Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
Presentation
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
2.What was the `debacle at Lucca`?
... 2. Who was his chief artistic rival in Florence? 3. What famous work is this individual responsible for? Where is it? When was it completed? What is the significance of this work? ...
... 2. Who was his chief artistic rival in Florence? 3. What famous work is this individual responsible for? Where is it? When was it completed? What is the significance of this work? ...
Directions
... What new types of books were published at this time? Almanacs, travel books, chivalry romances, and poetry Before Gutenberg’s invention, how were books printed? By hand Why was the invention so important? Made producing books inexpensive Slide 19 Use the web sites to answer the questions below What ...
... What new types of books were published at this time? Almanacs, travel books, chivalry romances, and poetry Before Gutenberg’s invention, how were books printed? By hand Why was the invention so important? Made producing books inexpensive Slide 19 Use the web sites to answer the questions below What ...
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
... taking the form of a political guidebook. In The Prince, Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power and keep it in spite of his enemies. In answering this question, he began with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, and corrupt. To succeed in such a wicked world, Machiavelli said, a p ...
Chapter 17
... Michelangelo, and Raphael showed the Renaissance spirit. All three artists demonstrated an interest in classical culture, a curiosity about the world, and a belief in human potential. Humanist writers expanded ideas about individuality. These ideas impressed scholars, students, and merchants who vis ...
... Michelangelo, and Raphael showed the Renaissance spirit. All three artists demonstrated an interest in classical culture, a curiosity about the world, and a belief in human potential. Humanist writers expanded ideas about individuality. These ideas impressed scholars, students, and merchants who vis ...
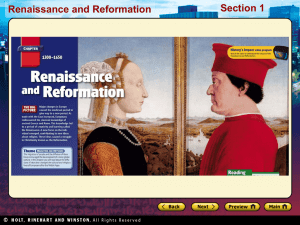
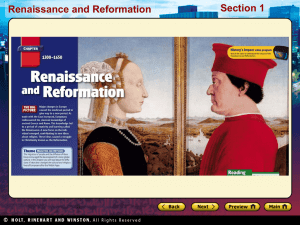
“Florence is widely considered as the birthplace of the Renaissance
... perspective. This technique placed subjects of a painting on firm ground in a proportionate setting, rather than floating them in air. Based both on Brunelleschi’s theories and on the works of Aristotle, church architect Leon Battista Alberti devised the first complex scientific formula for depictin ...
... perspective. This technique placed subjects of a painting on firm ground in a proportionate setting, rather than floating them in air. Based both on Brunelleschi’s theories and on the works of Aristotle, church architect Leon Battista Alberti devised the first complex scientific formula for depictin ...
10th Euro Studies 9.29.14
... Introduction: “Break with Medieval Political Theory” • What is politics (or the state) to Machiavelli? • What should “The Prince” or any other leader be concerned with? • What do you think the Church might have thought of Machiavelli’s writings? Why? • Discuss in your group and answer each question ...
... Introduction: “Break with Medieval Political Theory” • What is politics (or the state) to Machiavelli? • What should “The Prince” or any other leader be concerned with? • What do you think the Church might have thought of Machiavelli’s writings? Why? • Discuss in your group and answer each question ...
Document
... Patronage • Pope Julius II is biggest patron.. Powerful force in Roman and European politics and religion. • Transformed Rome, a ramshackle medieval town, into an artistic center to rival Florence. • Women were also key patrons, such as Queen Isabella d’Este • St. Peter’s church in Rome is rebuilt, ...
... Patronage • Pope Julius II is biggest patron.. Powerful force in Roman and European politics and religion. • Transformed Rome, a ramshackle medieval town, into an artistic center to rival Florence. • Women were also key patrons, such as Queen Isabella d’Este • St. Peter’s church in Rome is rebuilt, ...
High Renaissance Notes Vocab Renaissance Overview: c. 1500
... The term Mannerism comes from the Italian, maniera, a word used in the 16th century suggesting intellectual intricate subjects, highly skilled technique, and art concerned with beauty for its own sake. It ...
... The term Mannerism comes from the Italian, maniera, a word used in the 16th century suggesting intellectual intricate subjects, highly skilled technique, and art concerned with beauty for its own sake. It ...
Humanism and the Early Italian Renaissance
... 2. Food costs were high. 3. A terrible famine in the early thirteenth century on the subcontinent reduced the population by ten percent. 4. The Black Death struck in 1348 and recurred throughout the remainder of the century. 5. The population of Europe fell by forty percent between 1300 and 1400. 6. ...
... 2. Food costs were high. 3. A terrible famine in the early thirteenth century on the subcontinent reduced the population by ten percent. 4. The Black Death struck in 1348 and recurred throughout the remainder of the century. 5. The population of Europe fell by forty percent between 1300 and 1400. 6. ...
File
... Like Italian artists, the artists of northern Europe worked to portray their world realistically. However, their approach was different. Circumstance (the conditions that influence a situation) helps explain the differences. The large wall spaces of Italian churches had encouraged the art of fresco ...
... Like Italian artists, the artists of northern Europe worked to portray their world realistically. However, their approach was different. Circumstance (the conditions that influence a situation) helps explain the differences. The large wall spaces of Italian churches had encouraged the art of fresco ...
13.1 – The Renaissance in Italy
... Was the final break from Europe’s Medieval past Pointed toward new thinking about the physical ...
... Was the final break from Europe’s Medieval past Pointed toward new thinking about the physical ...
Growth of the Renaissance Guided Reading
... The Renaissance began in northern and central Italy. One reason why it began there was the prosperity of Italian citystates. In the Late Middle Ages, most of western Europe was made up of fiefs ruled by nobles. Above the nobles were monarchs. In Italy, however, growing towns developed into independe ...
... The Renaissance began in northern and central Italy. One reason why it began there was the prosperity of Italian citystates. In the Late Middle Ages, most of western Europe was made up of fiefs ruled by nobles. Above the nobles were monarchs. In Italy, however, growing towns developed into independe ...
The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650
... Was the final break from Europe’s Medieval past Pointed toward new thinking about the physical ...
... Was the final break from Europe’s Medieval past Pointed toward new thinking about the physical ...
Important Renaissance People: Artists
... those things his policies. 8. Most people are extremely selfish. 9. A promise is a sacred trust. ...
... those things his policies. 8. Most people are extremely selfish. 9. A promise is a sacred trust. ...
Renaissance – Uffizi Gallery Crawl
... • Many powerful people, Popes, Kings, Queens, and other Nobles and Aristocrats were Patrons of the Arts. Among the most famous patrons of the Renaissance were the Medici. They were a wealthy family of bankers and merchants. In fact, they were the most powerful leaders of Florence from the early 140 ...
... • Many powerful people, Popes, Kings, Queens, and other Nobles and Aristocrats were Patrons of the Arts. Among the most famous patrons of the Renaissance were the Medici. They were a wealthy family of bankers and merchants. In fact, they were the most powerful leaders of Florence from the early 140 ...
Renaissance and Reformation Section 1
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
Renaissance - Monroe County Schools
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
Renaissance
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
... What were some important new ideas of the Renaissance? Answer(s): inspiration from the ancient Greeks and Romans; humanism; secular focus; new theories in science ...
Palazzo Torres Lancellotti in Piazza Navona
... himself who was active in organizing the international league against the Infidel at the behest of Pope Pius V (whose likeness is part of the decoration). These frescoes are the work of Roman painters who have so far remained nameless (the only contribution documented being that of the Piedmontese C ...
... himself who was active in organizing the international league against the Infidel at the behest of Pope Pius V (whose likeness is part of the decoration). These frescoes are the work of Roman painters who have so far remained nameless (the only contribution documented being that of the Piedmontese C ...
The Renaissance
... and treaties. Over 400 years, these consolidations of kingdoms led to ‘super kingdoms’ with great resources (land, money, artisans) We see the change reflected in new terms for those who rule and those that are ruled: Kings became monarchs; subjects were soon to become citizens. To rule effectively, ...
... and treaties. Over 400 years, these consolidations of kingdoms led to ‘super kingdoms’ with great resources (land, money, artisans) We see the change reflected in new terms for those who rule and those that are ruled: Kings became monarchs; subjects were soon to become citizens. To rule effectively, ...
Michelangelo
... The Renaissance refers to Italian art and architecture of the 15th and 16th centuries and centered around the Tuscan city of Florence. ‘Renaissance” is a French word which means rebirth. It was an intellectual movement, which celebrated anything from the classics or the time of ancient Greece an ...
... The Renaissance refers to Italian art and architecture of the 15th and 16th centuries and centered around the Tuscan city of Florence. ‘Renaissance” is a French word which means rebirth. It was an intellectual movement, which celebrated anything from the classics or the time of ancient Greece an ...
Renaissance architecture

Renaissance architecture is the architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 17th centuries in different regions of Europe, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact.Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts as they are demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pilasters and lintels, as well as the use of semicircular arches, hemispherical domes, niches and aedicules replaced the more complex proportional systems and irregular profiles of medieval buildings.