07 PPT
... • If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no net movement of water into the cell; the cell becomes flaccid (limp), and the plant may wilt • In a hypertonic environment, plant cells lose water; eventually, the membrane pulls away from the wall, a usually lethal effect called plasm ...
... • If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no net movement of water into the cell; the cell becomes flaccid (limp), and the plant may wilt • In a hypertonic environment, plant cells lose water; eventually, the membrane pulls away from the wall, a usually lethal effect called plasm ...
chapter48
... More positive ions are pumped out than in. Neurons have three types of ion channels: 1. Ungated or passive ion channels, which are generally open. E.g., Na+, K+, Cl- and Ca2+ 2. Voltage activated ion channels are kept closed and respond only to voltage changes. 3. Chemically activated ion channels f ...
... More positive ions are pumped out than in. Neurons have three types of ion channels: 1. Ungated or passive ion channels, which are generally open. E.g., Na+, K+, Cl- and Ca2+ 2. Voltage activated ion channels are kept closed and respond only to voltage changes. 3. Chemically activated ion channels f ...
Chapter 33
... A nerve impulse starts when pressure or other sensory inputs disturb a neuron’s plasma membrane, causing sodium channels on a dendrite to open. Sodium ions flood into the neuron and the ...
... A nerve impulse starts when pressure or other sensory inputs disturb a neuron’s plasma membrane, causing sodium channels on a dendrite to open. Sodium ions flood into the neuron and the ...
Cells and Membranes
... Plasma membrane contains proteins that are used to take in and excrete small molecules o Proteins in membranes help bind cells together – adhesive molecules that join cells to cells to form tissues o Certain molecules pass through plasma membrane via proteins o Plasma membrane contains a variety of ...
... Plasma membrane contains proteins that are used to take in and excrete small molecules o Proteins in membranes help bind cells together – adhesive molecules that join cells to cells to form tissues o Certain molecules pass through plasma membrane via proteins o Plasma membrane contains a variety of ...
Nervous System - Buck Mountain Central School
... • The plasma membrane of almost all cells has an electrical potential of about -70 mV. In neurons this is called the resting potential. Both sides have a rich supply of positive and negative ions. There is a higher concentration of potassium ions (K) inside the cell and a higher concentration of so ...
... • The plasma membrane of almost all cells has an electrical potential of about -70 mV. In neurons this is called the resting potential. Both sides have a rich supply of positive and negative ions. There is a higher concentration of potassium ions (K) inside the cell and a higher concentration of so ...
Active Transport
... A student investigated the effect of pH on the activity of the enzyme amylase. She set up the apparatus shown in the diagram. The tubes were made from Visking tubing. Visking tubing is partially permeable. She added an equal volume of amylase solution and starch to each tube. ...
... A student investigated the effect of pH on the activity of the enzyme amylase. She set up the apparatus shown in the diagram. The tubes were made from Visking tubing. Visking tubing is partially permeable. She added an equal volume of amylase solution and starch to each tube. ...
Cell Membrane proteins
... Proteins constituting 25 to 75% of the mass the of various membranes of the cells .These proteins are divided into two general classes , based on the nature of their association with the membrane : 1. Integral membrane proteins , They are partially embedded in lipid bilayer or formed of transmembran ...
... Proteins constituting 25 to 75% of the mass the of various membranes of the cells .These proteins are divided into two general classes , based on the nature of their association with the membrane : 1. Integral membrane proteins , They are partially embedded in lipid bilayer or formed of transmembran ...
ch 48 nervous system
... are equal and opposite, and the resting potential across the membrane remains steady ...
... are equal and opposite, and the resting potential across the membrane remains steady ...
BIOAVAILABILITY Membranes
... Membrane proteins • Integral membrane proteins • Peripheral membrane proteins • Lipid anchored membrane proteins Membrane protein asymmetry Lipid protein interactions: hydrophobic matching, lipid sorting and lipid selectivity ...
... Membrane proteins • Integral membrane proteins • Peripheral membrane proteins • Lipid anchored membrane proteins Membrane protein asymmetry Lipid protein interactions: hydrophobic matching, lipid sorting and lipid selectivity ...
Chapter 1: Concepts and Methods in Biology - Rose
... i. Extracellular: [K+]e = 5 mM, [Na+]e = 150 mM; [Cl-]e = 120 mM ii. Intracellular: [K+]i = 150 mM, [Na+]i = 15 mM, [Cl-]i = 10 mM, [A-]i = 100 mM b. Relative permeability of plasma membrane to these ions and charged molecules c. Electrochemical forces drives ions through channels 3. Equilibrium pot ...
... i. Extracellular: [K+]e = 5 mM, [Na+]e = 150 mM; [Cl-]e = 120 mM ii. Intracellular: [K+]i = 150 mM, [Na+]i = 15 mM, [Cl-]i = 10 mM, [A-]i = 100 mM b. Relative permeability of plasma membrane to these ions and charged molecules c. Electrochemical forces drives ions through channels 3. Equilibrium pot ...
Passive and Active Transport
... • No energy is needed because the particles are already in motion. ...
... • No energy is needed because the particles are already in motion. ...
Gold Eyelid Weight Implants
... Bullous Keratopathy • Edema of the corneal endothelium • Very common and usually affects individuals over 50 years of age. ...
... Bullous Keratopathy • Edema of the corneal endothelium • Very common and usually affects individuals over 50 years of age. ...
File
... Negatives w/negatives, positives w/positives. “Happy homeostasis” prefers to be this way. ...
... Negatives w/negatives, positives w/positives. “Happy homeostasis” prefers to be this way. ...
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
plasma-membrane
... – Gradient – physical difference in properties such as temperature, pressure, or concentration ...
... – Gradient – physical difference in properties such as temperature, pressure, or concentration ...
Cell Membrane PPT
... Membrane Proteins – PROTEIN MOLECULES are EMBEDDED in the Lipid Bilayer – HELP to MOVE Material INTO and OUT of the Cell ...
... Membrane Proteins – PROTEIN MOLECULES are EMBEDDED in the Lipid Bilayer – HELP to MOVE Material INTO and OUT of the Cell ...
Dialysis lab - GarrettGeis
... 9. Record your observations of the solution in the bag, the solution in the beaker, and the measure you are using to evaluate movement of water in the “Initial State” row in the table below. In the tube ...
... 9. Record your observations of the solution in the bag, the solution in the beaker, and the measure you are using to evaluate movement of water in the “Initial State” row in the table below. In the tube ...
Chapter 2 – Interaction of Cell Structures ()
... Equal amounts of solute inside and outside Water concentration outside the cell is Less than the water concentration inside the cell More solute inside the cell ...
... Equal amounts of solute inside and outside Water concentration outside the cell is Less than the water concentration inside the cell More solute inside the cell ...
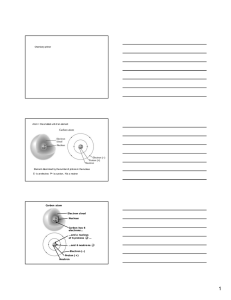
Membrane potential

Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. With respect to the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential range from –40 mV to –80 mV.All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Ion transporter/pump proteins actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradients across the membrane, and ion channels allow ions to move across the membrane down those concentration gradients. Ion pumps and ion channels are electrically equivalent to a set of batteries and resistors inserted in the membrane, and therefore create a voltage difference between the two sides of the membrane.Virtually all eukaryotic cells (including cells from animals, plants, and fungi) maintain a non-zero transmembrane potential, usually with a negative voltage in the cell interior as compared to the cell exterior ranging from –40 mV to –80 mV. The membrane potential has two basic functions. First, it allows a cell to function as a battery, providing power to operate a variety of ""molecular devices"" embedded in the membrane. Second, in electrically excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells, it is used for transmitting signals between different parts of a cell. Signals are generated by opening or closing of ion channels at one point in the membrane, producing a local change in the membrane potential. This change in the electric field can be quickly affected by either adjacent or more distant ion channels in the membrane. Those ion channels can then open or close as a result of the potential change, reproducing the signal.In non-excitable cells, and in excitable cells in their baseline states, the membrane potential is held at a relatively stable value, called the resting potential. For neurons, typical values of the resting potential range from –70 to –80 millivolts; that is, the interior of a cell has a negative baseline voltage of a bit less than one-tenth of a volt. The opening and closing of ion channels can induce a departure from the resting potential. This is called a depolarization if the interior voltage becomes less negative (say from –70 mV to –60 mV), or a hyperpolarization if the interior voltage becomes more negative (say from –70 mV to –80 mV). In excitable cells, a sufficiently large depolarization can evoke an action potential, in which the membrane potential changes rapidly and significantly for a short time (on the order of 1 to 100 milliseconds), often reversing its polarity. Action potentials are generated by the activation of certain voltage-gated ion channels.In neurons, the factors that influence the membrane potential are diverse. They include numerous types of ion channels, some of which are chemically gated and some of which are voltage-gated. Because voltage-gated ion channels are controlled by the membrane potential, while the membrane potential itself is influenced by these same ion channels, feedback loops that allow for complex temporal dynamics arise, including oscillations and regenerative events such as action potentials.