The Nervous System
... Cerebrum Larger portion of the brain that provides higher level mental ...
... Cerebrum Larger portion of the brain that provides higher level mental ...
Slide ()
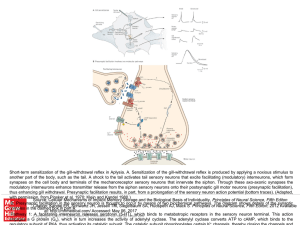
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... and are essential for movement, posture, breathing, circulation, digestion, and many other functions ...
... and are essential for movement, posture, breathing, circulation, digestion, and many other functions ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the dendrite through the cell body and then down the axon From the axon terminus, the signal is transferred to the next neuron Nerve impulses Neurons function because without any impulse, ...
... Motor – take impulses from the CNS to an effector (i.e. gland or muscle fiber) Nerve impulses move from the dendrite through the cell body and then down the axon From the axon terminus, the signal is transferred to the next neuron Nerve impulses Neurons function because without any impulse, ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... • The exam will be scored out of 60 points. • The exam will include 30 multiple choice questions (1 point each), 4 definitions (2 points each), and 5-6 short ...
... • The exam will be scored out of 60 points. • The exam will include 30 multiple choice questions (1 point each), 4 definitions (2 points each), and 5-6 short ...
thoughts - Budokon MD
... These three parts of the brain do not operate independently of one another. They have established numerous interconnections through which they influence one another. The brain’s nerve cells are known as neurons, which make up the organ’s so-called “gray matter.” The neurons transmit and gather elect ...
... These three parts of the brain do not operate independently of one another. They have established numerous interconnections through which they influence one another. The brain’s nerve cells are known as neurons, which make up the organ’s so-called “gray matter.” The neurons transmit and gather elect ...
File
... 12. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: A) association areas. B) synaptic gaps. C) interneurons. D) neural networks. ...
... 12. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: A) association areas. B) synaptic gaps. C) interneurons. D) neural networks. ...
Notes on Learning to Compute and Computing to Learn
... sites where multimodal integration actually takes place [10] – these studies were inspired, in part, by the earlier work on cats [21, 22]. Two experiments, one dealing with subjects’ mouth movements whilst looking at a videotape of the lower half of a face silently mouthing ...
... sites where multimodal integration actually takes place [10] – these studies were inspired, in part, by the earlier work on cats [21, 22]. Two experiments, one dealing with subjects’ mouth movements whilst looking at a videotape of the lower half of a face silently mouthing ...
doc Chapter 15 Notes
... We expect that the neurons die because they have been starved to death after being cut off from oxygen and glucose but research shows that it is the presence of excessive amounts of glutamate that kill the cells (as with excitotoxic lesions) - sodium-potassium transporters that regulate the balance ...
... We expect that the neurons die because they have been starved to death after being cut off from oxygen and glucose but research shows that it is the presence of excessive amounts of glutamate that kill the cells (as with excitotoxic lesions) - sodium-potassium transporters that regulate the balance ...
Mirror Neurons
... Purchasing institutions may not grant rights to any third party, nor make the material available to external organisations, without prior written permission from Uniview Worldwide Ltd. Uniview Worldwide Ltd maintains control of all copyright permissions and retains the right to request access to ass ...
... Purchasing institutions may not grant rights to any third party, nor make the material available to external organisations, without prior written permission from Uniview Worldwide Ltd. Uniview Worldwide Ltd maintains control of all copyright permissions and retains the right to request access to ass ...
The Brain - Academic Computer Center
... Wernicke’s area (Understanding of written and spoken language and in sounding unfamiliar words) ...
... Wernicke’s area (Understanding of written and spoken language and in sounding unfamiliar words) ...
Document
... Many students have encountered the material in this unit before, either in biology or in high school psychology. The trick, then, is to make this material clear but also different enough in orientation from what they have learned earlier so that it will engage their interest. To the extent that you ...
... Many students have encountered the material in this unit before, either in biology or in high school psychology. The trick, then, is to make this material clear but also different enough in orientation from what they have learned earlier so that it will engage their interest. To the extent that you ...
Neurons are the cells that carry messages between parts of the body
... The endocrine system uses chemicals released into the blood (hormones) to communicate between parts of the body. An organ that releases hormones is called a gland. The gland releases the hormones into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell ...
... The endocrine system uses chemicals released into the blood (hormones) to communicate between parts of the body. An organ that releases hormones is called a gland. The gland releases the hormones into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell ...
nervous system development and histology
... • A patch of tissue on the dorsal surface of the embryo that will become the nervous system • Development induced by chemical signals “growth factors”: several chemicals produced in developing and mature brain that stimulate neuron development and help neurons respond to injury ...
... • A patch of tissue on the dorsal surface of the embryo that will become the nervous system • Development induced by chemical signals “growth factors”: several chemicals produced in developing and mature brain that stimulate neuron development and help neurons respond to injury ...
June 14_Neuroanatomy & Audition
... If Na+ outflow causes the potential to reach -55 mV, an action potential will occur and the signal will be sent. This is known as the threshold potential. If the potential does not reach the threshold, no action potential will occur…thus it is an “All or None” ...
... If Na+ outflow causes the potential to reach -55 mV, an action potential will occur and the signal will be sent. This is known as the threshold potential. If the potential does not reach the threshold, no action potential will occur…thus it is an “All or None” ...
Chapter 35 Nervous System Notes Outline
... Name ______________________________________ Date_________________ Period ________________ Topic 35-1: Human Body Systems (Dragonfly Textbook Pages 890-896) Aim:_____________________________________________________________________________________ 1) How is the human body organized? ...
... Name ______________________________________ Date_________________ Period ________________ Topic 35-1: Human Body Systems (Dragonfly Textbook Pages 890-896) Aim:_____________________________________________________________________________________ 1) How is the human body organized? ...
PDF
... about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory neuron development, Hirohide Takebayashi and colleagues analyse sensory neuron phenotypes in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of Olig2 knockout mouse embryos, which lack motoneurons (see ...
... about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory neuron development, Hirohide Takebayashi and colleagues analyse sensory neuron phenotypes in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of Olig2 knockout mouse embryos, which lack motoneurons (see ...
of sleep
... • Manifest content: Freud’s term for the remembered story line of a dream • Latent content: Freud’s term for the underlying meaning of a dream • Freud’s wish-fulfillment theory: dreams act to discharge feelings that cannot be expressed in public – Little scientific validation – Dreams can have many ...
... • Manifest content: Freud’s term for the remembered story line of a dream • Latent content: Freud’s term for the underlying meaning of a dream • Freud’s wish-fulfillment theory: dreams act to discharge feelings that cannot be expressed in public – Little scientific validation – Dreams can have many ...
to read the full article
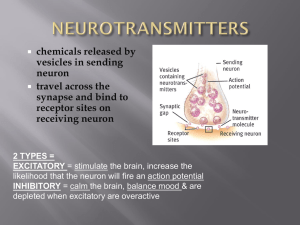
... Neurotransmitters are cleared away by one of three processes. Some are broken down by enzymes and removed through the blood stream (hence their presence may be detected in blood or urine samples). Others diffuse away to regions of the brain where there are no receptors to bind with while others are ...
... Neurotransmitters are cleared away by one of three processes. Some are broken down by enzymes and removed through the blood stream (hence their presence may be detected in blood or urine samples). Others diffuse away to regions of the brain where there are no receptors to bind with while others are ...
The biological Approach
... behavioural and psychological characteristics. • The expression of a genotype is inevitably influenced by environmental factors. • For example, the maximum height of an individual is dictated by the genotype but environmental factors such as nutrition will affect how likely the person is to achieve ...
... behavioural and psychological characteristics. • The expression of a genotype is inevitably influenced by environmental factors. • For example, the maximum height of an individual is dictated by the genotype but environmental factors such as nutrition will affect how likely the person is to achieve ...
BioCapture™ : Acquiring EEG data Quick Notes
... These patterns have particular frequency ranges and are associated with different states of brain function (e.g., waking and various levels of sleep). These patterns represent synchronized activity over a network of neurons. Delta waves are the slowest of the known EEG frequencies—no faster than 4 H ...
... These patterns have particular frequency ranges and are associated with different states of brain function (e.g., waking and various levels of sleep). These patterns represent synchronized activity over a network of neurons. Delta waves are the slowest of the known EEG frequencies—no faster than 4 H ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... Desire to understand the brain and to imitate some of its strength Traditional computers implement a sequence of logical and arithmetic operations but don’t have the ability to adapt their structure or learn Learn from examples, Generalisation ...
... Desire to understand the brain and to imitate some of its strength Traditional computers implement a sequence of logical and arithmetic operations but don’t have the ability to adapt their structure or learn Learn from examples, Generalisation ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...