Renaissance - cda college
... Italy. Part of the reason it began in Italy was because of the history of Rome and the Roman Empire. Another reason it began in Italy was because Italy had become very wealthy and the wealthy were willing to spend their money supporting artists and geniuses. City-states played a big role in the rule ...
... Italy. Part of the reason it began in Italy was because of the history of Rome and the Roman Empire. Another reason it began in Italy was because Italy had become very wealthy and the wealthy were willing to spend their money supporting artists and geniuses. City-states played a big role in the rule ...
The Italian Renaissance
... The nobles living in the country gave protection to the king in which they received land for it. When the threat of invasion from barbarians had lessened, people left the country for towns and cities so they could engage in more profitable pursuits. ...
... The nobles living in the country gave protection to the king in which they received land for it. When the threat of invasion from barbarians had lessened, people left the country for towns and cities so they could engage in more profitable pursuits. ...
Renaissance - jstachowiak
... Large churches and palaces constructed to display church prestige. Church placed political goals ahead of religious duties Promoted artistic projects and commissioned major artists. ...
... Large churches and palaces constructed to display church prestige. Church placed political goals ahead of religious duties Promoted artistic projects and commissioned major artists. ...
The Renaissance “Movement of creativity in art, writing, and thought”
... • Cities allowed people to meet and share ideas • Early 1300’s plague hits Europe killing 60 to 75 percent of the population • Very high merchant class in Italy • Rich history of Greece and Rome in Italy ...
... • Cities allowed people to meet and share ideas • Early 1300’s plague hits Europe killing 60 to 75 percent of the population • Very high merchant class in Italy • Rich history of Greece and Rome in Italy ...
12 worksheet
... 1. The Italian Renaissance was primarily a recovery of____________ culture. 2. Renaissance means 3.Economic developments included a revival of ______________. 4. According to Burckhardt, the Renaissance in Italy represented : 5. The Medici controlled the finances of_______________. 6. The commercial ...
... 1. The Italian Renaissance was primarily a recovery of____________ culture. 2. Renaissance means 3.Economic developments included a revival of ______________. 4. According to Burckhardt, the Renaissance in Italy represented : 5. The Medici controlled the finances of_______________. 6. The commercial ...
Chapter 1 Section 1
... – New attitudes toward culture and learning • Medieval times focused on spirituality and religious beliefs • Renaissance explored the richness and variety of human experiences – Society placed a new emphasis on individual achievement – Renaissance Ideal was a person with a wide variety of talent in ...
... – New attitudes toward culture and learning • Medieval times focused on spirituality and religious beliefs • Renaissance explored the richness and variety of human experiences – Society placed a new emphasis on individual achievement – Renaissance Ideal was a person with a wide variety of talent in ...
The Italian Renaissance
... Causes • Trade encouraged curiosity • Search for knowledge • Italian cities grew rich • Medici Family (Medee-chee) - used wealth to become a great patron of the arts ...
... Causes • Trade encouraged curiosity • Search for knowledge • Italian cities grew rich • Medici Family (Medee-chee) - used wealth to become a great patron of the arts ...
Ideas Lead to Questions that Fuel Discovery: Renaissance
... Baldassare Castiglione- ideal Renaissance man Painting- fresco, perspective Leonardo da Vinci Raphael Michelangelo Buonarroti William Shakespeare secular Protestant Reformation Martin Luther- 95 theses vernacular indulgence ...
... Baldassare Castiglione- ideal Renaissance man Painting- fresco, perspective Leonardo da Vinci Raphael Michelangelo Buonarroti William Shakespeare secular Protestant Reformation Martin Luther- 95 theses vernacular indulgence ...
Chapter Sixteen - Tamara Chrystyna Reay
... • Humanism: interest in the art and literature of ancient Greece and Rome • Artists admired the lifelike appearance of classical works • Gutenberg printing press • Mass production of books ...
... • Humanism: interest in the art and literature of ancient Greece and Rome • Artists admired the lifelike appearance of classical works • Gutenberg printing press • Mass production of books ...
sg1 west civ - Grants Pass School District 7
... language [L. Valla]. Some Italian thinkers were more secular [Machiavelli] than religious…spread by the printing press after the 1450s and challenged the universities and Church… promoted the idea of civic humanism in city states and more secular models for behavior. {Machiavelli, Castiglione} Flore ...
... language [L. Valla]. Some Italian thinkers were more secular [Machiavelli] than religious…spread by the printing press after the 1450s and challenged the universities and Church… promoted the idea of civic humanism in city states and more secular models for behavior. {Machiavelli, Castiglione} Flore ...
AP Chapter 22 HW High Renaissance
... 2. Discuss 5 characteristics of Mannerist painting that can be called “antiClassical” and that distinguish the Mannerist from the High Renaissance style. 3. Which Italian Mannerist sculptor most strongly influenced the development of French Renaissance art. Which Mannerist sculptor developed the com ...
... 2. Discuss 5 characteristics of Mannerist painting that can be called “antiClassical” and that distinguish the Mannerist from the High Renaissance style. 3. Which Italian Mannerist sculptor most strongly influenced the development of French Renaissance art. Which Mannerist sculptor developed the com ...
The Renaissance in Italy!
... The Renaissance was a time of creativity and change in many areas- political, social, economic, and cultural. Perhaps most important, however, were the changes that took place in the way people viewed themselves and their world. ...
... The Renaissance was a time of creativity and change in many areas- political, social, economic, and cultural. Perhaps most important, however, were the changes that took place in the way people viewed themselves and their world. ...
Renaissance Part 2
... entertaining and is usually secular (not religious) • May be religious if the author is pointing out what he/she perceives as wrongs of the church or church practices. ...
... entertaining and is usually secular (not religious) • May be religious if the author is pointing out what he/she perceives as wrongs of the church or church practices. ...
Renaissance Art
... • Renaissance artists were heroes!! • paid large amounts by the rulers of their city-states (patrons or sponsors) • had apprentices (students) ...
... • Renaissance artists were heroes!! • paid large amounts by the rulers of their city-states (patrons or sponsors) • had apprentices (students) ...
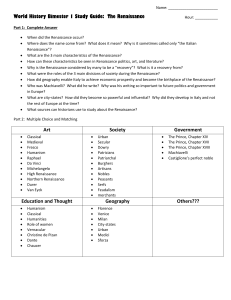
View Study Guide in MS Word
... Who was Machiavelli? What did he write? Why was his writing so important to future politics and government in Europe? What are city-states? How did they become so powerful and influential? Why did they develop in Italy and not the rest of Europe at the time? What sources can historians use to study ...
... Who was Machiavelli? What did he write? Why was his writing so important to future politics and government in Europe? What are city-states? How did they become so powerful and influential? Why did they develop in Italy and not the rest of Europe at the time? What sources can historians use to study ...
RenaissanceReformation Review sheet answers
... Use your notebook and readings we have done in class. 1. What was the Renaissance? Rebirth in arts, literature, architecture, etc. 2. The importance of the Medici family. They were patrons to the most influential artists of the Renaissance. It is rumored the Renaissance would have never happened wit ...
... Use your notebook and readings we have done in class. 1. What was the Renaissance? Rebirth in arts, literature, architecture, etc. 2. The importance of the Medici family. They were patrons to the most influential artists of the Renaissance. It is rumored the Renaissance would have never happened wit ...
Renaissance Unit Vocabulary List Word Definition or Associated
... Definition or Associated Work “Rebirth” of Classical (Greek & Roman) learning Movement that focused & glorified HUMANS ...
... Definition or Associated Work “Rebirth” of Classical (Greek & Roman) learning Movement that focused & glorified HUMANS ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... 1. wealthy people (now called upper class) had time to study and appreciate classics (Greek and Roman works). a. nobles and wealthy merchants b. Most wealthy women stayed at home as overseers of children’s education and overseers of servants. ...
... 1. wealthy people (now called upper class) had time to study and appreciate classics (Greek and Roman works). a. nobles and wealthy merchants b. Most wealthy women stayed at home as overseers of children’s education and overseers of servants. ...
The Italian Renaissance Chapter 5 section 1
... •Background: During the Renaissance. Italy was not unified, it was made up of independent “city states” which included: Milan, Venice, Rome, Florence, Pisa, Genoa and Mantua and the Kingdom of the 2 Sicilies. •Three leading city states were Florence, Rome and Venice. •New social order sprang up, wea ...
... •Background: During the Renaissance. Italy was not unified, it was made up of independent “city states” which included: Milan, Venice, Rome, Florence, Pisa, Genoa and Mantua and the Kingdom of the 2 Sicilies. •Three leading city states were Florence, Rome and Venice. •New social order sprang up, wea ...
Renaissance architecture

Renaissance architecture is the architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 17th centuries in different regions of Europe, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact.Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts as they are demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pilasters and lintels, as well as the use of semicircular arches, hemispherical domes, niches and aedicules replaced the more complex proportional systems and irregular profiles of medieval buildings.