Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 5:Spinal cord The
... bundle of axons covering full length of the body. Its primary function is to facilitate reflex movements. The animation given below demonstrates the mechanism of reflex action. ...
... bundle of axons covering full length of the body. Its primary function is to facilitate reflex movements. The animation given below demonstrates the mechanism of reflex action. ...
Nervous System Exam.tst
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3) The term central nervous system refers to the: A) brain and cranial nerves B) spinal cord and spinal nerves C) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves D) brain and spinal cord E) autonomic and ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3) The term central nervous system refers to the: A) brain and cranial nerves B) spinal cord and spinal nerves C) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves D) brain and spinal cord E) autonomic and ...
Stem Cells and Ectoderm
... ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ...
Differentiation
... Establishing Neural Cells from the Ectoderm • Competence: multipotent cells with the ability to form neurons with the right signals • Specification: the right signals are there but cell change could still be repressed by other signals • Determination: the cells have entered the neuronal pathway and ...
... Establishing Neural Cells from the Ectoderm • Competence: multipotent cells with the ability to form neurons with the right signals • Specification: the right signals are there but cell change could still be repressed by other signals • Determination: the cells have entered the neuronal pathway and ...
Brain Neurotransmitters
... • Caffeine belongs to the xanthine chemical group. • Adenosine is a naturally occurring xanthine in the brain that is used as a neurotransmitter at some synapses. • One effect of caffeine is to interfere with adenosine at multiple sites in the brain including the reticular formation. ...
... • Caffeine belongs to the xanthine chemical group. • Adenosine is a naturally occurring xanthine in the brain that is used as a neurotransmitter at some synapses. • One effect of caffeine is to interfere with adenosine at multiple sites in the brain including the reticular formation. ...
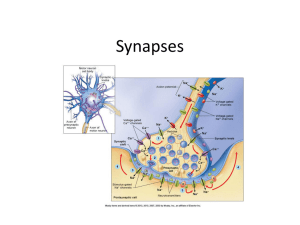
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... – Cell membranes are continuous – in cardiac muscle and some smooth muscle cells ...
... – Cell membranes are continuous – in cardiac muscle and some smooth muscle cells ...
Note 11.1 - The Nervous System
... The Structure and Organization of the Human Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – is the body’s coordinating centre for mechanical and chemical actions; made up of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – are all the parts of the nervous system, excluding the brain and s ...
... The Structure and Organization of the Human Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – is the body’s coordinating centre for mechanical and chemical actions; made up of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – are all the parts of the nervous system, excluding the brain and s ...
CNS Autonomic NS
... • Coding and processing of stimuli allows us to determine the stimulus type, intensity, location, and duration • Type determined by the cortex in response to where the input comes from; 1:1 association between type of receptor and sensation is called labeled line coding • Location determined by whic ...
... • Coding and processing of stimuli allows us to determine the stimulus type, intensity, location, and duration • Type determined by the cortex in response to where the input comes from; 1:1 association between type of receptor and sensation is called labeled line coding • Location determined by whic ...
2-3 nervous sys Sp13
... Brain and spinal cord from brain/spinal cord to muscles or Peripheral nervous Central nervous glands system (PNS) system (CNS) ...
... Brain and spinal cord from brain/spinal cord to muscles or Peripheral nervous Central nervous glands system (PNS) system (CNS) ...
Psychology - WordPress.com
... Humanistic Psychologist, agrees w/ Maslow. Ppl need environment, it provides them generousness, acceptance, and empathy. SELF ACTUASLIZATION, Fully Functioning Ppl. ...
... Humanistic Psychologist, agrees w/ Maslow. Ppl need environment, it provides them generousness, acceptance, and empathy. SELF ACTUASLIZATION, Fully Functioning Ppl. ...
A natural example of different circuit architectures for analogous
... membrane and synaptic parameters might produce relatively similar network outputs. However, there is still a general assumption that similar behaviors in related animal species originate from a common neural architecture. In this study, we show that two species produce similar behaviors using hom ...
... membrane and synaptic parameters might produce relatively similar network outputs. However, there is still a general assumption that similar behaviors in related animal species originate from a common neural architecture. In this study, we show that two species produce similar behaviors using hom ...
Abstract n Bio - Prof Arto Nurmikko
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... 1. Essentially the same as described in muscle impulse. 2. Neuron not carrying an impulse is said to be _______________, where the Na+ ions are more abundant on the outside and the K+ ions are most abundant on the inside. 3. A stimulus, like a __________________ that is released from another neuron ...
... 1. Essentially the same as described in muscle impulse. 2. Neuron not carrying an impulse is said to be _______________, where the Na+ ions are more abundant on the outside and the K+ ions are most abundant on the inside. 3. A stimulus, like a __________________ that is released from another neuron ...
Nervous Tissue
... A neuron consists of a cell body where the nucleus, mitochondria, and other cell structures can be found. At one end of the neuron are the dendrites, multiples tree-like structures that acts as the receiving portion of the neuron. The other end is the axon, where the nerve impulse travels through to ...
... A neuron consists of a cell body where the nucleus, mitochondria, and other cell structures can be found. At one end of the neuron are the dendrites, multiples tree-like structures that acts as the receiving portion of the neuron. The other end is the axon, where the nerve impulse travels through to ...
4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
... Q: What is the nervous system? A network of billions of nerve cells linked together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body In the brain, roughly 100 billion (1011) neurons and 100 trillion (1014) synapses (connections between nerve cells) ...
... Q: What is the nervous system? A network of billions of nerve cells linked together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body In the brain, roughly 100 billion (1011) neurons and 100 trillion (1014) synapses (connections between nerve cells) ...
Slides - Mathematics of Networks meetings
... rather than using popular connectionist models Biological characteristics of the model needed to include: - Action potential “Signals” in the form of spikes of fixed amplitude - Modeling recurrent networks - Random delays between spikes - Conveying information along axons via variable spike rates - ...
... rather than using popular connectionist models Biological characteristics of the model needed to include: - Action potential “Signals” in the form of spikes of fixed amplitude - Modeling recurrent networks - Random delays between spikes - Conveying information along axons via variable spike rates - ...
Practice Exam 3 ANSWERS
... a. is propagated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels b. occurs whenever a pre-synaptic nerve fires a charge to a post synaptic nerve c. is carried out only whenever half of the neural threshold is reached d. moves bidirectionally away from the cell body 4. Saltatory conduction is made po ...
... a. is propagated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels b. occurs whenever a pre-synaptic nerve fires a charge to a post synaptic nerve c. is carried out only whenever half of the neural threshold is reached d. moves bidirectionally away from the cell body 4. Saltatory conduction is made po ...
Neuroscience, Genetics, and Behavior
... Neuroscience, Genetics, and Behavior • Neural and Hormonal Systems • The Peripheral Nervous System • The Central Nervous System ...
... Neuroscience, Genetics, and Behavior • Neural and Hormonal Systems • The Peripheral Nervous System • The Central Nervous System ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... temperature from the body. • Across the fissure, the corresponding motor cortex controls body movements. • Neurons associated with the head are located at the bottom of the fissure and those of the toes are at the top. • There are considerably more neurons associated with the face and hands than oth ...
... temperature from the body. • Across the fissure, the corresponding motor cortex controls body movements. • Neurons associated with the head are located at the bottom of the fissure and those of the toes are at the top. • There are considerably more neurons associated with the face and hands than oth ...
2014 chemical signal..
... -express a range of receptors and transporters similar to those present in neuron , and also release mediators (glutamate, lipid mediator and growth factors) -they respond to chemical signals from neurons, from neighboring astrocyte and microglial cells. ...
... -express a range of receptors and transporters similar to those present in neuron , and also release mediators (glutamate, lipid mediator and growth factors) -they respond to chemical signals from neurons, from neighboring astrocyte and microglial cells. ...
The Two Messenger Services of the Brain
... What is a Neuron? Neurons are single cells in the nervous system They can NOT be replaced so they must last a lifetime!! If the body of a neuron dies, the whole cell will die (such as in polio) Each neuron has an axon, a cell body and dendrites. Spaces between neurons are called synapses. ...
... What is a Neuron? Neurons are single cells in the nervous system They can NOT be replaced so they must last a lifetime!! If the body of a neuron dies, the whole cell will die (such as in polio) Each neuron has an axon, a cell body and dendrites. Spaces between neurons are called synapses. ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. ...
The Living Network Lab focuses its group is
... area of human fetuses naturally aborted at the tenth week of gestation (Vescovi (1999)). The stem cells can be isolated and cultured in-vitro as they have the ability to proliferate forming at first neurospheres that, as multipotent progenitors, can differentiate if suitably stimulated and become ne ...
... area of human fetuses naturally aborted at the tenth week of gestation (Vescovi (1999)). The stem cells can be isolated and cultured in-vitro as they have the ability to proliferate forming at first neurospheres that, as multipotent progenitors, can differentiate if suitably stimulated and become ne ...