Segmental Facilitation
... depression or anxiety rather than from a peripheral painful input. – (Stress may sensitize emotional centers in the amygdale and limbic cortex, to precipitate anxiety and affective disorders that are amplified and endure long after the stress has abated). ...
... depression or anxiety rather than from a peripheral painful input. – (Stress may sensitize emotional centers in the amygdale and limbic cortex, to precipitate anxiety and affective disorders that are amplified and endure long after the stress has abated). ...
Neural Interaction in Cat Primary Auditory Cortex. Dependence on
... “noise” from the newly formed synaptic connections. ...
... “noise” from the newly formed synaptic connections. ...
State-dependent and cell type-specific temporal processing in
... amplitudes6,11,13, the size of receptive fields14–17, and noise correlations between pairs of neurons18,19. As cortical neurons are highly heterogeneous across cortical layers20,21, the effects of cortical states are also heterogeneous depending on cell classes: with respect to spontaneous activity, ...
... amplitudes6,11,13, the size of receptive fields14–17, and noise correlations between pairs of neurons18,19. As cortical neurons are highly heterogeneous across cortical layers20,21, the effects of cortical states are also heterogeneous depending on cell classes: with respect to spontaneous activity, ...
THE PEDAL NEURONS OF APLYSIA PUNCTATA
... The recording techniques were those previously used by Hughes & Tauc (1963) and Dorsett (1967). Nerves containing an axon of a neuron were identified by triggering the upper beam of the oscilloscope on the rising edge of the intracellular spike whilst displaying an external recording from the nerve ...
... The recording techniques were those previously used by Hughes & Tauc (1963) and Dorsett (1967). Nerves containing an axon of a neuron were identified by triggering the upper beam of the oscilloscope on the rising edge of the intracellular spike whilst displaying an external recording from the nerve ...
Tutorial 6: Developmental Biology
... Formation of organs from the 3 germ layers formed during gastrulation ...
... Formation of organs from the 3 germ layers formed during gastrulation ...
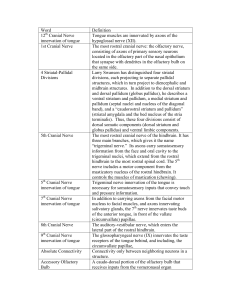
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... consummatory behavior. Appetitive behavior is the initial behavior triggered by high levels of a motivation. Appetitive behavior can lead to an instinctive action pattern that is part of a “fixed action pattern” (instinctive motivation and related actions). The narrowed ventricle that passes through ...
... consummatory behavior. Appetitive behavior is the initial behavior triggered by high levels of a motivation. Appetitive behavior can lead to an instinctive action pattern that is part of a “fixed action pattern” (instinctive motivation and related actions). The narrowed ventricle that passes through ...
6.1 The Nervous System - Blyth-Exercise
... - Still very rapid, but involves more interneurons Crossed-Extensor Reflex - When one arm or leg automatically compensates for a reflex action in the opposing arm or leg - The reflex involves multiple synapses and muscle groups ...
... - Still very rapid, but involves more interneurons Crossed-Extensor Reflex - When one arm or leg automatically compensates for a reflex action in the opposing arm or leg - The reflex involves multiple synapses and muscle groups ...
Neuropeptide-Mediated Facilitation and Inhibition of Sensory Inputs
... The connective tissue and meninx primitiva were removed from the dorsal surface of the spinal cord. The spinal cord–notochord preparation was split into three pools by placing Vaseline barriers at different positions (see Fig. 1A). One barrier was placed ;15 segments rostral to the tip of the tail f ...
... The connective tissue and meninx primitiva were removed from the dorsal surface of the spinal cord. The spinal cord–notochord preparation was split into three pools by placing Vaseline barriers at different positions (see Fig. 1A). One barrier was placed ;15 segments rostral to the tip of the tail f ...
Document
... Chemoreceptors sensitive to acid, glucose and amino acids have been demonstrated which, in essence, allows "tasting" of lumenal contents. Sensory receptors in muscle respond to ...
... Chemoreceptors sensitive to acid, glucose and amino acids have been demonstrated which, in essence, allows "tasting" of lumenal contents. Sensory receptors in muscle respond to ...
Circuits and Circuit Disorders of the Basal Ganglia
... direct pathway is thought to inhibit GPi and SNr, whereas activation of striatal neurons that give rise to the indirect pathway may exert a net excitatory effect on these output nuclei. The most researched cortico-subcortical circuit is the “motor circuit” because of its importance for movement diso ...
... direct pathway is thought to inhibit GPi and SNr, whereas activation of striatal neurons that give rise to the indirect pathway may exert a net excitatory effect on these output nuclei. The most researched cortico-subcortical circuit is the “motor circuit” because of its importance for movement diso ...
Edge of chaos and prediction of computational performance for
... Keywords: Neural networks; Spiking networks; Edge of chaos; Microcircuits; Computational performance; Network dynamics ...
... Keywords: Neural networks; Spiking networks; Edge of chaos; Microcircuits; Computational performance; Network dynamics ...
PDF-document - homepage.ruhr-uni
... 50 ms (n = 34, range: 15–135 ms); at the upper target, it was 72 ms (n = 29, range: 30–130 ms); at the left target, it was 60 ms (n = 28, range: 20–110 ms); at the right target, it was 50 ms (n = 29, range: 30–100 ms); and at the lower target, it was 65 ms (n = 26, range: 30–155 ms). There was no si ...
... 50 ms (n = 34, range: 15–135 ms); at the upper target, it was 72 ms (n = 29, range: 30–130 ms); at the left target, it was 60 ms (n = 28, range: 20–110 ms); at the right target, it was 50 ms (n = 29, range: 30–100 ms); and at the lower target, it was 65 ms (n = 26, range: 30–155 ms). There was no si ...
Identification of Basolateral Amygdala Projection Cells and
... of BLA interneurons (fast-spiking cells), thought to express parvalbumin and accounting for roughly 50% of BLA interneurons (Mascagni and McDonald 2003), have a comparatively more depolarized membrane potential, are often spontaneously active at rest, and generate trains of short-duration spikes tha ...
... of BLA interneurons (fast-spiking cells), thought to express parvalbumin and accounting for roughly 50% of BLA interneurons (Mascagni and McDonald 2003), have a comparatively more depolarized membrane potential, are often spontaneously active at rest, and generate trains of short-duration spikes tha ...
PDF
... The development of the thymus was studied with histological, electron microscopical (TEM) and histochemical methods in 100 fetuses (beagle) from 47 litters, between day 19 of gestation and day 21 after birth. The three earliest samples investigated were 19,20 and 21 day old embryos in which no organ ...
... The development of the thymus was studied with histological, electron microscopical (TEM) and histochemical methods in 100 fetuses (beagle) from 47 litters, between day 19 of gestation and day 21 after birth. The three earliest samples investigated were 19,20 and 21 day old embryos in which no organ ...
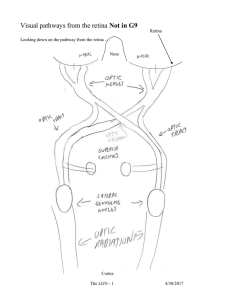
Why light
... Registration refers to the fact that the projections of activity in layers 3 and 4 are at the same place in their respective layers, even though the stimulation is from different eyes. That is, the activity generated by stimulus A is at the same end of both LGN layers. The activity generated by stim ...
... Registration refers to the fact that the projections of activity in layers 3 and 4 are at the same place in their respective layers, even though the stimulation is from different eyes. That is, the activity generated by stimulus A is at the same end of both LGN layers. The activity generated by stim ...
Viewpoint Synaptic Connectivity and Neuronal Morphology: Two
... questions, I consider the wiring up of a large highly interconnected neuronal network, such as the cortical column. Implementation of such a network in the allotted volume requires all the salient features of neuronal morphology: the existence of branching dendrites and axons and the presence of den ...
... questions, I consider the wiring up of a large highly interconnected neuronal network, such as the cortical column. Implementation of such a network in the allotted volume requires all the salient features of neuronal morphology: the existence of branching dendrites and axons and the presence of den ...
Exam 5 Study Guide
... Explain the structure of an idealized neuron, including the functions of all the parts: cell body, dendrites, dendritic spines, axon hillock, axon, axon collateral, myelin sheath, neurofibril node (node of Ranvier), axon terminal, synaptic knobs. Be able to identify these parts on a diagram or model ...
... Explain the structure of an idealized neuron, including the functions of all the parts: cell body, dendrites, dendritic spines, axon hillock, axon, axon collateral, myelin sheath, neurofibril node (node of Ranvier), axon terminal, synaptic knobs. Be able to identify these parts on a diagram or model ...
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
... Surgery on the anterior commissure (AC) was carried out under aseptic conditions and anesthesia with sodium pentobarbital (25–30 mgykg). The right hemisphere was retracted from the falx with a brain spoon. An aspirator was used to make a sagittal incision #5 mm in length in the corpus callosum, ente ...
... Surgery on the anterior commissure (AC) was carried out under aseptic conditions and anesthesia with sodium pentobarbital (25–30 mgykg). The right hemisphere was retracted from the falx with a brain spoon. An aspirator was used to make a sagittal incision #5 mm in length in the corpus callosum, ente ...
Induction of NADPH diaphoraselnitric oxide synthase in the spinal
... In rats subjected to multiple blasts and killed at 3 hours after the final blast, a large number of neurons in the ventral horn in both the cervical and lumbar segments of the spinal cord was induced to express NADPH-d activity (Figs. 7-9). The number of NADPHd reactive motoneurons was greater than ...
... In rats subjected to multiple blasts and killed at 3 hours after the final blast, a large number of neurons in the ventral horn in both the cervical and lumbar segments of the spinal cord was induced to express NADPH-d activity (Figs. 7-9). The number of NADPHd reactive motoneurons was greater than ...
Chapter 2
... Large bundle of axons connecting brain’s two hemispheres Relays information between two sides ...
... Large bundle of axons connecting brain’s two hemispheres Relays information between two sides ...
Motor functions
... The lower motor neuron (infranuclear) • Within a few days after motor nerve section, the individual denervated muscle fibres begin to contract spontaneously. • This contraction of isolated muscle fibre is known as fibrilation and cannot be seen through the intact skin, but it can be recorded as a sm ...
... The lower motor neuron (infranuclear) • Within a few days after motor nerve section, the individual denervated muscle fibres begin to contract spontaneously. • This contraction of isolated muscle fibre is known as fibrilation and cannot be seen through the intact skin, but it can be recorded as a sm ...
Development of the Auditory Areas
... deep and superficial layers is shown after [3H] thymidine injections on E17 and EI8 (Figs. 12-2 and 12-3). Practically all of the neurons in layer VI and many of the neurons in layer V (especially anteriorly, Fig. 12-2) are unlabeled, while the majority of neurons in layers IV-II are labeled. To ana ...
... deep and superficial layers is shown after [3H] thymidine injections on E17 and EI8 (Figs. 12-2 and 12-3). Practically all of the neurons in layer VI and many of the neurons in layer V (especially anteriorly, Fig. 12-2) are unlabeled, while the majority of neurons in layers IV-II are labeled. To ana ...