A Neural Model of Rule Generation in Inductive Reasoning
... In order to solve this matrix, the subject needs to generate three rules: (a) the number of triangles increases by one across the row, (b) the orientation of the triangles is constant across the row, (c) each cell in a row contains one background shape from the set {circle, square, diamond}. Subject ...
... In order to solve this matrix, the subject needs to generate three rules: (a) the number of triangles increases by one across the row, (b) the orientation of the triangles is constant across the row, (c) each cell in a row contains one background shape from the set {circle, square, diamond}. Subject ...
Patterns of neuronal migration in the embryonic cortex
... understanding the patterns of neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex. Studies based largely on realtime imaging of migrating neurons in situ in both rodent and primate cortex have contributed significantly to a more complete description of the routes that neurons take to reach their pr ...
... understanding the patterns of neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex. Studies based largely on realtime imaging of migrating neurons in situ in both rodent and primate cortex have contributed significantly to a more complete description of the routes that neurons take to reach their pr ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release ...
... euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release ...
Neurons - LPS.org
... this discussion, we will examine neuron parts following the order in which information travels. A neuron has endings known as dendrites, which receive information. Dendrites look like branches, and in fact the word dendrite comes from the Greek word for “tree.” The neuron’s thickest part is the soma ...
... this discussion, we will examine neuron parts following the order in which information travels. A neuron has endings known as dendrites, which receive information. Dendrites look like branches, and in fact the word dendrite comes from the Greek word for “tree.” The neuron’s thickest part is the soma ...
D. What Causes Multiple Sclerosis?
... tracts are affected, including those of the cerebral hemispheres, infratentorium, and spinal cord. MS lesions, known as plaques, may form in CNS white matter in any location; thus, clinical presentations may be diverse. Continuing lesion formation in MS often leads to physical disability and, someti ...
... tracts are affected, including those of the cerebral hemispheres, infratentorium, and spinal cord. MS lesions, known as plaques, may form in CNS white matter in any location; thus, clinical presentations may be diverse. Continuing lesion formation in MS often leads to physical disability and, someti ...
Topic 9
... The EP-cadherin (named because it appeared initially similar to both the E-cadherin and the P-cadherin) is required for adhesion in the blastomere Without these proteins, the formation of the blastocoel is not possible. ...
... The EP-cadherin (named because it appeared initially similar to both the E-cadherin and the P-cadherin) is required for adhesion in the blastomere Without these proteins, the formation of the blastocoel is not possible. ...
Input to the Cerebellar Cortex
... 2.The cerebellum receives continuously updated information about the desired sequence of muscle contractions from the brain motor control areas; it also receives continuous sensory information from the peripheral parts of the body, giving sequential changes in the status of each part of the body—its ...
... 2.The cerebellum receives continuously updated information about the desired sequence of muscle contractions from the brain motor control areas; it also receives continuous sensory information from the peripheral parts of the body, giving sequential changes in the status of each part of the body—its ...
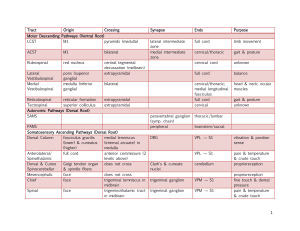
L4- Student Copy Motor Tracts
... The motor cortex lies anterior to the central sulcus and occupies the posterior third of the frontal lobe. Motor signals from the motor cortex are sent through pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts to terminate on motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem . The activity of the lower motor neuro ...
... The motor cortex lies anterior to the central sulcus and occupies the posterior third of the frontal lobe. Motor signals from the motor cortex are sent through pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts to terminate on motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem . The activity of the lower motor neuro ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... 2. Have your partner stand across from you and gently toss ten cotton balls toward your goggles. Your partner should not give you any warning before tossing the cotton balls 3. Count the number of times you blink and the number of times you are able to keep blinking ...
... 2. Have your partner stand across from you and gently toss ten cotton balls toward your goggles. Your partner should not give you any warning before tossing the cotton balls 3. Count the number of times you blink and the number of times you are able to keep blinking ...
PDF
... of the 8- somite stage embryos, i.e. at approximately 120-140 jum along the axis of measurement. The large elongate mesencephalic sulcus had fully subdivided into two separate sulci. The sulcus immediately anterior to the preotic sulcus was not always visible; its disappearance may be as a result of ...
... of the 8- somite stage embryos, i.e. at approximately 120-140 jum along the axis of measurement. The large elongate mesencephalic sulcus had fully subdivided into two separate sulci. The sulcus immediately anterior to the preotic sulcus was not always visible; its disappearance may be as a result of ...
Action potential
... “Information” travels within the nervous system as propagated electrical signals (action potentials) The most important information (vision, balance, motor commands) is carried by large-diameter, ...
... “Information” travels within the nervous system as propagated electrical signals (action potentials) The most important information (vision, balance, motor commands) is carried by large-diameter, ...
Lecture 3 NS_2015
... Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft (20-30 nm thick). Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and the activated receptors trigger some postsynaptic eve ...
... Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft (20-30 nm thick). Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and the activated receptors trigger some postsynaptic eve ...
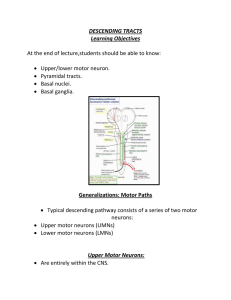
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Most synapse with association neurons in spinal cord central gray. Components: ...
... Most synapse with association neurons in spinal cord central gray. Components: ...
Which Model to Use for the Liquid State Machine?
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... A holding signal is generated by neurons in the INC. On receiving the pulsed excitation from RiMLF axons, INC neurons transduce this signal into a very long-lasting chain of action potentials. Since INC neurons project their axons into the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei, they transmit the long-last ...
... A holding signal is generated by neurons in the INC. On receiving the pulsed excitation from RiMLF axons, INC neurons transduce this signal into a very long-lasting chain of action potentials. Since INC neurons project their axons into the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei, they transmit the long-last ...
Test yourself on lesions in section pictures
... Q2. Analgesia and thermoanesthesia on the left hand, had previously burned the little finger of left hand but was unaware until smelled the burning skin. On Exam: Reduced pain and temperature sense involving the 8th cervical and first thoracic dermatomes of the left hand, but tactile discrimination ...
... Q2. Analgesia and thermoanesthesia on the left hand, had previously burned the little finger of left hand but was unaware until smelled the burning skin. On Exam: Reduced pain and temperature sense involving the 8th cervical and first thoracic dermatomes of the left hand, but tactile discrimination ...
ch12Boundarygabor
... (primary visual centre) • Neurons are edge detectors fires when an edge of a particular (LGN) orientation is present infrequent output ...
... (primary visual centre) • Neurons are edge detectors fires when an edge of a particular (LGN) orientation is present infrequent output ...
to specify axonal trajectories and target specificity of Jessell, 2000; Shira-
... to specify axonal trajectories and target specificity of individual motor neuron subtypes (Jessell, 2000; Shirasaki and Pfaff, 2002). Whether LIM homeodomain transcription factors act similarly to specify the architecture of limbic-hypothalamic circuitry needs to be confirmed, for this would imply t ...
... to specify axonal trajectories and target specificity of individual motor neuron subtypes (Jessell, 2000; Shirasaki and Pfaff, 2002). Whether LIM homeodomain transcription factors act similarly to specify the architecture of limbic-hypothalamic circuitry needs to be confirmed, for this would imply t ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... of the nerves are associated with the special senses of smell, vision, hearing, and equilibrium and have only sensory fibers. Five other nerves are primarily motor in function but do have some sensory fibers for proprioception. The remaining four nerves consist of significant amounts of both sensory ...
... of the nerves are associated with the special senses of smell, vision, hearing, and equilibrium and have only sensory fibers. Five other nerves are primarily motor in function but do have some sensory fibers for proprioception. The remaining four nerves consist of significant amounts of both sensory ...
File
... • Presynaptic terminal: is the first part of the synapse & is usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conduct ...
... • Presynaptic terminal: is the first part of the synapse & is usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conduct ...
Ephrin ligands and neural crest cell migration - Development
... SUMMARY Little is known about the mechanisms that direct neural crest cells to the appropriate migratory pathways. Our aim was to determine how neural crest cells that are specified as neurons and glial cells only migrate ventrally and are prevented from migrating dorsolaterally into the skin, where ...
... SUMMARY Little is known about the mechanisms that direct neural crest cells to the appropriate migratory pathways. Our aim was to determine how neural crest cells that are specified as neurons and glial cells only migrate ventrally and are prevented from migrating dorsolaterally into the skin, where ...
13. What determines the magnitude of the graded potential? (p. 240)
... 3. Drug Z prevents sodium inactivation (“h”) gates from moving from their resting position (“resting” refers to their position when the membrane is at its RMP). How would administration of Drug Z affect the function of a neuron? ...
... 3. Drug Z prevents sodium inactivation (“h”) gates from moving from their resting position (“resting” refers to their position when the membrane is at its RMP). How would administration of Drug Z affect the function of a neuron? ...
presentation
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...