Veterinary Developmental Anatomy Class Notes
... The temporary epithelioid transforms to a secondary mesenchyme which ultimately forms muscle and connective tissue (including cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons, dermis, fascia, and adipose tissue). Thus, the term “mesenchyme” refers to the morphologic appearance of embryonic tissue. Although mos ...
... The temporary epithelioid transforms to a secondary mesenchyme which ultimately forms muscle and connective tissue (including cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons, dermis, fascia, and adipose tissue). Thus, the term “mesenchyme” refers to the morphologic appearance of embryonic tissue. Although mos ...
Protein Interacting with Never in Mitosis A
... that originate from adult GABAergic neuronal differentiation but suppressed tooth pulp tissue are neuglial differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells, ral crest–derived adult which may serve as useful sources of neuro- and stem cells capable of gliogenesis in degenerative disorders of the CNS. ...
... that originate from adult GABAergic neuronal differentiation but suppressed tooth pulp tissue are neuglial differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells, ral crest–derived adult which may serve as useful sources of neuro- and stem cells capable of gliogenesis in degenerative disorders of the CNS. ...
Dorsal View Ventral View Dorsal View
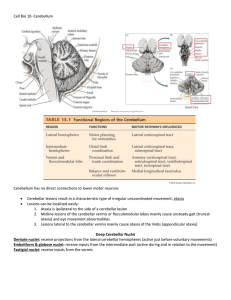
... Cerebellar Input and Output pathways INPUT-1: Mossy fibers, ascend through the cerebellar white matter and form excitatory synapses on granule cells Granule cells’ axons form parallel fibers, each of these fibers form excitatory synapses with numerous Purkinje Cells. All output from the cerebellar ...
... Cerebellar Input and Output pathways INPUT-1: Mossy fibers, ascend through the cerebellar white matter and form excitatory synapses on granule cells Granule cells’ axons form parallel fibers, each of these fibers form excitatory synapses with numerous Purkinje Cells. All output from the cerebellar ...
Problems of the Nervous System
... Spinal cord injuries require medical care. Swelling of the spinal cord or the tissue around it can result in temporary loss of nerve function. If the spinal cord is severed, paralysis results. ...
... Spinal cord injuries require medical care. Swelling of the spinal cord or the tissue around it can result in temporary loss of nerve function. If the spinal cord is severed, paralysis results. ...
Cross-talk between nervous and immune systems
... energy metabolism, neuronal regulation and function, reproduction, pregnancy and embryogenesis. In spite of the large number of cytokines all of them have several properties in common: low molecular weight (overall lower than 80kD), highly potent as they exert their effect at the picomolar range, an ...
... energy metabolism, neuronal regulation and function, reproduction, pregnancy and embryogenesis. In spite of the large number of cytokines all of them have several properties in common: low molecular weight (overall lower than 80kD), highly potent as they exert their effect at the picomolar range, an ...
Problems of the Nervous System
... Spinal cord injuries require medical care. Swelling of the spinal cord or the tissue around it can result in temporary loss of nerve function. If the spinal cord is severed, paralysis results. ...
... Spinal cord injuries require medical care. Swelling of the spinal cord or the tissue around it can result in temporary loss of nerve function. If the spinal cord is severed, paralysis results. ...
From Neurons to Brain: Adaptive Self
... 2D systems. 2. A mechanism for adaptive self-organization on the meso (about 1mm − 1cm) and macro scale (above 1cm). The contemporary view is that the brain structure is essentially deterministic on a large scale but probabilistic on a small scale [1]. As a consequence the network has no optimal st ...
... 2D systems. 2. A mechanism for adaptive self-organization on the meso (about 1mm − 1cm) and macro scale (above 1cm). The contemporary view is that the brain structure is essentially deterministic on a large scale but probabilistic on a small scale [1]. As a consequence the network has no optimal st ...
BLoA Neurotransmission
... between the two neurons. The change in potential is going to affect little vesicles, little blobs of membrane inside the presynaptic neuron. These vesicles contain the neurotransmitters, which are synthesized in the presynaptic cell, and stored in the vesicles ...
... between the two neurons. The change in potential is going to affect little vesicles, little blobs of membrane inside the presynaptic neuron. These vesicles contain the neurotransmitters, which are synthesized in the presynaptic cell, and stored in the vesicles ...
Chapter 2: The Biological Basis of Behavior
... b. Within a neuron, information flows from dendrites to cell body to axon. c. Some neurons have axons that are several feet long. d. Neurons in the central nervous system have myelin sheaths, while those in the peripheral nervous system do not. 4 yr.: 75% r = .29 ...
... b. Within a neuron, information flows from dendrites to cell body to axon. c. Some neurons have axons that are several feet long. d. Neurons in the central nervous system have myelin sheaths, while those in the peripheral nervous system do not. 4 yr.: 75% r = .29 ...
The nervous system - Science for Yr9@E
... glands of the body. Structure The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1. the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2. the peripheral system which connects the central ner ...
... glands of the body. Structure The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1. the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. These structures are protected by bone and cushioned from injury by the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2. the peripheral system which connects the central ner ...
a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve
... The fibers ol'the optic nerve are the axons orthe cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina. They converge on the o(1tic disc and exit li'ol11 the eye. about 3 or 4 mm to the nasal side of its center. as the optic nerve The libel's orthe optic nerve arc myelinated. but the sheaths arc j(JI'med li' ...
... The fibers ol'the optic nerve are the axons orthe cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina. They converge on the o(1tic disc and exit li'ol11 the eye. about 3 or 4 mm to the nasal side of its center. as the optic nerve The libel's orthe optic nerve arc myelinated. but the sheaths arc j(JI'med li' ...
The Brain
... – Reservoir of circulating fluid that, along w/ blood, the brain monitors for changes in the internal environment • Changes in CO2 content of CSF trigger homeostatic responses in the resp. control centers of the brainstem that help regulate the overall CO2 content and pH of the body ...
... – Reservoir of circulating fluid that, along w/ blood, the brain monitors for changes in the internal environment • Changes in CO2 content of CSF trigger homeostatic responses in the resp. control centers of the brainstem that help regulate the overall CO2 content and pH of the body ...
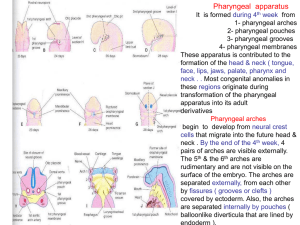
02-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... thymus gland. These bilateral primordia come together in the median plane then descends into the superior mediastinum. The bilobed form remains throughout life The primordia of both glands lose their connections & migrate into neck. The parathyroid separate from the thymus & lie on the dorsal surfac ...
... thymus gland. These bilateral primordia come together in the median plane then descends into the superior mediastinum. The bilobed form remains throughout life The primordia of both glands lose their connections & migrate into neck. The parathyroid separate from the thymus & lie on the dorsal surfac ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... can have many presynaptic neurones forming synaptic junctions with it. Pre synaptic neurones depolarise (excitatory) or hyperpolarise (inhibitory) the post synaptic membrane locally. The sum of their effects takes place at the axon hillock ...
... can have many presynaptic neurones forming synaptic junctions with it. Pre synaptic neurones depolarise (excitatory) or hyperpolarise (inhibitory) the post synaptic membrane locally. The sum of their effects takes place at the axon hillock ...
Growth arrest specific gene 7 is associated with schizophrenia and
... cones as they interact with actin filaments contributing to growth cone advance and turning in filopodia, and consequently govern axon guidance and synaptic plasticity [8]. Abnormalities in those processes may alter the strength of information processing and thus participate in the pathogenesis of h ...
... cones as they interact with actin filaments contributing to growth cone advance and turning in filopodia, and consequently govern axon guidance and synaptic plasticity [8]. Abnormalities in those processes may alter the strength of information processing and thus participate in the pathogenesis of h ...
19. Visual (2)
... ligaments to increase the covexity of the lens, thus focusing the image. The pupil is constricted to increase the depth of the focus. The pathways of it comprise the optic nerve; optic tract; lateral geniculate body; optic radiation and visual area of the cerebral cortex which is connected by the su ...
... ligaments to increase the covexity of the lens, thus focusing the image. The pupil is constricted to increase the depth of the focus. The pathways of it comprise the optic nerve; optic tract; lateral geniculate body; optic radiation and visual area of the cerebral cortex which is connected by the su ...
Differentiating Upper from Lower Motor Neuron Lesions
... skeletal muscle cells. Some students will ask about the LMNs located at the level of the transection/injury and wouldn’t their involvement result in LMN signs. This is true, yes there can be involvement of LMNs at the level of the SCI. For this injury, a transection located between the cervical and ...
... skeletal muscle cells. Some students will ask about the LMNs located at the level of the transection/injury and wouldn’t their involvement result in LMN signs. This is true, yes there can be involvement of LMNs at the level of the SCI. For this injury, a transection located between the cervical and ...
neural models of head-direction cells
... Redish et al. (1996) modelled the relationship between ATN and PSc. Each area was represented by a CANN, consisting of an excitatory and an inhibitory layer of nodes to maintain a single hill of activation. They based this on observations that PSc represents current heading, whereas ATN represents f ...
... Redish et al. (1996) modelled the relationship between ATN and PSc. Each area was represented by a CANN, consisting of an excitatory and an inhibitory layer of nodes to maintain a single hill of activation. They based this on observations that PSc represents current heading, whereas ATN represents f ...
Spinal cord- 2 - Weebly
... The corticospinal tracts are often called the pyramidal tracts because they form pyramid-shaped enlargements on the anterior surface of the medulla concerned with controlling skilled movements of the distal extremities (facilitation of alpha and gamma motor neurons which innervate the distal flex ...
... The corticospinal tracts are often called the pyramidal tracts because they form pyramid-shaped enlargements on the anterior surface of the medulla concerned with controlling skilled movements of the distal extremities (facilitation of alpha and gamma motor neurons which innervate the distal flex ...
2nd 9 weeks
... I can differentiate visceral, cardiac, and skeletal muscle tissues based on their structure and physiological role in the movement of body parts and/or substances through body parts. I can explain and model, using appropriate terminology, the anatomy of a skeletal muscle and a muscle fiber, and rela ...
... I can differentiate visceral, cardiac, and skeletal muscle tissues based on their structure and physiological role in the movement of body parts and/or substances through body parts. I can explain and model, using appropriate terminology, the anatomy of a skeletal muscle and a muscle fiber, and rela ...
Embryology PowerPoint Presentation
... – The continual modification of structures from conception to maturity due to the growth, differentiation and reorganization of cells – Developmental Stages: • Prenatal – development from conception to birth • Postnatal – development from birth through maturity ...
... – The continual modification of structures from conception to maturity due to the growth, differentiation and reorganization of cells – Developmental Stages: • Prenatal – development from conception to birth • Postnatal – development from birth through maturity ...