File
... – few animals can survive extreme temperature conditions Homeotherms can colonise a wider range of habitats than poikilotherms (for which habitat is determined by external temperatures) Body size (specifically SA:Vol ratio) will determine an animal's ability to ...
... – few animals can survive extreme temperature conditions Homeotherms can colonise a wider range of habitats than poikilotherms (for which habitat is determined by external temperatures) Body size (specifically SA:Vol ratio) will determine an animal's ability to ...
species population community Habitat Niche
... • These interactions can be competitive (e.g. frogs and small fish compete for aquatic larva), herbivory (e.g. rabbits eat the grasses of the dunes), predation (e.g. blue herons eat the green frogs), parasitism (e.g. leeches suck the blood of a fish) or mutualism (e.g. lichens are a cooperative rela ...
... • These interactions can be competitive (e.g. frogs and small fish compete for aquatic larva), herbivory (e.g. rabbits eat the grasses of the dunes), predation (e.g. blue herons eat the green frogs), parasitism (e.g. leeches suck the blood of a fish) or mutualism (e.g. lichens are a cooperative rela ...
Ecology Vocabulary Flash Cards
... 26. Pioneer Species: the first organisms to live in a new habitat; usually small, fast growing plants 27. Climax community: An stable community achieved after succession. 28. Succession: The gradual change of an ecosystem to a more stable one (an established forest). 29. Primary Succession: The grad ...
... 26. Pioneer Species: the first organisms to live in a new habitat; usually small, fast growing plants 27. Climax community: An stable community achieved after succession. 28. Succession: The gradual change of an ecosystem to a more stable one (an established forest). 29. Primary Succession: The grad ...
Limiting factors study guide:
... When a bird eats a worm, the bird is the predator After one species disappears, the other species in the ecosystem are thrown out of balance Limiting factors determine an area’s carrying capacity because animals need resources to survive Competition is when two members of the same species fight over ...
... When a bird eats a worm, the bird is the predator After one species disappears, the other species in the ecosystem are thrown out of balance Limiting factors determine an area’s carrying capacity because animals need resources to survive Competition is when two members of the same species fight over ...
Ecology
... replacement of species after a major disruption in a community where there has been life before. ...
... replacement of species after a major disruption in a community where there has been life before. ...
PowerPoint_Ecosystem Organization and Limiting Factors
... Population-a group of one species of organisms living in the same place and breeding. Example: Group of Bears or a School of Fish. ...
... Population-a group of one species of organisms living in the same place and breeding. Example: Group of Bears or a School of Fish. ...
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities 4
... warm air rises and cold air sinks as this movement occurs it causes wind ...
... warm air rises and cold air sinks as this movement occurs it causes wind ...
The Organization of Life
... extreme environments, also known as extremophiles • An extremophile (from Latin extremus meaning "extreme" and Greek philiā (φιλία) meaning "love") is an organism that thrives in and may even require physically or geochemically extreme conditions that are detrimental to most life on Earth. ...
... extreme environments, also known as extremophiles • An extremophile (from Latin extremus meaning "extreme" and Greek philiā (φιλία) meaning "love") is an organism that thrives in and may even require physically or geochemically extreme conditions that are detrimental to most life on Earth. ...
Species Relationships PPT
... • When two organisms are in a relationship and one species benefits and the other one is not helped or harmed. • Example: Remora fish swim close by sharks to catch food scraps from the shark. The remora is benefited because it gets food while the shark is unaffected – not helped or harmed. ...
... • When two organisms are in a relationship and one species benefits and the other one is not helped or harmed. • Example: Remora fish swim close by sharks to catch food scraps from the shark. The remora is benefited because it gets food while the shark is unaffected – not helped or harmed. ...
Slide 1
... Monday, May 22, 2017 A-Day Objective: YWBAT identify an invasive species. Drill: What is an invasive species? Give me at lease one example of an invasive species here on Kent Island. ...
... Monday, May 22, 2017 A-Day Objective: YWBAT identify an invasive species. Drill: What is an invasive species? Give me at lease one example of an invasive species here on Kent Island. ...
Microsoft Word - Chapter 06
... Plant species that happen to do well in soils and conditions where they have been introduced, or those that have been freed from their herbivores and parasites, may spread quickly, often with seeds that disperse long distances. Invasive plant species can overrun vast regions, competing with and disp ...
... Plant species that happen to do well in soils and conditions where they have been introduced, or those that have been freed from their herbivores and parasites, may spread quickly, often with seeds that disperse long distances. Invasive plant species can overrun vast regions, competing with and disp ...
Glossary
... The fitness of an organism for its environment including the process by which it becomes fit and is able to survive and to reproduce. autotrophs An organism that can produce their own food usually by photosynthesis. behavior All responses made by an organism to changes in the environment. community ...
... The fitness of an organism for its environment including the process by which it becomes fit and is able to survive and to reproduce. autotrophs An organism that can produce their own food usually by photosynthesis. behavior All responses made by an organism to changes in the environment. community ...
Communities: How Do Species Interact?
... numbers and kinds of organisms in a particular area over time. • Habitation of a completely new environment is called primary succession. • Reestablishment of life after serious damage is called secondary succession. ...
... numbers and kinds of organisms in a particular area over time. • Habitation of a completely new environment is called primary succession. • Reestablishment of life after serious damage is called secondary succession. ...
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities
... Is an ecosystem in which water either covers the soil or is present at or near the surface for at least part of the year. Nutrient rich, highly productive, and serve as breeding grounds for many organisms. Purify water by filtering pollutants and help prevent ...
... Is an ecosystem in which water either covers the soil or is present at or near the surface for at least part of the year. Nutrient rich, highly productive, and serve as breeding grounds for many organisms. Purify water by filtering pollutants and help prevent ...
Sustaining Biodiversity – The Species Approach
... extinctions can be considered: − Endangered: numbers of individuals so low that it may become extinct in part or all of its natural range ...
... extinctions can be considered: − Endangered: numbers of individuals so low that it may become extinct in part or all of its natural range ...
Ecology Part 1
... • A key consideration of ecology is that living organisms affect other living organisms. • All the living organisms that inhabit an environment are called biotic factors. • Examples: plants, animals, fungi, protists, bacteria • All organisms depend on others directly or indirectly for food, shelter, ...
... • A key consideration of ecology is that living organisms affect other living organisms. • All the living organisms that inhabit an environment are called biotic factors. • Examples: plants, animals, fungi, protists, bacteria • All organisms depend on others directly or indirectly for food, shelter, ...
biodiversity - Association of American Geographers
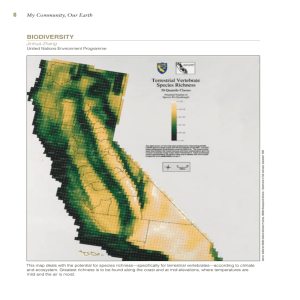
... This map deals with the potential for species richness—specifically for terrestrial vertebrates—according to climate and ecosystem. Greatest richness is to be found along the coast and at mid-elevations, where temperatures are mild and the air is moist. ...
... This map deals with the potential for species richness—specifically for terrestrial vertebrates—according to climate and ecosystem. Greatest richness is to be found along the coast and at mid-elevations, where temperatures are mild and the air is moist. ...
An Organism`s Niche
... An Organism’s Niche • The unique role of a species within an ecosystem is a niche • An ecosystem is all of the organisms living in an area together with their physical environment ...
... An Organism’s Niche • The unique role of a species within an ecosystem is a niche • An ecosystem is all of the organisms living in an area together with their physical environment ...
power point notes
... • Coevolution – long term, interdependent changes take place in two species as a result of their interaction. ...
... • Coevolution – long term, interdependent changes take place in two species as a result of their interaction. ...
1.2 PowerPoint - WordPress.com
... Ecosystems can take up many hectares of land or can be small, such as a tide pool or a rotting log. A habitat is where an organism lives. ...
... Ecosystems can take up many hectares of land or can be small, such as a tide pool or a rotting log. A habitat is where an organism lives. ...
Interactions Among living Things
... • Niche- role of an organism in its habitat or how it makes its living – Type of food – How it gets food – How other organism use it as food – How it reproduces ...
... • Niche- role of an organism in its habitat or how it makes its living – Type of food – How it gets food – How other organism use it as food – How it reproduces ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.