The Renaissance Spreads
... The Northern Renaissance The monarchs of England & France were strong patrons of the arts Italian ideas mingled with northern traditions and developed their own distinct characteristics Artists were especially interested in realism The idea of human dignity caused many northern humanists to plan a ...
... The Northern Renaissance The monarchs of England & France were strong patrons of the arts Italian ideas mingled with northern traditions and developed their own distinct characteristics Artists were especially interested in realism The idea of human dignity caused many northern humanists to plan a ...
Renaissance intro and art
... Starts in Italy – why? • Buildings and objects from Ancient Rome were still in italy - Italy had been the centre of the Roman empire • many greek manuscripts had been brought to italy for safekeeping by greek scholars in 1453 after the fall of Constantinople • Italian merchants were richer than els ...
... Starts in Italy – why? • Buildings and objects from Ancient Rome were still in italy - Italy had been the centre of the Roman empire • many greek manuscripts had been brought to italy for safekeeping by greek scholars in 1453 after the fall of Constantinople • Italian merchants were richer than els ...
File - Ms. Fitzgibbon`s World History Class
... How did art communicate the ideas of the Renaissance? Sit with your group (see list on board) ...
... How did art communicate the ideas of the Renaissance? Sit with your group (see list on board) ...
To what extent was the Italian Renaissance a break from the Middle
... After the fall of the Roman Empire in A.D. 476, a new era of European civilization began, known as the Middle Ages. During this thousand-year period of transformation, Europe experienced the rise of towns and trade, the development of feudalism and, most importantly, the growing power of the Catholi ...
... After the fall of the Roman Empire in A.D. 476, a new era of European civilization began, known as the Middle Ages. During this thousand-year period of transformation, Europe experienced the rise of towns and trade, the development of feudalism and, most importantly, the growing power of the Catholi ...
Unit One
... Writers and artists began to express their new view on life and the printing press allowed for a revival in education and the availability of texts Many were influenced by Greco-Roman classical styles preserved by Muslim and Byzantine scholars. Western Europeans came in contact with them through t ...
... Writers and artists began to express their new view on life and the printing press allowed for a revival in education and the availability of texts Many were influenced by Greco-Roman classical styles preserved by Muslim and Byzantine scholars. Western Europeans came in contact with them through t ...
Ch. 12 Slides - Italian Renaissance
... for education and leadership among women The Renaissance did not bring any significant change to the status of women. The only change is that elite women now presided over social gatherings but merely as decorative figures. The few exceptions of women writers and painters were those who were able to ...
... for education and leadership among women The Renaissance did not bring any significant change to the status of women. The only change is that elite women now presided over social gatherings but merely as decorative figures. The few exceptions of women writers and painters were those who were able to ...
UNIT TEST #2 REVIEW
... One of the most important inventions of the Renaissance was the PRINTING PRESS which was invented by Johann Gutenberg. It was so important because books and Bibles could be printed– this allowed more people to be able to READ! ...
... One of the most important inventions of the Renaissance was the PRINTING PRESS which was invented by Johann Gutenberg. It was so important because books and Bibles could be printed– this allowed more people to be able to READ! ...
Renaissance Homework
... Directions: Read each question carefully. Answer each question in a complete sentence, restating the question in the answer. 1. Identify some of the artistic contributions Florence made to Renaissance society. ...
... Directions: Read each question carefully. Answer each question in a complete sentence, restating the question in the answer. 1. Identify some of the artistic contributions Florence made to Renaissance society. ...
Chapter 5 Study Guide—Renaissance and Reformation
... 10. Castiglione—wrote The Book of the Courtier which described the characteristics of the perfect Renaissance noble, was followed for centuries 11. The Divine Comedy—written by Dante, is about a soul’s imaginary journey through hell, purgatory, and heaven (or paradise) 12. The Canterbury Tales—writt ...
... 10. Castiglione—wrote The Book of the Courtier which described the characteristics of the perfect Renaissance noble, was followed for centuries 11. The Divine Comedy—written by Dante, is about a soul’s imaginary journey through hell, purgatory, and heaven (or paradise) 12. The Canterbury Tales—writt ...
Renaissance humanism refers to several different, but
... What This Has to Do with Me In Rome, I was as happy and excited to be alive as I have ever been. Everything was stimulating to me, everything was interesting. My concerns about being able to enjoy history all but slipped away that first day as we drove and walked through Rome. I already knew about m ...
... What This Has to Do with Me In Rome, I was as happy and excited to be alive as I have ever been. Everything was stimulating to me, everything was interesting. My concerns about being able to enjoy history all but slipped away that first day as we drove and walked through Rome. I already knew about m ...
Early Renaissance
... – Written in classical style – Discoursed on the foolishness and misguided pompousness of the ...
... – Written in classical style – Discoursed on the foolishness and misguided pompousness of the ...
Unit 13 - Student Notes _Renaissance_ 9R
... where wealth from trade sparked the Renaissance A new middle class of bankers, merchants, & skilled craftsmen gained lots of power The Medici family were wealthy bankers who used their wealth to turn Florence into Italy’s most artistic city ...
... where wealth from trade sparked the Renaissance A new middle class of bankers, merchants, & skilled craftsmen gained lots of power The Medici family were wealthy bankers who used their wealth to turn Florence into Italy’s most artistic city ...
Chapter 13 Vocab - Everglades High School
... • Raphael – painter; blended Christian and classical styles; famous works include The School of Athens and his portrayals of the Madonna • Niccolò Machiavelli – wrote The Prince, describing how to rule in an age of ruthless power politics Section 2 • Johann Gutenberg – person who invented a printing ...
... • Raphael – painter; blended Christian and classical styles; famous works include The School of Athens and his portrayals of the Madonna • Niccolò Machiavelli – wrote The Prince, describing how to rule in an age of ruthless power politics Section 2 • Johann Gutenberg – person who invented a printing ...
The Renaissance - Valhalla High School
... • The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas and allowed more people to become educated. ...
... • The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas and allowed more people to become educated. ...
The Renaissance, 1300-1600 Essential Question 2
... • Ideal person is one who has a wide variety of knowledge and skill in a wide variety of subjects • Best Example: Leonardo da Vinci Painter, sculptor, inventor, musician, philosopher, scientist, writer • Baldassare Castiglione’s The Courtier • Be able to speak/read Latin and Greek • Knowledge of his ...
... • Ideal person is one who has a wide variety of knowledge and skill in a wide variety of subjects • Best Example: Leonardo da Vinci Painter, sculptor, inventor, musician, philosopher, scientist, writer • Baldassare Castiglione’s The Courtier • Be able to speak/read Latin and Greek • Knowledge of his ...
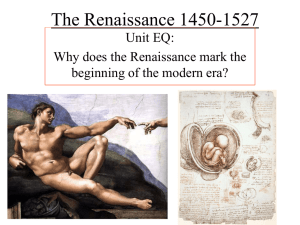
The Renaissance 1450-1527 - farmington public schools
... “Although the elements of continuity are clear, the characteristic outlook of the Middle Ages was as different from that of the modern age as it was from that of the ancient world” • Human intellect/reason CAN interpret the natural world through science ...
... “Although the elements of continuity are clear, the characteristic outlook of the Middle Ages was as different from that of the modern age as it was from that of the ancient world” • Human intellect/reason CAN interpret the natural world through science ...
The Renaissance in Northern Europe
... France invited Italian Masters to travel to and live in their countries – Francis I of France invited Leonardo to retire in France and Leonardo lived out his last years there. ...
... France invited Italian Masters to travel to and live in their countries – Francis I of France invited Leonardo to retire in France and Leonardo lived out his last years there. ...
The Renaissance
... Chaucer: Canterbury Tales: series of stories told by travelers on pilgrimage to Shrine of Tomas Becket Machiavelli: The Prince: speaks of deceitful leaders & way gov’t should operate FRANCE French invasions – brought back Italian architects & artists Chateaux – castles Rabelais – physician / monk (b ...
... Chaucer: Canterbury Tales: series of stories told by travelers on pilgrimage to Shrine of Tomas Becket Machiavelli: The Prince: speaks of deceitful leaders & way gov’t should operate FRANCE French invasions – brought back Italian architects & artists Chateaux – castles Rabelais – physician / monk (b ...
Renaissance in Northern Europe
... came to see Ancient Roman ruins. Scholars came to see the great library at the Vatican in Rome (this was the place the Catholic Pope called home). Brueghel and other artists came to Italy to study art. C) Renaissance ideas also spread by way of the printed word. Between 1438 and 1454 Johannes Gutenb ...
... came to see Ancient Roman ruins. Scholars came to see the great library at the Vatican in Rome (this was the place the Catholic Pope called home). Brueghel and other artists came to Italy to study art. C) Renaissance ideas also spread by way of the printed word. Between 1438 and 1454 Johannes Gutenb ...
Mr - Nutley Schools
... Where were the following reformers from. What were their main problems with the Catholic Church? What was the outcome of their particular situation? Martin Luther: Germany; wanted to stop the sale of indulgences as well as have the people translate the Bible for themselves; he was excommunicated and ...
... Where were the following reformers from. What were their main problems with the Catholic Church? What was the outcome of their particular situation? Martin Luther: Germany; wanted to stop the sale of indulgences as well as have the people translate the Bible for themselves; he was excommunicated and ...
The Renaissance, 1300-1600
... New Types of Literature Focused on human concerns, values, problems, self-expression Wrote in the vernacular (local language) Francesco Petrarch= poet/writer; sonnets to Laura (love, human interest); “Father of Renaissance” Niccolo’ Machiavelli= The Prince (1513) a. Sees human behavior “as it really ...
... New Types of Literature Focused on human concerns, values, problems, self-expression Wrote in the vernacular (local language) Francesco Petrarch= poet/writer; sonnets to Laura (love, human interest); “Father of Renaissance” Niccolo’ Machiavelli= The Prince (1513) a. Sees human behavior “as it really ...
Beginning of Renaissance
... • Humanists believe in the power of the human mind, that the potential of the human mind is limitless. Church believed opposite. • Made progress in anatomy, geography, astronomy, medicine. Most notable was Leonardo da Vinci's studies of the human anatomy. ...
... • Humanists believe in the power of the human mind, that the potential of the human mind is limitless. Church believed opposite. • Made progress in anatomy, geography, astronomy, medicine. Most notable was Leonardo da Vinci's studies of the human anatomy. ...
H202_2_Early_Renaissance
... John Dunstable was not just the first truly great English composer, he was also musical godfather to the Renaissance. In the middle of the 15th Century poet Martin le Franc described how Dufay had adopted the English manner championed by Dunstable (la contenance Angloise) and how, to Continental ear ...
... John Dunstable was not just the first truly great English composer, he was also musical godfather to the Renaissance. In the middle of the 15th Century poet Martin le Franc described how Dufay had adopted the English manner championed by Dunstable (la contenance Angloise) and how, to Continental ear ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.