Chapter 22: Development and Aging
... The notochord forms from mesoderm. During neurulation, the nervous system develops from midline ectoderm, just above the notochord; the notochord induces formation of the nervous system. A neural plate is seen first, then a neural tube; the anterior neural tube becomes the brain. At the neurula stag ...
... The notochord forms from mesoderm. During neurulation, the nervous system develops from midline ectoderm, just above the notochord; the notochord induces formation of the nervous system. A neural plate is seen first, then a neural tube; the anterior neural tube becomes the brain. At the neurula stag ...
Ch.10
... types of sensory receptors • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
... types of sensory receptors • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
Chapter Two - Texas Christian University
... carry those messages to the spinal cord or brain. • Motor (efferent) Neurons-neurons that carry messages from the spinal cord or the brain to the muscles and glands • Interneurons (association) Neurons- neurons that carry messages from one neuron to another. ...
... carry those messages to the spinal cord or brain. • Motor (efferent) Neurons-neurons that carry messages from the spinal cord or the brain to the muscles and glands • Interneurons (association) Neurons- neurons that carry messages from one neuron to another. ...
Nervous Systems
... How far can you safely drive behind the car in front if you are travelling at 60 mph? ...
... How far can you safely drive behind the car in front if you are travelling at 60 mph? ...
The Nervous System
... – Recognizes certain neurotransmitters, thus allowing it to begin a postsynaptic potential in the dendrite ...
... – Recognizes certain neurotransmitters, thus allowing it to begin a postsynaptic potential in the dendrite ...
1. Learning Depends on Integration of Brain Structures
... opportunity individuals have to explore and become actively involved with it, the more intricate the patterns for learning, thought, and creativity become. The latest infant research reveals that the breain is profoundly flexible, sensitie, and plastic and deeply dependent on and influenced by event ...
... opportunity individuals have to explore and become actively involved with it, the more intricate the patterns for learning, thought, and creativity become. The latest infant research reveals that the breain is profoundly flexible, sensitie, and plastic and deeply dependent on and influenced by event ...
Nervous System:
... Ion pumps in the cell membranes of neurons release three positively charged sodium ions, while taking in only two positively charged potassium ions which creates a negative charge inside the cell. The space inside the neuron now has a resting potential, which is a kind of membrane potential, because ...
... Ion pumps in the cell membranes of neurons release three positively charged sodium ions, while taking in only two positively charged potassium ions which creates a negative charge inside the cell. The space inside the neuron now has a resting potential, which is a kind of membrane potential, because ...
The Mammalian Nervous System: Structure and
... •Primary somatosensory motor cortex—behind the central sulcus; receives touch and pressure information •Involves attending to complex stimuli ...
... •Primary somatosensory motor cortex—behind the central sulcus; receives touch and pressure information •Involves attending to complex stimuli ...
Inhibitory Control of Hippocampal Inhibitory Neurons
... Distribution of neurons specialized for inhibiting inhibitory neurons, and their role played in the operation of hippocampus ...
... Distribution of neurons specialized for inhibiting inhibitory neurons, and their role played in the operation of hippocampus ...
Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of
... right hemispheres by mental activity. longitudinal fissure Center for all conscious and divided into cerebral living. lobes. Also contains cerebral cortex (gray matter), white matter, basal ganglia, diencephalon Bridge of nerve fibers Connects cerebral that connects one hemispheres, relaying cerebra ...
... right hemispheres by mental activity. longitudinal fissure Center for all conscious and divided into cerebral living. lobes. Also contains cerebral cortex (gray matter), white matter, basal ganglia, diencephalon Bridge of nerve fibers Connects cerebral that connects one hemispheres, relaying cerebra ...
Hourly2_2012 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... T F 10. Some slow pain signals reach the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus after a synaptic relay in the brainstem reticular formation. T F 11. The face area of the postcentral gyrus gets its primary thalamic input from the ventral posteromedial (VPM) nucleus of the thalamus. T F 12. The lens is t ...
... T F 10. Some slow pain signals reach the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus after a synaptic relay in the brainstem reticular formation. T F 11. The face area of the postcentral gyrus gets its primary thalamic input from the ventral posteromedial (VPM) nucleus of the thalamus. T F 12. The lens is t ...
The Nervous System
... to detect stimuli Uses motor neurons to carry signals from CNS to other parts of the body ...
... to detect stimuli Uses motor neurons to carry signals from CNS to other parts of the body ...
Option A.3 Pt 1 - Peoria Public Schools
... Rods and cones are photoreceptors located in the retina. • Describe the retina. a. A thin layer of light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. • Describe what rods and cones do for the eye. a. Rods and cones work together to detect the image focused on the retina. ...
... Rods and cones are photoreceptors located in the retina. • Describe the retina. a. A thin layer of light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. • Describe what rods and cones do for the eye. a. Rods and cones work together to detect the image focused on the retina. ...
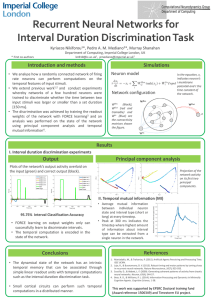
Recurrent Neural Networks for Interval Duration Discrimination Task
... • We analyse how a randomly connected network of firing rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stim ...
... • We analyse how a randomly connected network of firing rate neurons can perform computations on the temporal features of input stimuli. • We extend previous work1,2 and conduct experiments whereby networks of a few hundred neurons were trained to discriminate whether the time between two input stim ...
The Nervous System
... the cell body. Most axons have a myelin sheath that insulates the nerve fiber and speeds the transmission of impulses. III. The Central Nervous System A. Spinal Cord 1. cylinder of nerve tissue about 18 inches long and as thick as your index finger 2. runs down the central canal of the spine and is ...
... the cell body. Most axons have a myelin sheath that insulates the nerve fiber and speeds the transmission of impulses. III. The Central Nervous System A. Spinal Cord 1. cylinder of nerve tissue about 18 inches long and as thick as your index finger 2. runs down the central canal of the spine and is ...
Quiz 6 study guide
... N20. Contrast the specific mechanisms by which lidocaine and ethanol cause anesthesia. N21. Neurons A, B, C, and D form chemical synapses with neuron E. (Neurons A, B, C, and D are presynaptic; neuron E is post-synaptic.) a. When neuron A fires a single action potential, neuron E fires an action pot ...
... N20. Contrast the specific mechanisms by which lidocaine and ethanol cause anesthesia. N21. Neurons A, B, C, and D form chemical synapses with neuron E. (Neurons A, B, C, and D are presynaptic; neuron E is post-synaptic.) a. When neuron A fires a single action potential, neuron E fires an action pot ...
Pregnancy & Human Development
... • The above occurs over the course of the second week following conception. • Implantation – occurs on about day 6 or so, as the blastocyst burrows into the endometrium. ...
... • The above occurs over the course of the second week following conception. • Implantation – occurs on about day 6 or so, as the blastocyst burrows into the endometrium. ...
Introduction of the Nervous System
... interneurons which are found in the CNS. More complex reflexes may have their integration center in the spinal cord, in the brainstem, or in the cerebrum where conscious thoughts are initiated. In humans: the polysynaptic reflex is the sudden movement to protect life and limb. An example usually giv ...
... interneurons which are found in the CNS. More complex reflexes may have their integration center in the spinal cord, in the brainstem, or in the cerebrum where conscious thoughts are initiated. In humans: the polysynaptic reflex is the sudden movement to protect life and limb. An example usually giv ...
Physiological Nature
... with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory – Also, executive control needed to suppress inappropriate unconscious priming is known to involve the anterior cingulate gyrus Previous experiences that influence behavior ...
... with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory – Also, executive control needed to suppress inappropriate unconscious priming is known to involve the anterior cingulate gyrus Previous experiences that influence behavior ...
Vestibulospinal Tract - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... Fibers from lateral vestibular nucleus travel ipsilaterally within the entire length of the cord in the anterior part of the lateral funiculus laminas VII, VIII, and IX and directly to the α and gamma motor neurons and interneurons, with somatotopic organization. Stimulation causes extension The ves ...
... Fibers from lateral vestibular nucleus travel ipsilaterally within the entire length of the cord in the anterior part of the lateral funiculus laminas VII, VIII, and IX and directly to the α and gamma motor neurons and interneurons, with somatotopic organization. Stimulation causes extension The ves ...
Slide ()
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System - dr
... Breathing, heart rate, visceral activities, sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves Higher levels of respiratory control, sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves Acts as a filter for ascending sensory information that is projected to the primary cortex and basal nuclei. Filled with CSF ...
... Breathing, heart rate, visceral activities, sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves Higher levels of respiratory control, sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves Acts as a filter for ascending sensory information that is projected to the primary cortex and basal nuclei. Filled with CSF ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... spicy food; and when people believe they are receiving a painkiller. Thinking Critically: Does Acupuncture Relieve Pain? What am I being asked to believe or accept? Acupuncturists assert that twirling a needle in the skin can relieve pain caused by just about any stimulus. What evidence is available ...
... spicy food; and when people believe they are receiving a painkiller. Thinking Critically: Does Acupuncture Relieve Pain? What am I being asked to believe or accept? Acupuncturists assert that twirling a needle in the skin can relieve pain caused by just about any stimulus. What evidence is available ...
Nervous System - Intermediate School Biology
... Central Nervous System: the brain and spinal cord. Describe the location and function of the following parts of the brain: cerebrum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Describe the cross section of the spinal cord indicating the following: white matter, grey matter cen ...
... Central Nervous System: the brain and spinal cord. Describe the location and function of the following parts of the brain: cerebrum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Describe the cross section of the spinal cord indicating the following: white matter, grey matter cen ...