Unit XIV: Regulation
... - Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems - Ganglia - Highly developed sense organs Antenna, eye, hairs, taste buds ...
... - Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems - Ganglia - Highly developed sense organs Antenna, eye, hairs, taste buds ...
Nervous System
... cause depolarization and promote action potential generation, whereas inhibitory neurotransmitters cause hyperpolarization and depress action potential generation. generation •The effect of a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic membrane depends on the properties of the receptor, not on the nature o ...
... cause depolarization and promote action potential generation, whereas inhibitory neurotransmitters cause hyperpolarization and depress action potential generation. generation •The effect of a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic membrane depends on the properties of the receptor, not on the nature o ...
peripheral nervous system
... -Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) degrades ACh -Causes muscle relaxation ...
... -Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) degrades ACh -Causes muscle relaxation ...
sleep
... • In the course of his social development and labor activity second signal system, which based on using verbal signals, develop. • This system includes perception of words, reading and speech. • The development of the second signaling system was incredibly broadened and changed quality of higher ner ...
... • In the course of his social development and labor activity second signal system, which based on using verbal signals, develop. • This system includes perception of words, reading and speech. • The development of the second signaling system was incredibly broadened and changed quality of higher ner ...
NAS 150 The Skeletal System Brilakis Fall, 2003
... Occipital lobe: located at the back of the brain and is associated with interpreting visual stimuli and information. The primary visual cortex, which receives and interprets information from the retinas of the eyes, is located in the occipital lobe. Damage to this lobe can cause visual problems such ...
... Occipital lobe: located at the back of the brain and is associated with interpreting visual stimuli and information. The primary visual cortex, which receives and interprets information from the retinas of the eyes, is located in the occipital lobe. Damage to this lobe can cause visual problems such ...
The Nervous System: Overview The nervous system Divisions of the
... Extension of cytoplasm, originating from the cell body; Project nerve impulses away from the cell body, towards other nerve cells ...
... Extension of cytoplasm, originating from the cell body; Project nerve impulses away from the cell body, towards other nerve cells ...
Nervous System
... Motor neurons pass their impulses to muscle cells. The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is a called a synapse. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse ...
... Motor neurons pass their impulses to muscle cells. The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is a called a synapse. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse ...
chapter 4
... 4.2 Psychophysics is the study of the relationship between physical stimuli and the psychological experience of them. Three basic principles apply across all the senses: There is no one-to-one correspondence between physical and psychological reality; sensation and perception are active, not passive ...
... 4.2 Psychophysics is the study of the relationship between physical stimuli and the psychological experience of them. Three basic principles apply across all the senses: There is no one-to-one correspondence between physical and psychological reality; sensation and perception are active, not passive ...
brain09.3
... such data and using them to answer the question of how neural coding actually takes place. The analytical method developed by the Hebrew University researchers should be able to provide an indication, for example, of how many neurons encode a given stimulus such as reactions to a face or a movement ...
... such data and using them to answer the question of how neural coding actually takes place. The analytical method developed by the Hebrew University researchers should be able to provide an indication, for example, of how many neurons encode a given stimulus such as reactions to a face or a movement ...
Function
... burning or aching sensation often accompanied by mood swings. • Damage to the thalamus can result in coma. • Fatal Familial Insomnia is a hereditary prion disease in which degeneration of the thalamus occurs, causing the patient to gradually lose his ability to sleep and progressing to a state of to ...
... burning or aching sensation often accompanied by mood swings. • Damage to the thalamus can result in coma. • Fatal Familial Insomnia is a hereditary prion disease in which degeneration of the thalamus occurs, causing the patient to gradually lose his ability to sleep and progressing to a state of to ...
1. What are some major differences between
... 7. How do emotions influence perception? Attention? Give some everyday examples of emotional influences on perceptual and cognitive functions. Direct and indirect pathways from the amgydala to sensory cortices provide information about the emotional salience or importance of perceived stimuli (see p ...
... 7. How do emotions influence perception? Attention? Give some everyday examples of emotional influences on perceptual and cognitive functions. Direct and indirect pathways from the amgydala to sensory cortices provide information about the emotional salience or importance of perceived stimuli (see p ...
Abstract Browser - Journal of Neuroscience
... Our understanding of mammalian olfactory coding has been impeded by the paucity of information about the odorant receptors (ORs) that respond to a given odorant ligand in awake, freely behaving animals. Identifying the ORs that respond in vivo to a given odorant ligand from among the ⬃1100 ORs in mi ...
... Our understanding of mammalian olfactory coding has been impeded by the paucity of information about the odorant receptors (ORs) that respond to a given odorant ligand in awake, freely behaving animals. Identifying the ORs that respond in vivo to a given odorant ligand from among the ⬃1100 ORs in mi ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology, Nervous System and Special
... Current passes ______________ of the neurons, membrane depolarizes only at the _____________ Less ion movement in and out makes it faster, myelin also increases the fiber _________, thereby reducing resistance 14. Order the six events accounting for transmission across a chemical synapse. __________ ...
... Current passes ______________ of the neurons, membrane depolarizes only at the _____________ Less ion movement in and out makes it faster, myelin also increases the fiber _________, thereby reducing resistance 14. Order the six events accounting for transmission across a chemical synapse. __________ ...
Tieӧs Pharmaceuticals uses Cyclica`s platform to discover novel
... novel small molecule inhibitors that can be used to target metabolic behaviors unique to cancer cells. By achieving this, Tieös will help fill a growing void by providing patients with treatment options that will actively improve function, tolerability, and ultimately lead to tangible mortality bene ...
... novel small molecule inhibitors that can be used to target metabolic behaviors unique to cancer cells. By achieving this, Tieös will help fill a growing void by providing patients with treatment options that will actively improve function, tolerability, and ultimately lead to tangible mortality bene ...
Unit 13 Autonomic Nervous System
... • Angina • Cardiac arrhythmias – More side effects – Propranolol (Inderal) ...
... • Angina • Cardiac arrhythmias – More side effects – Propranolol (Inderal) ...
Rabbit anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Rabbit anti-Sigma
... The sigma (σ) receptor (sigma-1R, Oprs1 protein, opioid receptor sigma 1) and its agonists are implicated in a variety of cellular functions, biological processes and diseases, including cancer biology, psychosis, regulation of neurotransmitter function, motor, endocrine and immune systems.1 Two sig ...
... The sigma (σ) receptor (sigma-1R, Oprs1 protein, opioid receptor sigma 1) and its agonists are implicated in a variety of cellular functions, biological processes and diseases, including cancer biology, psychosis, regulation of neurotransmitter function, motor, endocrine and immune systems.1 Two sig ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... two sensory systems. For instance, when he smells a rose, he recognizes the odor but he cannot visualize the flower without actually looking at it. The part of Matthew's brain that was damaged is probably the A. amygdala. B. hippocampus. C. reticular formation. D. hypothalamus. Which of the followin ...
... two sensory systems. For instance, when he smells a rose, he recognizes the odor but he cannot visualize the flower without actually looking at it. The part of Matthew's brain that was damaged is probably the A. amygdala. B. hippocampus. C. reticular formation. D. hypothalamus. Which of the followin ...
Medicinal chemistry 1 (7303301) - E-Learning/An
... Course Description: The aim of this course is to introduce the basic concepts of medicinal chemistry. Study the physicochemical properties of the drugs and study their distribution, metabolism and excretion. The course will discuss specific drug classes by covering its chemistry, some synthesis, mec ...
... Course Description: The aim of this course is to introduce the basic concepts of medicinal chemistry. Study the physicochemical properties of the drugs and study their distribution, metabolism and excretion. The course will discuss specific drug classes by covering its chemistry, some synthesis, mec ...
Biology 13A
... 7. Typical sympathetic postganglionic fibers that release norepinephrine at neuroeffector junctions are classified as a. cholinergic b. adrenergic c. norephinephric d. nonsecretory e. none of the above 8. The sympathetic division of the ANS includes which of the following? a. three segmentally arran ...
... 7. Typical sympathetic postganglionic fibers that release norepinephrine at neuroeffector junctions are classified as a. cholinergic b. adrenergic c. norephinephric d. nonsecretory e. none of the above 8. The sympathetic division of the ANS includes which of the following? a. three segmentally arran ...
The Nervous System
... Key Concepts and Important Terms • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • ...
... Key Concepts and Important Terms • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • ...
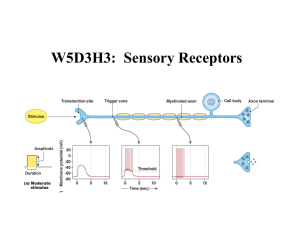
W5D3H3: Sensory Receptors
... In the somatosensory system, various different sensory receptors capture different stimuli and convey them to the sensory cortex. Each type of receptor is specialised, that is, receives the stimulus to which it is predetermined to receive. Immediately as it is stimulated, the receptor sends a signal ...
... In the somatosensory system, various different sensory receptors capture different stimuli and convey them to the sensory cortex. Each type of receptor is specialised, that is, receives the stimulus to which it is predetermined to receive. Immediately as it is stimulated, the receptor sends a signal ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.