Northern Renaissance
... interest helped to secularize northern Italy. • Letters of credit served to expand the supply of money and expedite trade. • New accounting and bookkeeping practices (use of Arabic numerals) ...
... interest helped to secularize northern Italy. • Letters of credit served to expand the supply of money and expedite trade. • New accounting and bookkeeping practices (use of Arabic numerals) ...
The Church in the Renaissance
... “Renaissance papacy” refers to the line of popes from the end of the Great Schism (1417) - the beginnings of the Reformation (early 16th C.) ...
... “Renaissance papacy” refers to the line of popes from the end of the Great Schism (1417) - the beginnings of the Reformation (early 16th C.) ...
17.1 Italy Birthplace of the Renaissance
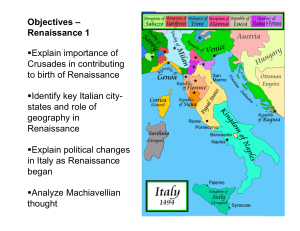
... The crusades spurred trade and growing city-states in Italy Northern Italy was urban while the rest of Europe was still rural Cities were places where people shared ideas and intellectual growth occurred Bubonic plague killed 60% of the population bringing economic changes Survivors could demand hig ...
... The crusades spurred trade and growing city-states in Italy Northern Italy was urban while the rest of Europe was still rural Cities were places where people shared ideas and intellectual growth occurred Bubonic plague killed 60% of the population bringing economic changes Survivors could demand hig ...
Chapter 15 Renaissance and Reformation
... a. Wealthy educated merchants and bankers b. Became patrons (supporters) of the arts 1) Medici’s - Powerful family in Florence – “Patron of the Arts” 2) Isabella d’Este – Provided financial support to artists ...
... a. Wealthy educated merchants and bankers b. Became patrons (supporters) of the arts 1) Medici’s - Powerful family in Florence – “Patron of the Arts” 2) Isabella d’Este – Provided financial support to artists ...
File
... Patrons are people who paid artists to produce works They played an important role in promoting the arts during the Renaissance Patrons included members of the new wealthy merchant class They also included members of the government and the Church Artists made works to decorate private homes or to di ...
... Patrons are people who paid artists to produce works They played an important role in promoting the arts during the Renaissance Patrons included members of the new wealthy merchant class They also included members of the government and the Church Artists made works to decorate private homes or to di ...
Daily Lecture and Discussion Notes
... E. The architect Filippo Brunelleschi created a new architecture based on Roman classical buildings. His church of San Lorenzo in Florence does not overwhelm the worshipper, as Gothic cathedrals might, but offers a space to fit human needs. Renaissance architects also sought to reflect a human-cente ...
... E. The architect Filippo Brunelleschi created a new architecture based on Roman classical buildings. His church of San Lorenzo in Florence does not overwhelm the worshipper, as Gothic cathedrals might, but offers a space to fit human needs. Renaissance architects also sought to reflect a human-cente ...
Document
... Catholic Reformation) was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War (1648), and was initiated in response to the Protestant ...
... Catholic Reformation) was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War (1648), and was initiated in response to the Protestant ...
The Renaissance - Duxbury Public Schools
... a broom closet and walking out with it hidden under his coat after the museum had closed After keeping the painting in his apartment for two years, the man grew impatient and was caught when he attempted to sell it to an art dealer; it was exhibited all over Italy and returned to the Louvre in 1913 ...
... a broom closet and walking out with it hidden under his coat after the museum had closed After keeping the painting in his apartment for two years, the man grew impatient and was caught when he attempted to sell it to an art dealer; it was exhibited all over Italy and returned to the Louvre in 1913 ...
Renaissance and Reformation
... 1. Cities and City-States –Italy = urban areas & large towns –Rest of Europe = rural –Bubonic plague led to decreased population and increased wages & art ...
... 1. Cities and City-States –Italy = urban areas & large towns –Rest of Europe = rural –Bubonic plague led to decreased population and increased wages & art ...
Week 10 - Renaissance
... speaking, please the devout better than any painting in Italy, which will never cause him to shed a tear, whereas that of Flanders will cause him to shed many…In Flanders they paint with a view to external exactness or such things as may cheer you and of which you cannot speak ill, as for example sa ...
... speaking, please the devout better than any painting in Italy, which will never cause him to shed a tear, whereas that of Flanders will cause him to shed many…In Flanders they paint with a view to external exactness or such things as may cheer you and of which you cannot speak ill, as for example sa ...
Name
... 16. Anabaptist-from Greek, means to baptize again, believed only adult baptism valid 17. Anglican Church- the name for the church of England whom the King was the head 18. Protestant (Origin)-comes from the name given some German Princes who protested against joining forces with the pope against Lut ...
... 16. Anabaptist-from Greek, means to baptize again, believed only adult baptism valid 17. Anglican Church- the name for the church of England whom the King was the head 18. Protestant (Origin)-comes from the name given some German Princes who protested against joining forces with the pope against Lut ...
invented during the Middle Ages.
... necessary as a result of increased trade in Europe during the Middle Ages. The period of time from the 14th to the 16th century is known as the Renaissance. A key feature of the Renaissance was an increased focus on individuals. A rediscovery of classical writings contributed to the ...
... necessary as a result of increased trade in Europe during the Middle Ages. The period of time from the 14th to the 16th century is known as the Renaissance. A key feature of the Renaissance was an increased focus on individuals. A rediscovery of classical writings contributed to the ...
Northern Renaissance
... lawyers claim first place, the most self-satisfied class of people, as they roll their rock of Sisyphus and string together six hundred laws in the same breath, no matter whether relevant or not, piling up opinion on opinion and gloss on gloss to make their profession seem the most difficult of all. ...
... lawyers claim first place, the most self-satisfied class of people, as they roll their rock of Sisyphus and string together six hundred laws in the same breath, no matter whether relevant or not, piling up opinion on opinion and gloss on gloss to make their profession seem the most difficult of all. ...
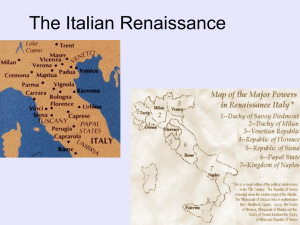
The Italian Renaissance
... Origins of the Renaissance - Economic growth was the basis for the Renaissance - Northern Italy was centrally located and benefited from the crusades and the spice trade - The Renaissance started in Florence and follows the success of the Medici family - Florentine merchants (the Medicis) gained co ...
... Origins of the Renaissance - Economic growth was the basis for the Renaissance - Northern Italy was centrally located and benefited from the crusades and the spice trade - The Renaissance started in Florence and follows the success of the Medici family - Florentine merchants (the Medicis) gained co ...
The Renaissance - Dr. Afxendiou`s Classes
... • Ruler keeps power by any means necessary • The end justifies the means • Be good when possible, and evil when necessary ...
... • Ruler keeps power by any means necessary • The end justifies the means • Be good when possible, and evil when necessary ...
European Society in the Age of the Renaissance
... more powerful than the Middle Age Styles. Ex. The Florentine Academy and the revival of Platonism. • Secularism – concern with material world instead of the spiritual. Enjoy the here and now! Ex. G. Boccaccio’s The Decameron, discussed usury and its acceptance as well as the idea that it is harmful ...
... more powerful than the Middle Age Styles. Ex. The Florentine Academy and the revival of Platonism. • Secularism – concern with material world instead of the spiritual. Enjoy the here and now! Ex. G. Boccaccio’s The Decameron, discussed usury and its acceptance as well as the idea that it is harmful ...
NOTES- Renaissance
... Thomas More: humanist writer from England who wrote Utopia about the perfect society. Wrote in the Classical language ...
... Thomas More: humanist writer from England who wrote Utopia about the perfect society. Wrote in the Classical language ...
Renaissance Artists
... The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art ...
... The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art ...
Renaissance Artists
... The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art ...
... The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art ...
Renaissance Artists
... The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art ...
... The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art ...
Renaissance flashcards
... Painter and sculptor, painted the Sistine Chapel (Last Judgement) and sculpted statue of David and Pieta. ...
... Painter and sculptor, painted the Sistine Chapel (Last Judgement) and sculpted statue of David and Pieta. ...
File - Science Hill Visual Art
... Refers to the period between the end of the High Renaissance and the beginning of the Baroque period. Was originally a derogatory term applied to painters who had a formal, mannered style that imitated various aspects of Raphael’s and Michelangelo’s works. Included in the Mannerist style are feature ...
... Refers to the period between the end of the High Renaissance and the beginning of the Baroque period. Was originally a derogatory term applied to painters who had a formal, mannered style that imitated various aspects of Raphael’s and Michelangelo’s works. Included in the Mannerist style are feature ...
File - World History
... both war and plague. Those who survived wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit. They began to question institutions of the Middle Ages, which had been unable to prevent war or to relieve suffering brought by the plague. Some people questioned the Church, which taught Christians to endure suff ...
... both war and plague. Those who survived wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit. They began to question institutions of the Middle Ages, which had been unable to prevent war or to relieve suffering brought by the plague. Some people questioned the Church, which taught Christians to endure suff ...