Biogeography VI
... •c is higher in biodiverse areas •z is higher where species richness rises quickly with area ...
... •c is higher in biodiverse areas •z is higher where species richness rises quickly with area ...
Biodiversity Conservation in NB, Presentation for "Seeing the Forest
... • PROV./FED. MINISTERS AGREEMENT TO COMPLETE PROTECTED AREA NETWORK (12%) NEW ENDANGERED SP. LEGISLATION (2012) • BIODIVERSITY POLICY (2009) ...
... • PROV./FED. MINISTERS AGREEMENT TO COMPLETE PROTECTED AREA NETWORK (12%) NEW ENDANGERED SP. LEGISLATION (2012) • BIODIVERSITY POLICY (2009) ...
key - Scioly.org
... e. home base. 70. Resource partitioning would be most likely to occur between a. sympatric populations of a predator and its prey. b. sympatric populations of species with similar ecological niches. c. sympatric populations of a flowering plant and its specialized insect pollinator. d. allopatric po ...
... e. home base. 70. Resource partitioning would be most likely to occur between a. sympatric populations of a predator and its prey. b. sympatric populations of species with similar ecological niches. c. sympatric populations of a flowering plant and its specialized insect pollinator. d. allopatric po ...
Topic 1 - Interactions Within Ecosystems
... Needs are basic to survival, whereas, ‘ wants ’ are things that just make survival more comfortable or enjoyable. Each time a need or a want is satisfied, natural resources or energy are used up. This impacts the environment we live in. Transporting food from all around the world, just so we can hav ...
... Needs are basic to survival, whereas, ‘ wants ’ are things that just make survival more comfortable or enjoyable. Each time a need or a want is satisfied, natural resources or energy are used up. This impacts the environment we live in. Transporting food from all around the world, just so we can hav ...
Biodiversity of World Biomes
... The Biosphere • In 2002 , about 1.7 million species had been discovered and identified by biologists. • The sum of Earth’s ecosystems, the Biosphere encompasses all parts of the planet inhabited by living things. ...
... The Biosphere • In 2002 , about 1.7 million species had been discovered and identified by biologists. • The sum of Earth’s ecosystems, the Biosphere encompasses all parts of the planet inhabited by living things. ...
Biodiversity of World Biomes
... • Immerse students in the study of biodiversity through a blended delivery of disciplinary knowledge (pre-trip Web-based assignments, lectures and discussions in the field, post-trip assignments) and an experiential field study. • Learn the principle ecological and evolutionary mechanisms leading to ...
... • Immerse students in the study of biodiversity through a blended delivery of disciplinary knowledge (pre-trip Web-based assignments, lectures and discussions in the field, post-trip assignments) and an experiential field study. • Learn the principle ecological and evolutionary mechanisms leading to ...
Feeding-of
... often die if natural environmental conditions and appropriate food sources are not present in the right amount and quality to sustain them. Feeding increases animal density for the short and long term. On the long term, increased reproductive success or young survival can lead to overcrowding and in ...
... often die if natural environmental conditions and appropriate food sources are not present in the right amount and quality to sustain them. Feeding increases animal density for the short and long term. On the long term, increased reproductive success or young survival can lead to overcrowding and in ...
Unit 5
... explanations of ecological phenomena. Examining questions from all areas of biology as well as many physical sciences are all part of ecology. Describe the relationship between ecology and evolution. Evolution can be described as a change in a population over time. Ecology has to do with organisms ...
... explanations of ecological phenomena. Examining questions from all areas of biology as well as many physical sciences are all part of ecology. Describe the relationship between ecology and evolution. Evolution can be described as a change in a population over time. Ecology has to do with organisms ...
Document
... 3.1 page 64-68, Biology Biosphere: consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists. This includes water, land and the atmosphere. Ecology: study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment. Biotic Factor: any living part of the e ...
... 3.1 page 64-68, Biology Biosphere: consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists. This includes water, land and the atmosphere. Ecology: study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment. Biotic Factor: any living part of the e ...
Chapter 3.3 PowerPoint Presentation
... • Native species are species that naturally inhabit an area – British Columbia is home to about 3,000 species of native plants, including ferns, wildflowers, shrubs and trees. These native plants have co-evolved with animals, fungi, and microbes to form a complex network of relationships. ...
... • Native species are species that naturally inhabit an area – British Columbia is home to about 3,000 species of native plants, including ferns, wildflowers, shrubs and trees. These native plants have co-evolved with animals, fungi, and microbes to form a complex network of relationships. ...
Changes in Ecosystems
... 1.05 Determine the interaction of organisms within an ecosystem. Ecological Succession • Ecological Succession is the natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural process ...
... 1.05 Determine the interaction of organisms within an ecosystem. Ecological Succession • Ecological Succession is the natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural process ...
ANSWERS Biology Interim Study Guide
... 12. Matter is recycled in the biosphere because organisms do not use it up, but transform and recycle it. However, energy flows in one direction. 13. List the two ways in which water enters the atmosphere. Evaporation and transpiration 14. Water falls back down to earth’s surface as precipitation 15 ...
... 12. Matter is recycled in the biosphere because organisms do not use it up, but transform and recycle it. However, energy flows in one direction. 13. List the two ways in which water enters the atmosphere. Evaporation and transpiration 14. Water falls back down to earth’s surface as precipitation 15 ...
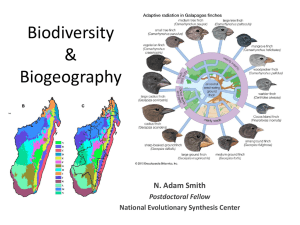
Biodiversity and Biogeography
... What Wallace was trying to say 1. Variation occurs in nature 2. Variation may result in different reproductive success. 3. Species (populations) with higher fitness will persist 4. This leads to divergence from ancestral species. ...
... What Wallace was trying to say 1. Variation occurs in nature 2. Variation may result in different reproductive success. 3. Species (populations) with higher fitness will persist 4. This leads to divergence from ancestral species. ...
Ch05_Interactions_Environments
... We have to remember as env change species change, some species can adapt some not. Evolution - A change in the kinds of organisms that exist and in their characteristics. Study of fossil records show as new species come into being, other species disappear. This is called Speciation - Production ...
... We have to remember as env change species change, some species can adapt some not. Evolution - A change in the kinds of organisms that exist and in their characteristics. Study of fossil records show as new species come into being, other species disappear. This is called Speciation - Production ...
Hermit Anemone video
... Commensalism: Oak Gall Wasps and Oak Trees The oak gall wasp stings the oak tree. The tree then grows a GALL which is a nest for the wasp’s babies. When the larva hatch, they eat their way out of the gall. Does not help or hurt the oak tree ...
... Commensalism: Oak Gall Wasps and Oak Trees The oak gall wasp stings the oak tree. The tree then grows a GALL which is a nest for the wasp’s babies. When the larva hatch, they eat their way out of the gall. Does not help or hurt the oak tree ...
Ecosystems Anne Muns
... • Limiting factors can be biotic (living) or abiotic (non-living) components of an environment. • Examples would be competition for food from other organisms (biotic) or temperature changes (abiotic). • Natural disaster such as drought or hurricane can also be limiting. ...
... • Limiting factors can be biotic (living) or abiotic (non-living) components of an environment. • Examples would be competition for food from other organisms (biotic) or temperature changes (abiotic). • Natural disaster such as drought or hurricane can also be limiting. ...
Service Learning Project: Goodbye Invasives…
... Branch Center of Hashawha to prepare for a picnic area coming soon. • Invasive Plants Removed: Rubus phoenicolasius, Lonicera maackii, Rosa multiflora • Dedicate 30 hours to removing invasive species ...
... Branch Center of Hashawha to prepare for a picnic area coming soon. • Invasive Plants Removed: Rubus phoenicolasius, Lonicera maackii, Rosa multiflora • Dedicate 30 hours to removing invasive species ...
Organisms
... Explain in the notes section of your interactive notebook, copy the questions on the left and answer the following questions on the right hand side: 1) What happened to the animals at each level of the food web 2) Summarize your understanding of ...
... Explain in the notes section of your interactive notebook, copy the questions on the left and answer the following questions on the right hand side: 1) What happened to the animals at each level of the food web 2) Summarize your understanding of ...
Wk 8
... Phytoplankton require light, CO2 (inorganic carbon) and nutrients (P, N, etc.) to grow through photosynthesis; most aquatic environments are nutrient limited. ...
... Phytoplankton require light, CO2 (inorganic carbon) and nutrients (P, N, etc.) to grow through photosynthesis; most aquatic environments are nutrient limited. ...
The fossil record, biostratigraphy and diversity of life
... becoming buried in sediments is small 2. Lack of hard parts - For soft parts of organisms to be preserved, it is necessary to isolate them from oxygen almost immediately after death. This most likely occurs when organisms are rapidly buried in fine-grained sediment in anoxic water; this only happens ...
... becoming buried in sediments is small 2. Lack of hard parts - For soft parts of organisms to be preserved, it is necessary to isolate them from oxygen almost immediately after death. This most likely occurs when organisms are rapidly buried in fine-grained sediment in anoxic water; this only happens ...
natural selection
... animals, and microorganisms that occur over wide geographic areas and have distinctive physical characteristics 5. BIOSPHERE all the world’s biomes, along with its ...
... animals, and microorganisms that occur over wide geographic areas and have distinctive physical characteristics 5. BIOSPHERE all the world’s biomes, along with its ...
Commensalism
... Moss growing on trees benefits by being raised above forest floor competition, while the tree doesn't get much out of the deal either way. A desert holly shrub provides shade for young creosote bush. A cactus wren builds its nest in a cholla cactus to protect its young from predators such as raven. ...
... Moss growing on trees benefits by being raised above forest floor competition, while the tree doesn't get much out of the deal either way. A desert holly shrub provides shade for young creosote bush. A cactus wren builds its nest in a cholla cactus to protect its young from predators such as raven. ...
Environmental-Science-Jeopardy
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.