LECTURE OUTLINE
... Conduction of an Action Potential The action potential travels down an axon one small section at a time. Transmission across a Synapse Every axon branches into many fine endings, each tipped with an axon terminal. Each terminal lies very close to either the dendrite or cell body of another neuron. T ...
... Conduction of an Action Potential The action potential travels down an axon one small section at a time. Transmission across a Synapse Every axon branches into many fine endings, each tipped with an axon terminal. Each terminal lies very close to either the dendrite or cell body of another neuron. T ...
Nerve Tissue Notes
... Nerve Cell – The Neuron • Axon sends impulses – Myelin sheath, made of Schwann cells, wraps around axons and speeds up signals ...
... Nerve Cell – The Neuron • Axon sends impulses – Myelin sheath, made of Schwann cells, wraps around axons and speeds up signals ...
Nervous System Function
... is the NT) inside the cell Change function of cell (e.g., change protein production to permanently alter cell function for learning) ...
... is the NT) inside the cell Change function of cell (e.g., change protein production to permanently alter cell function for learning) ...
Zipf’s Law Arises Naturally from Hidden Structure
... sequences, and neural activity. Partly because it is so unexpected, a great deal of effort has gone into explaining it. So far, almost all explanations are either domain specific or require fine-tuning. For instance, in biology, one explanation for observations of Zipf’s law is that biological syste ...
... sequences, and neural activity. Partly because it is so unexpected, a great deal of effort has gone into explaining it. So far, almost all explanations are either domain specific or require fine-tuning. For instance, in biology, one explanation for observations of Zipf’s law is that biological syste ...
Nolte – Chapter 2 (Development of the Nervous System)
... Leads to the nervous system, epidermis, and nervous system These cells all have an affinity to become neurons (since the express bone morphogenetic proteins) The organizer has a BMP inhibitor. o Endoderm Yields the gut o Mesoderm Muscle and tissues o A neural plate initially forms as a lon ...
... Leads to the nervous system, epidermis, and nervous system These cells all have an affinity to become neurons (since the express bone morphogenetic proteins) The organizer has a BMP inhibitor. o Endoderm Yields the gut o Mesoderm Muscle and tissues o A neural plate initially forms as a lon ...
Chapter 2
... How Drugs Work • Drugs similar in shape to neurotransmitters can stimulate receptor cites just like neurotransmitters do ...
... How Drugs Work • Drugs similar in shape to neurotransmitters can stimulate receptor cites just like neurotransmitters do ...
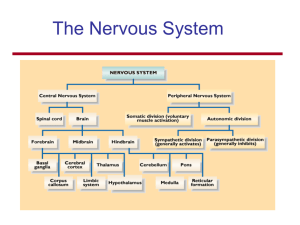
Structure of the Nervous System
... The supply of blood to the brain is a relatively closed system in which most substances cannot pass from the blood to the brain. While there are pores (openings) in the capillaries that supply other parts of the body, such pores don't occur in the capillaries of the brain. This phenomenon is referre ...
... The supply of blood to the brain is a relatively closed system in which most substances cannot pass from the blood to the brain. While there are pores (openings) in the capillaries that supply other parts of the body, such pores don't occur in the capillaries of the brain. This phenomenon is referre ...
The Nervous System
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
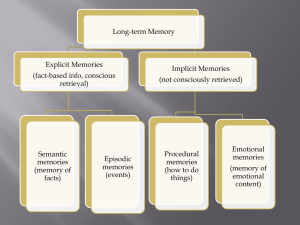
When neurons form memories
... Long-term memory is a hallmark trait of the functioning of our CNS. The second experience is never exactly the same as the first. Each event leaves a trace in our brain that shapes the way future encounters are handled. However, it appears that the neocortical brain areas that produce our conscious ...
... Long-term memory is a hallmark trait of the functioning of our CNS. The second experience is never exactly the same as the first. Each event leaves a trace in our brain that shapes the way future encounters are handled. However, it appears that the neocortical brain areas that produce our conscious ...
The Nervous System - Ione Community Charter School
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
The Nervous System
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
... So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . . 1. Receptors in the skin sense touch or other stimuli. 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a r ...
Chapter 13- Central NS
... (ipsilateral). This is how information is linked between thecerebellum and the cerebral cortex. ...
... (ipsilateral). This is how information is linked between thecerebellum and the cerebral cortex. ...
A Gaussian Approach to Neural Nets with Multiple Memory Domains
... threshold fluctuations, in which the neural connections are set up by means of chemical markers, revealed the existence of multiple memory domains. This behaviour appears both in Poisson and Gaussian approaches for the neural connectivity. Here, we extend these studies to non-isolated neural nets wi ...
... threshold fluctuations, in which the neural connections are set up by means of chemical markers, revealed the existence of multiple memory domains. This behaviour appears both in Poisson and Gaussian approaches for the neural connectivity. Here, we extend these studies to non-isolated neural nets wi ...
Simple model of spiking neurons
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
Neural Oscillations
... faster and better with just E-to-I projections Network with just I-to-E cross-circuit projections: I cells fire single spikes rather then doublets, so E cells again receive two I spikes – Synchrony is always stable – Can also form stable anti-phase solution To prove that map reduction works they als ...
... faster and better with just E-to-I projections Network with just I-to-E cross-circuit projections: I cells fire single spikes rather then doublets, so E cells again receive two I spikes – Synchrony is always stable – Can also form stable anti-phase solution To prove that map reduction works they als ...
Simple model of spiking neurons
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
Unit 2 PowerPoint 2.1 and 2.2
... sheath, like an insulated electrical wire Myelinated neurons are typically found in the peripheral nerves (sensory and motor neurons), while non-myelinated neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord. ...
... sheath, like an insulated electrical wire Myelinated neurons are typically found in the peripheral nerves (sensory and motor neurons), while non-myelinated neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord. ...
The Nervous System
... B. The development of motor control indicates the progressive myelination and maturation of a child’s nervous system. ...
... B. The development of motor control indicates the progressive myelination and maturation of a child’s nervous system. ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which a neutral conditioned stimulus (CS) is paired with a naturally aversive unconditioned stimulus (US) leading the CS to evoke a fearful reaction even in absence of the US (Pavlov, 1927). In some cases, this fear of the conditioned danger ...
... Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which a neutral conditioned stimulus (CS) is paired with a naturally aversive unconditioned stimulus (US) leading the CS to evoke a fearful reaction even in absence of the US (Pavlov, 1927). In some cases, this fear of the conditioned danger ...
Ch 13 - lanoue
... The “Catcher” - Hold your thumb and index finger two inches apart while your partner drops a ruler between them. The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates thei ...
... The “Catcher” - Hold your thumb and index finger two inches apart while your partner drops a ruler between them. The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates thei ...
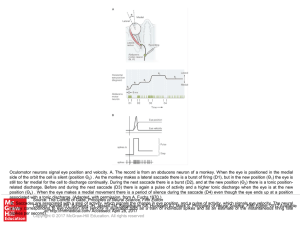
Slide ()
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...