Environmental Science Jeopardy
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
1 - MHSAPEnvironmental
... A) house only 10% of all species of vascular plants. D) contain few endemic species. B) are home to nearly 20% of the world's population. E) All of the above C) are all located in tropical regions. 14. The current conflict between humans and elephants is based on: A) biotic pollution. B) over-huntin ...
... A) house only 10% of all species of vascular plants. D) contain few endemic species. B) are home to nearly 20% of the world's population. E) All of the above C) are all located in tropical regions. 14. The current conflict between humans and elephants is based on: A) biotic pollution. B) over-huntin ...
1 - MHSAPEnvironmental
... E) that too often the protected areas are in highly populated areas. 42. Which of the following represents an unsuccessful captive-breeding and reintroduction program? A) Guam rails B) black-footed ferrets C) thick-billed parrots D) Golden toads E) whooping cranes 44. One of the controversies associ ...
... E) that too often the protected areas are in highly populated areas. 42. Which of the following represents an unsuccessful captive-breeding and reintroduction program? A) Guam rails B) black-footed ferrets C) thick-billed parrots D) Golden toads E) whooping cranes 44. One of the controversies associ ...
Slide 1
... • The evolution of an ecosystem • Primary- no soil there before (bare rock) • Secondary- soil present, ecosystem disturbed • Pioneer species- first to colonize area • Climax community- end result, mature ecosystem • Takes a long time- 100-2000 years ...
... • The evolution of an ecosystem • Primary- no soil there before (bare rock) • Secondary- soil present, ecosystem disturbed • Pioneer species- first to colonize area • Climax community- end result, mature ecosystem • Takes a long time- 100-2000 years ...
edge effects - AaronFreeman
... Species that play roles affecting many other organisms in an ecosystem Strong interaction with other species affect health and survival of species species whose removal would effect many others as they ...
... Species that play roles affecting many other organisms in an ecosystem Strong interaction with other species affect health and survival of species species whose removal would effect many others as they ...
Food, song and speciation
... varies according to the fishes’ preferred habitat in, say, its depth on a coral reef, and certain species evolve colours and patterns to exploit the prevailing light conditions14. But the Galápagos finches are unusual in that the ecological adaptation itself is constrained to cause a change in a sig ...
... varies according to the fishes’ preferred habitat in, say, its depth on a coral reef, and certain species evolve colours and patterns to exploit the prevailing light conditions14. But the Galápagos finches are unusual in that the ecological adaptation itself is constrained to cause a change in a sig ...
Camera Trap Animal Diversity and Census Lab
... to another for small, often vulnerable animals. Therefore if they were removed, only those animals which could survive in the open and escape predation easily would remain (McCain and Childs 5). Using camera traps is a great way of documenting wildlife without disturbing it. Although with them we kn ...
... to another for small, often vulnerable animals. Therefore if they were removed, only those animals which could survive in the open and escape predation easily would remain (McCain and Childs 5). Using camera traps is a great way of documenting wildlife without disturbing it. Although with them we kn ...
Succession
... formed (moving/melting glaciers, area covered by lava, rocky outcropping, sand dunes, etc.) ...
... formed (moving/melting glaciers, area covered by lava, rocky outcropping, sand dunes, etc.) ...
Exam 6 Review - Iowa State University
... 4.) What is constructed by following the fate of a cohort, from birth until all are dead? A) climograph B) life table C) rate table D) mortality table 5.) Which of the following are important biotic factors that affect the structure and organization of biotic communities? A) precipitation, wind B) n ...
... 4.) What is constructed by following the fate of a cohort, from birth until all are dead? A) climograph B) life table C) rate table D) mortality table 5.) Which of the following are important biotic factors that affect the structure and organization of biotic communities? A) precipitation, wind B) n ...
SC20F Ecology Unit Review Name: 1. Define the following terms
... 5. Explain the following ecological pyramids: a. Pyramid of energy Shows the amount of energy transferred from Level to level. Lots of energy at the bottom, less at the top (only 10% is transferred) b. Pyramid of biomass Shows the relative abundance of each trophic level. Very large amount of bioma ...
... 5. Explain the following ecological pyramids: a. Pyramid of energy Shows the amount of energy transferred from Level to level. Lots of energy at the bottom, less at the top (only 10% is transferred) b. Pyramid of biomass Shows the relative abundance of each trophic level. Very large amount of bioma ...
NJBCT Third Quarter Review
... An ecologist performed a study to determine how the rate of photosynthetic activity in a lake changed from month to month. The results of the study are shown in the graph above. What conclusion is best supported by the evidence? A. Photosynthetic organisms were dormant during the months of April thr ...
... An ecologist performed a study to determine how the rate of photosynthetic activity in a lake changed from month to month. The results of the study are shown in the graph above. What conclusion is best supported by the evidence? A. Photosynthetic organisms were dormant during the months of April thr ...
Food Web Game
... Have students tell you if certain populations will grow or decline. The teacher can represent nature and cause any type of problem to occur; for example, a wildfire could occur, but some birds were able to fly ...
... Have students tell you if certain populations will grow or decline. The teacher can represent nature and cause any type of problem to occur; for example, a wildfire could occur, but some birds were able to fly ...
Buzzle – Zoology Terms – Glossary of Biology Terms and Definitions
... plumage (in most cases) arethe feathers that grow after the first complete molt, and is present at the time of the bird's non-breeding season. Batesian Mimicry: In a situation where a harmless species has evolved to replicate the warning signal given by a harmful species (directed at a common preda ...
... plumage (in most cases) arethe feathers that grow after the first complete molt, and is present at the time of the bird's non-breeding season. Batesian Mimicry: In a situation where a harmless species has evolved to replicate the warning signal given by a harmful species (directed at a common preda ...
NJ BCT Review - Part 3 - Nutley Public Schools
... An ecologist performed a study to determine how the rate of photosynthetic activity in a lake changed from month to month. The results of the study are shown in the graph above. What conclusion is best supported by the evidence? A. Photosynthetic organisms were dormant during the months of April thr ...
... An ecologist performed a study to determine how the rate of photosynthetic activity in a lake changed from month to month. The results of the study are shown in the graph above. What conclusion is best supported by the evidence? A. Photosynthetic organisms were dormant during the months of April thr ...
Ecological Succession
... http://alaska.usgs.gov/science/kasatochi/field_work/field_work.php http://geology.com/usgs/kasatochi-volcano/ ...
... http://alaska.usgs.gov/science/kasatochi/field_work/field_work.php http://geology.com/usgs/kasatochi-volcano/ ...
Ecology Notes 2 - Succession and Populations NEW
... grown exponentially and is expected to continue to do so. • Population growth will naturally slow down as it nears its carrying capacity due to an increase in the death rate and a decrease in the birth rate as a result of: – Food and water shortages – Pollution of the environment – Spread of disease ...
... grown exponentially and is expected to continue to do so. • Population growth will naturally slow down as it nears its carrying capacity due to an increase in the death rate and a decrease in the birth rate as a result of: – Food and water shortages – Pollution of the environment – Spread of disease ...
Biol
... biome, tropical rain forest biome, basic characteristics of biomes; such as temperature, examples of vegetation found there, examples of animals and adaptations also permafrost, arboreal, 2 parts of our desert, causes of deserts, desertification, 4 layers of trees in tropical rain forest, tropical d ...
... biome, tropical rain forest biome, basic characteristics of biomes; such as temperature, examples of vegetation found there, examples of animals and adaptations also permafrost, arboreal, 2 parts of our desert, causes of deserts, desertification, 4 layers of trees in tropical rain forest, tropical d ...
CHANGES OVER TIME
... traveled and tried to make connections about the relationships among those organisms. – Diversity of living things – Remains of ancient organisms – Unique characteristics of organisms on the Galapagos. ...
... traveled and tried to make connections about the relationships among those organisms. – Diversity of living things – Remains of ancient organisms – Unique characteristics of organisms on the Galapagos. ...
Chapter 14
... 1. slow physical changes over time (ex. Trees growing large) 2. sudden natural or human disturbance (ex. Clearing a forest for land development) 3. natural disaster (ex. Hurricane, tornado, eruption) o Primary Succession is when succession occurs on land surfaces where no soil exists, for example, r ...
... 1. slow physical changes over time (ex. Trees growing large) 2. sudden natural or human disturbance (ex. Clearing a forest for land development) 3. natural disaster (ex. Hurricane, tornado, eruption) o Primary Succession is when succession occurs on land surfaces where no soil exists, for example, r ...
emodule 4b - Notes Milenge
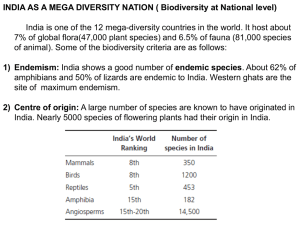
... 3) Invasive species: Invasion is considered as the second most important threat to biodiversity after habitat destruction. Alien species, which locally become dominant and invade natural communities, are referred to as invasive species. Further, IUCN also defines alien invasive species, as a specie ...
... 3) Invasive species: Invasion is considered as the second most important threat to biodiversity after habitat destruction. Alien species, which locally become dominant and invade natural communities, are referred to as invasive species. Further, IUCN also defines alien invasive species, as a specie ...
Understanding populations
... competition, because both have reduced access to a limiting resource, even if one individual ultimately gets the resource. • 2nd key point: Competition can be both intraspecific and interspecific ...
... competition, because both have reduced access to a limiting resource, even if one individual ultimately gets the resource. • 2nd key point: Competition can be both intraspecific and interspecific ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.