the digestive system? ...
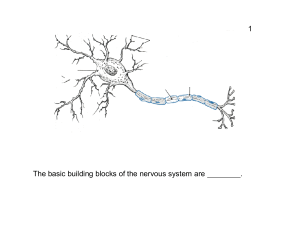
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... the synaptic gaps between neurons. (Don’t be specific.) ...
... the synaptic gaps between neurons. (Don’t be specific.) ...
Nervous System
... The nervous system of many animals consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. This system allows animals to obtain quick feedback about their surroundings and to react immediately. The nervous system can be separated into two divisions, the central nervous system which includes the brain an ...
... The nervous system of many animals consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. This system allows animals to obtain quick feedback about their surroundings and to react immediately. The nervous system can be separated into two divisions, the central nervous system which includes the brain an ...
addiction
... amphetamines and other addictive drugs alter the brains pleasure circuits. Activating this circuit, also called the reward circuit, produces a feel-good sensation. Eating cheesecake or tacos or any other food you love activates it. So does sex, winning a competition, acing a test, receiving praise a ...
... amphetamines and other addictive drugs alter the brains pleasure circuits. Activating this circuit, also called the reward circuit, produces a feel-good sensation. Eating cheesecake or tacos or any other food you love activates it. So does sex, winning a competition, acing a test, receiving praise a ...
DOC
... Neurons communicate using chemical messengers called NEUROTRANSMITTERS. A neuron sends an electrical signal that triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. Like a lock and key, the chemical attaches to a special receptor on another neuron. The message is sent. Some neurotransmitters tell the next n ...
... Neurons communicate using chemical messengers called NEUROTRANSMITTERS. A neuron sends an electrical signal that triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. Like a lock and key, the chemical attaches to a special receptor on another neuron. The message is sent. Some neurotransmitters tell the next n ...
Slide 1
... – Study behavioral manifestations • Animal models, brain lesions – Human brain imaging techniques • Renaissance in the study of emotion • Affective neuroscience • Neural basis of emotion and mood ...
... – Study behavioral manifestations • Animal models, brain lesions – Human brain imaging techniques • Renaissance in the study of emotion • Affective neuroscience • Neural basis of emotion and mood ...