Nervous System
... • Cerebral cortex • Nerve cells lie in sheets on the surface of the cerebrum • Gyri – folds in the sheets • Sulci – grooves that separate the gyri ...
... • Cerebral cortex • Nerve cells lie in sheets on the surface of the cerebrum • Gyri – folds in the sheets • Sulci – grooves that separate the gyri ...
Chapter 24 Nervous Systems
... - a scanning and imaging technology used to study brain functions. - used on conscious patients, - monitors changes in blood oxygen usage in the brain. - correlates to regions of intense brain function. ...
... - a scanning and imaging technology used to study brain functions. - used on conscious patients, - monitors changes in blood oxygen usage in the brain. - correlates to regions of intense brain function. ...
Nervous System Notes
... • What is the main job of the brain? The brain’s main role is to process all information (ingoing and outgoing messages) for immediate response or storage of memories. • What are the 3 main types of inputs and what do they respond to? 1. Electromagnetic ~ response to light. 2. Mechanical ~ response ...
... • What is the main job of the brain? The brain’s main role is to process all information (ingoing and outgoing messages) for immediate response or storage of memories. • What are the 3 main types of inputs and what do they respond to? 1. Electromagnetic ~ response to light. 2. Mechanical ~ response ...
How do maggots and worms navigate temperature
... As seen in image 2 the turning rate was shifted by 90 degrees celcius to the input temperature signal showing the motion output is the first derivative of the sensory input dT/dt. It would have been nice to be able to see the effect over a longer time period. Other arbitrary input functions such as ...
... As seen in image 2 the turning rate was shifted by 90 degrees celcius to the input temperature signal showing the motion output is the first derivative of the sensory input dT/dt. It would have been nice to be able to see the effect over a longer time period. Other arbitrary input functions such as ...
Bill Deakin University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
... The Neuroscience and Psychiatry Unit aims to understand the neurobiology of common mental illness and new principles of treatment using neuroimaging together with cognitive and drug challenges. We will tailor the research training experiences to the individual needs of the ECNP visiting scientist. C ...
... The Neuroscience and Psychiatry Unit aims to understand the neurobiology of common mental illness and new principles of treatment using neuroimaging together with cognitive and drug challenges. We will tailor the research training experiences to the individual needs of the ECNP visiting scientist. C ...
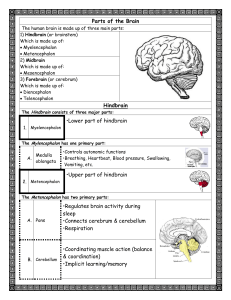
Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
... •Regulates brain activity during sleep •Connects cerebrum & cerebellum •Respiration ...
... •Regulates brain activity during sleep •Connects cerebrum & cerebellum •Respiration ...
3 - smw15.org
... memories – Milner (1968): the classic case of H.M. – Only in 2008 (at the time of his death at age 82), was his name revealed as ...
... memories – Milner (1968): the classic case of H.M. – Only in 2008 (at the time of his death at age 82), was his name revealed as ...
The Nervous System
... Recurrent attacks of disturbed brain funtion Seizure characteristics may include: altered state of consciousness, convulsive uncontrolled movements,disturbances of feeling or behavior. May experience Aura-involves the senses, may hear or smell-usually consistent & remains the same. ...
... Recurrent attacks of disturbed brain funtion Seizure characteristics may include: altered state of consciousness, convulsive uncontrolled movements,disturbances of feeling or behavior. May experience Aura-involves the senses, may hear or smell-usually consistent & remains the same. ...
Thrills That Kill
... In the past, it was thought that all memory was in the brain. However, Gazzaniga (1988) reports that memory occurs throughout the nervous system. So every thought you have is “felt” throughout your entire body because the receptors for the chemicals in your brain are found on the surfaces of cells t ...
... In the past, it was thought that all memory was in the brain. However, Gazzaniga (1988) reports that memory occurs throughout the nervous system. So every thought you have is “felt” throughout your entire body because the receptors for the chemicals in your brain are found on the surfaces of cells t ...
Ch 2 Physiology - Texas A&M University
... and an axon. • Neurons are not directly attached but are indirectly connected by synapses. • One neuron sends an electrical signal to another neuron by releasing ...
... and an axon. • Neurons are not directly attached but are indirectly connected by synapses. • One neuron sends an electrical signal to another neuron by releasing ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... The endocrine system constitutes the second great communi cating system of the body, with the first being the nervous system. The endocrine system consists of ductless glands which secrete hormones. A hormone is a chemical substance synthesized by a specific organ or tissue and secreted directly ...
... The endocrine system constitutes the second great communi cating system of the body, with the first being the nervous system. The endocrine system consists of ductless glands which secrete hormones. A hormone is a chemical substance synthesized by a specific organ or tissue and secreted directly ...
Gamma Band Oscillation
... Singer and Gray recorded both multi-unit activity and local field potentials (LFP) from single electrodes placed in the Primary visual cortex of anesthetised and paralyzed cats. Using a correlational analysis of cell activity and Fourier analysis, they noticed that a significant proportion of the re ...
... Singer and Gray recorded both multi-unit activity and local field potentials (LFP) from single electrodes placed in the Primary visual cortex of anesthetised and paralyzed cats. Using a correlational analysis of cell activity and Fourier analysis, they noticed that a significant proportion of the re ...
The Brain.
... touch, and movement from the rest of the body – such as distance and position of objects. It is also responsible for reading and arithmetic. Injury to this area, or lack of accurate sensory information from the lower levels of the brain, create an inability to discriminate between different stimuli, ...
... touch, and movement from the rest of the body – such as distance and position of objects. It is also responsible for reading and arithmetic. Injury to this area, or lack of accurate sensory information from the lower levels of the brain, create an inability to discriminate between different stimuli, ...
the search for principles of neuronal organization
... Many neuroscientists seem to feel guilty about the level of the explanations they are proposing: those working on the physiology of neurones imagine that explanations in terms of molecules would be more satisfying. This stems in large part from the introduction of many new molecular biological metho ...
... Many neuroscientists seem to feel guilty about the level of the explanations they are proposing: those working on the physiology of neurones imagine that explanations in terms of molecules would be more satisfying. This stems in large part from the introduction of many new molecular biological metho ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 07 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System, Part 3
... Damage to Broca’s and/or Wernicke’s areas can cause aphasia. For right-handed people, these sensitive areas are located on the brain’s left hemisphere. Broca’s area: helps to convert phonemic information into motor commands and lies close to motor areas controlling the vocal articulature Wernicke’s ...
... Damage to Broca’s and/or Wernicke’s areas can cause aphasia. For right-handed people, these sensitive areas are located on the brain’s left hemisphere. Broca’s area: helps to convert phonemic information into motor commands and lies close to motor areas controlling the vocal articulature Wernicke’s ...
a musical instrument using in vitro neural networks
... difference between fluctuations of the potentials recorded between two electrodes, one of which is a reference electrode). This activity corresponds to variations of field potentials of the clusters of neurons located within the vicinity of each electrode. The signals from each electrode are amplifi ...
... difference between fluctuations of the potentials recorded between two electrodes, one of which is a reference electrode). This activity corresponds to variations of field potentials of the clusters of neurons located within the vicinity of each electrode. The signals from each electrode are amplifi ...
Nervous Systems
... the following questions. No talking!!!!!!! 1. The parts of the body that make up the Peripheral Nervous System are the _______ and __________. 2. A _____________ has 4 parts and carries message sent from the brain all over the body. 3. A __________ is the part of a neuron that sends the messages to ...
... the following questions. No talking!!!!!!! 1. The parts of the body that make up the Peripheral Nervous System are the _______ and __________. 2. A _____________ has 4 parts and carries message sent from the brain all over the body. 3. A __________ is the part of a neuron that sends the messages to ...
Brain Functional Organization
... satisfying constraints resulting from possessed knowledge = possible to attain dynamic states of the brain. There exist many local, alternative or sub-optimal, solutions => local context (internal) changes the interpretation. Time flies like an arrow Fruit flies like a banana Long-term memory is the ...
... satisfying constraints resulting from possessed knowledge = possible to attain dynamic states of the brain. There exist many local, alternative or sub-optimal, solutions => local context (internal) changes the interpretation. Time flies like an arrow Fruit flies like a banana Long-term memory is the ...
neurons
... Neural Communication Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
... Neural Communication Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
Beyond Spikes: Neural Codes and the Chemical Vocabulary of
... neighboring neuron’s potential, this cannot be employed as a general method for neural signaling. After all, neurons routinely communicate with other neurons far outside the influence of the extraordinarily weak electric and magnetic fields that they generate. The only way for one neuron to know tha ...
... neighboring neuron’s potential, this cannot be employed as a general method for neural signaling. After all, neurons routinely communicate with other neurons far outside the influence of the extraordinarily weak electric and magnetic fields that they generate. The only way for one neuron to know tha ...
Introduction to Psychology Quiz #1 1. The main divisions of the
... a. Psychologists conduct research in laboratories. b. Psychologists conduct research on humans and animals. c. Psychologists use methods such as introspection and psychoanalysis. d. Psychologists uncover the causes of events by systematically collecting empirical evidence. ...
... a. Psychologists conduct research in laboratories. b. Psychologists conduct research on humans and animals. c. Psychologists use methods such as introspection and psychoanalysis. d. Psychologists uncover the causes of events by systematically collecting empirical evidence. ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here
... b. Beta waves have a higher frequency than alpha waves and are less regular, usually occurring when the brain is mentally focused. c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but ...
... b. Beta waves have a higher frequency than alpha waves and are less regular, usually occurring when the brain is mentally focused. c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but ...
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
... ● The brain of an ALS patient is significantly smaller than a brain of a normal person. This is because neurons start to break down and die causing a decrease in brain matter. The neurons that are affected are noticed to be in different parts of the brain. ...
... ● The brain of an ALS patient is significantly smaller than a brain of a normal person. This is because neurons start to break down and die causing a decrease in brain matter. The neurons that are affected are noticed to be in different parts of the brain. ...
Simulations of an Extrinsic Stochastic Model of the
... • Create a Computer Simulated Test-bed to model a biological system developed by Rui de Figueiredo. • An extrinsic stochastic model for the development, as a functions of age, of the average neuron/synapse population densities in cortical regions of the human brain. • The model describes the behavio ...
... • Create a Computer Simulated Test-bed to model a biological system developed by Rui de Figueiredo. • An extrinsic stochastic model for the development, as a functions of age, of the average neuron/synapse population densities in cortical regions of the human brain. • The model describes the behavio ...