Differences between the Italian an Northern Renaissance The
... enormous Holy Roman Empire. Its Dukes, during the last 100 years it existed, were given monikers of "the Good," "the Fearless" and "the Bold" (although apparently the last "Bold" Duke wasn't quite bold enough, as Burgundy was absorbed by both France and the Holy Roman Empire at the end of his reign. ...
... enormous Holy Roman Empire. Its Dukes, during the last 100 years it existed, were given monikers of "the Good," "the Fearless" and "the Bold" (although apparently the last "Bold" Duke wasn't quite bold enough, as Burgundy was absorbed by both France and the Holy Roman Empire at the end of his reign. ...
7th Chapter 11 Exam DO NOT WRITE ON EXAM
... ____ 16. How are the ideas of the Middle Ages and the ideas of the Renaissance different? a. Both periods had thinkers who were interested in religion, but Renaissance thinkers were interested in other ideas, too. b. Both periods had thinkers who thought the sun revolved around Earth, but Renaissanc ...
... ____ 16. How are the ideas of the Middle Ages and the ideas of the Renaissance different? a. Both periods had thinkers who were interested in religion, but Renaissance thinkers were interested in other ideas, too. b. Both periods had thinkers who thought the sun revolved around Earth, but Renaissanc ...
- the University of Huddersfield Repository
... Leeds Metropolitan University, I worked in a building that was left unfinished, a fact was not particularly remarkable except that it gave rise to a rich and fertile dialogue within the academic community about the role of architecture in ‘city making’ (cosmopoiesis). Built in the early 70s, the ori ...
... Leeds Metropolitan University, I worked in a building that was left unfinished, a fact was not particularly remarkable except that it gave rise to a rich and fertile dialogue within the academic community about the role of architecture in ‘city making’ (cosmopoiesis). Built in the early 70s, the ori ...
Northern Renaissance - High Point Regional School District
... Netherlandish, active by 1406, died 1444) ...
... Netherlandish, active by 1406, died 1444) ...
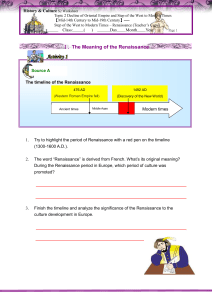
1 The word "renaissance" ("rinascenza" in Italian) is French for
... During most of the Renaissance, the political power of Florence was concentrated in the hands of a few wealthy merchants, who dominated the wool industry. Like the rich families of Venice, these merchants competed with one another in building the grandest palaces for themselves in the city and villa ...
... During most of the Renaissance, the political power of Florence was concentrated in the hands of a few wealthy merchants, who dominated the wool industry. Like the rich families of Venice, these merchants competed with one another in building the grandest palaces for themselves in the city and villa ...
Renaissance and Reformation
... Crusades led to more trade opportunities with the east Rise of a merchant class Development of a commercial revolution ...
... Crusades led to more trade opportunities with the east Rise of a merchant class Development of a commercial revolution ...
HOW TO USE THE RENAISSANCE PRINTAbLE fROM HARMONY
... cutting, reading, observing, and coloring to learn a bit about the Renaissance art history time period. This unit only scratches the surface and if you are interested in learning more, please see Harmony Fine Arts Grades 2 and 6 for more Medieval and Renaissance art. ...
... cutting, reading, observing, and coloring to learn a bit about the Renaissance art history time period. This unit only scratches the surface and if you are interested in learning more, please see Harmony Fine Arts Grades 2 and 6 for more Medieval and Renaissance art. ...
Papers, Revisions, and Deadlines - WesFiles
... lost Golden Age, the world of the ancients. Although they did not succeed in their goal, they ended up by inspiring a new Golden Age. This seminar explores the intellectual and cultural history of Renaissance Italy. What was the Italian Renaissance? Who created and supported it and why? Whom did it ...
... lost Golden Age, the world of the ancients. Although they did not succeed in their goal, they ended up by inspiring a new Golden Age. This seminar explores the intellectual and cultural history of Renaissance Italy. What was the Italian Renaissance? Who created and supported it and why? Whom did it ...
teacher`s guide teacher`s guide teacher`s guide
... he Renaissance was a unique, distinctive time in European history. It was a time when people looked back to ancient Greek and Roman civilizations for inspiration, and in doing so ignited revolutions in science, technology, religion, medicine, politics, exploration and the arts. By looking at what wa ...
... he Renaissance was a unique, distinctive time in European history. It was a time when people looked back to ancient Greek and Roman civilizations for inspiration, and in doing so ignited revolutions in science, technology, religion, medicine, politics, exploration and the arts. By looking at what wa ...
Unit
... What was the probably meaning of the Portrait of Giovanni Arnolfini and His Wife? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ List some of the signs of wealth shown in this p ...
... What was the probably meaning of the Portrait of Giovanni Arnolfini and His Wife? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ List some of the signs of wealth shown in this p ...
к½Â·°l¬F
... The Renaissance has abundant contents. It has huge changes in the aspects of art, literature, science and architecture. Choose the figure you are most familiar with from the above materials. Fill them in the proper blanks and introduce their important ...
... The Renaissance has abundant contents. It has huge changes in the aspects of art, literature, science and architecture. Choose the figure you are most familiar with from the above materials. Fill them in the proper blanks and introduce their important ...
Renaissance and Reformation
... Crusades led to more trade opportunities with the east Rise of a merchant class Development of a commercial revolution ...
... Crusades led to more trade opportunities with the east Rise of a merchant class Development of a commercial revolution ...
High Renaissance - HCC Learning Web
... • Occurred after the Middle Ages (period of religious fervor) • Born out of a movement called “Humanism” • Divided into three periods: – Early Renaissance: 14th -15th century – High Renaissance: 15th -16th century – Late Renaissance (Mannerism): 16th –early 17th century ...
... • Occurred after the Middle Ages (period of religious fervor) • Born out of a movement called “Humanism” • Divided into three periods: – Early Renaissance: 14th -15th century – High Renaissance: 15th -16th century – Late Renaissance (Mannerism): 16th –early 17th century ...
Differences between the Italian an Northern Renaissance Italian
... enormous Holy Roman Empire. Its Dukes, during the last 100 years it existed, were given monikers of "the Good," "the Fearless" and "the Bold" (although apparently the last "Bold" Duke wasn't quite bold enough, as Burgundy was absorbed by both France and the Holy Roman Empire at the end of his reign. ...
... enormous Holy Roman Empire. Its Dukes, during the last 100 years it existed, were given monikers of "the Good," "the Fearless" and "the Bold" (although apparently the last "Bold" Duke wasn't quite bold enough, as Burgundy was absorbed by both France and the Holy Roman Empire at the end of his reign. ...
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... Supported by patrons like Isabella d’Este, dozens of talented artists worked in northern Italy. As the Renaissance advanced, artistic styles changed. Medieval artists used religious subjects and tried to convey a spiritual ideal. Renaissance artists also often portrayed religious subjects, but they ...
... Supported by patrons like Isabella d’Este, dozens of talented artists worked in northern Italy. As the Renaissance advanced, artistic styles changed. Medieval artists used religious subjects and tried to convey a spiritual ideal. Renaissance artists also often portrayed religious subjects, but they ...
Document
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
Andrea del Sarto (1486–1530)
... del Grano, where he created the Baptism of Christ. Andrea's works are of great importance in the evolution of Florentine painting, especially the Holy Families. His Madonnas are notable for their softly atmospheric qualities and the richness of their colour, in contrast to the linear definition and ...
... del Grano, where he created the Baptism of Christ. Andrea's works are of great importance in the evolution of Florentine painting, especially the Holy Families. His Madonnas are notable for their softly atmospheric qualities and the richness of their colour, in contrast to the linear definition and ...
File - Mrs. Abbott OPHS
... He painted The Last Supper on a dry wall rather than on wet plaster, so it is not a true fresco. He used a double layer of dried plaster over a stone wall, he added an undercoat of white lead to enhance the brightness of the oil and tempera that was applied on top. These techniques were important fo ...
... He painted The Last Supper on a dry wall rather than on wet plaster, so it is not a true fresco. He used a double layer of dried plaster over a stone wall, he added an undercoat of white lead to enhance the brightness of the oil and tempera that was applied on top. These techniques were important fo ...
Curriculum Vitae - Wake Forest University
... EVA/AVE: Women in Renaissance and Baroque Prints, National Gallery of Art, Washington, DC, November 25, 1990-April 28, 1991; National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa, October 10, ...
... EVA/AVE: Women in Renaissance and Baroque Prints, National Gallery of Art, Washington, DC, November 25, 1990-April 28, 1991; National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa, October 10, ...
Medieval & Renaissance Compared
... Wealthy bankers & to Italian city-states & merchants wanted to a wealthy middle class show off their new status of bankers & merchants by commissioning art ...
... Wealthy bankers & to Italian city-states & merchants wanted to a wealthy middle class show off their new status of bankers & merchants by commissioning art ...
Art and Artists of the Renaissance
... • Michelangelo’s plan was to depict the salvation of the human race by God as told through the allegory of the Old Testament. • For Renaissance Christians, every element and story in the Old Testament had both a literal and a mystical meaning. • The Old Testament had been retained by the Christian C ...
... • Michelangelo’s plan was to depict the salvation of the human race by God as told through the allegory of the Old Testament. • For Renaissance Christians, every element and story in the Old Testament had both a literal and a mystical meaning. • The Old Testament had been retained by the Christian C ...
Oration on the Dignity of Man
... reader, and he is free and independent enough to apply his own judgment to what he reads – Hamlet’s speech in Act II, “What a piece of work is a man! How noble in reason, how infinite in faculty, in form and moving how express and admirable, in action how like an angel, in apprehension how like a go ...
... reader, and he is free and independent enough to apply his own judgment to what he reads – Hamlet’s speech in Act II, “What a piece of work is a man! How noble in reason, how infinite in faculty, in form and moving how express and admirable, in action how like an angel, in apprehension how like a go ...
Chapter1Assessment
... The Northern Renaissance Section 2 (pages 46–53) 11. What did northern European rulers do to encourage the spread of Renaissance ideas? (HI 1) 12. How were the Christian humanists different from the humanists of the Italian Renaissance? (10.1.1) ...
... The Northern Renaissance Section 2 (pages 46–53) 11. What did northern European rulers do to encourage the spread of Renaissance ideas? (HI 1) 12. How were the Christian humanists different from the humanists of the Italian Renaissance? (10.1.1) ...
The Intellectual and Artistic Renaissance
... apparent in its intellectual & artistic movements. • One intellectual movement was humanism. • Humanism was based on the classics, the literary works of ancient Greece and Rome. • Humanists studied the subjects that are now known as the humanities - poetry, philosophy, & history. • Petrarch generate ...
... apparent in its intellectual & artistic movements. • One intellectual movement was humanism. • Humanism was based on the classics, the literary works of ancient Greece and Rome. • Humanists studied the subjects that are now known as the humanities - poetry, philosophy, & history. • Petrarch generate ...
Renaissance architecture

Renaissance architecture is the architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 17th centuries in different regions of Europe, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact.Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts as they are demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pilasters and lintels, as well as the use of semicircular arches, hemispherical domes, niches and aedicules replaced the more complex proportional systems and irregular profiles of medieval buildings.