Specific and Nonspecific Plasticity of the Primary
... and did not appropriately represent the sharpness of the curve. • For each frequency-threshold curve, they defined the broadly tuned neuron when its Q-30 dB was﹤6.0 and the sharply tuned neuron whenitsQ-30 dB was larger than 9.0.Neurons with aQ-30 dB between 6.0 and9.0 were classified as intermediat ...
... and did not appropriately represent the sharpness of the curve. • For each frequency-threshold curve, they defined the broadly tuned neuron when its Q-30 dB was﹤6.0 and the sharply tuned neuron whenitsQ-30 dB was larger than 9.0.Neurons with aQ-30 dB between 6.0 and9.0 were classified as intermediat ...
Factors that affect Drug Metabolism
... polar metabolites of the original chemicals. In the case of pharmaceutical drugs, Phase I reactions can lead either to activation or inactivation of the drug. Phase I reactions (also termed nonsynthetic reactions) may occur by oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, cyclization, and decyclization reaction ...
... polar metabolites of the original chemicals. In the case of pharmaceutical drugs, Phase I reactions can lead either to activation or inactivation of the drug. Phase I reactions (also termed nonsynthetic reactions) may occur by oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, cyclization, and decyclization reaction ...
Document
... disease, type II diabetes, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (human form of Mad Cow’s disease), and many more …. • In some cases it is not clear if the fibrils are the result of the disease or the cause. • Fibrils can form dense plaques which physically disrupt tissue • The formation of fibrils depletes the ...
... disease, type II diabetes, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (human form of Mad Cow’s disease), and many more …. • In some cases it is not clear if the fibrils are the result of the disease or the cause. • Fibrils can form dense plaques which physically disrupt tissue • The formation of fibrils depletes the ...
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
... monitoring for errors. Injury in this area also produce susceptibility to mental overload. ...
... monitoring for errors. Injury in this area also produce susceptibility to mental overload. ...
Why We Sleep: The Temporal Organization of
... patients appear sleepy but are unable to fall asleep. Yet large lesions of the thalamus seem to have little effect on the EEG or sleep in animals [59,60], suggesting that other, nonthalamic, lesions may also be involved in stroke or fatal familial insomnia patients. The importance of the hypothalamu ...
... patients appear sleepy but are unable to fall asleep. Yet large lesions of the thalamus seem to have little effect on the EEG or sleep in animals [59,60], suggesting that other, nonthalamic, lesions may also be involved in stroke or fatal familial insomnia patients. The importance of the hypothalamu ...
Sources
... induced coma and loss of protective reflexes resulting from the administration of one or more general anesthetic agents. A variety of medications may be administered, with the overall aim of ensuring unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, relaxation of skeletal muscles, and loss of control of reflexes ...
... induced coma and loss of protective reflexes resulting from the administration of one or more general anesthetic agents. A variety of medications may be administered, with the overall aim of ensuring unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, relaxation of skeletal muscles, and loss of control of reflexes ...
30. Autonomic NS. Sympathetic nervous system
... • Cell bodies of neurons #1 lie in the lateral gray horns of the spinal cord • The axons of neurons #1 leave the spinal cord via the ventral root • These axons pass to the spinal nerve • Axons leave the spinal nerve via the white branches (rami communicantes) • Connect with the sympathetic chain gan ...
... • Cell bodies of neurons #1 lie in the lateral gray horns of the spinal cord • The axons of neurons #1 leave the spinal cord via the ventral root • These axons pass to the spinal nerve • Axons leave the spinal nerve via the white branches (rami communicantes) • Connect with the sympathetic chain gan ...
Psychopharmacology - University of South Alabama
... • A class of amines that includes indolamines such as serotonin and catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. ...
... • A class of amines that includes indolamines such as serotonin and catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. ...
Can we conquer pain?
... does not interfere with normal activities but low enough that it can be evoked before frank tissue damage occurs. This threshold is not fixed and can be shifted either up or down, which may be either adaptive or maladaptive. Shifts in pain threshold and responsiveness are an expression of neural pla ...
... does not interfere with normal activities but low enough that it can be evoked before frank tissue damage occurs. This threshold is not fixed and can be shifted either up or down, which may be either adaptive or maladaptive. Shifts in pain threshold and responsiveness are an expression of neural pla ...
Serum Total Protein
... Introduction • The key roles which plasma proteins play in bodily function, together with the relative ease of assaying them, makes their determination a valuable diagnostic tool as well as a way to monitor clinical progress. • In very general terms, variations in plasma protein concentrations can ...
... Introduction • The key roles which plasma proteins play in bodily function, together with the relative ease of assaying them, makes their determination a valuable diagnostic tool as well as a way to monitor clinical progress. • In very general terms, variations in plasma protein concentrations can ...
Nervous Systems
... • Action potentials do not travel between different neurons • Yet, it is still necessary to send the “signal” from one neuron to the next • To do this, there has to be a way to send a signal across the space that exists between one neuron and another (synaptic cleft or gap ...
... • Action potentials do not travel between different neurons • Yet, it is still necessary to send the “signal” from one neuron to the next • To do this, there has to be a way to send a signal across the space that exists between one neuron and another (synaptic cleft or gap ...
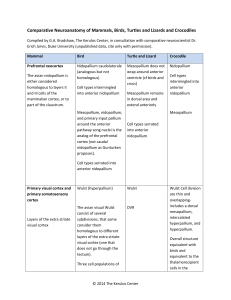
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards and Crocodiles Compiled by G.A. Bradshaw, The Kerulos Center, in consultation with comparative neuroscientist Dr. Erich Jarvis, Duke University (unpublished data, cite only with permission). ...
... Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards and Crocodiles Compiled by G.A. Bradshaw, The Kerulos Center, in consultation with comparative neuroscientist Dr. Erich Jarvis, Duke University (unpublished data, cite only with permission). ...
2/pg
... Organization of nervous systems • Evolution of nervous systems – electrical signaling important for single cells – nerve nets – bilateral symmetry • central nervous system evolved – central vs. peripheral • neurons became more specialized • cephalization – head nervous system bigger, more complex, m ...
... Organization of nervous systems • Evolution of nervous systems – electrical signaling important for single cells – nerve nets – bilateral symmetry • central nervous system evolved – central vs. peripheral • neurons became more specialized • cephalization – head nervous system bigger, more complex, m ...
A unifying view of the basis of social cognition
... • No, they postulated that side by side with the sensory descriptions of the observed social stimuli, internal representations of the state associated with these actions or emotions are evoked in the observer ‘as if” they were performing a similar action or experiencing a similar emotion. ...
... • No, they postulated that side by side with the sensory descriptions of the observed social stimuli, internal representations of the state associated with these actions or emotions are evoked in the observer ‘as if” they were performing a similar action or experiencing a similar emotion. ...
NIPS/Dec99/notebook3
... involving the forelimbs, with no or minimal deficiencies in grasping with the hindlimbs (14). Obviously, the hindlimbs are used more for postural support than for tactile exploration. Noncorticospinal corticonuclear neurons have slow-conducting axons, in comparison with those of the corticospinal ne ...
... involving the forelimbs, with no or minimal deficiencies in grasping with the hindlimbs (14). Obviously, the hindlimbs are used more for postural support than for tactile exploration. Noncorticospinal corticonuclear neurons have slow-conducting axons, in comparison with those of the corticospinal ne ...
3 - smw15.org
... Is comprised of several structures that lie on the dorsal surface of the forebrain Nucleus Basalis Receives input from the hypothalamus and basal ganglia Sends axons that release acetylcholine to the cerebral cortex Key part of the brains system for arousal, wakefulness, and attention ...
... Is comprised of several structures that lie on the dorsal surface of the forebrain Nucleus Basalis Receives input from the hypothalamus and basal ganglia Sends axons that release acetylcholine to the cerebral cortex Key part of the brains system for arousal, wakefulness, and attention ...
PDF
... were mixed to produce the GFP-loxP-nls sequence, a second loxP site added at the 3⬘ by PCR, and the resulting GFP-loxP-nls-loxP cassette cloned in the p6NST90 plasmid. Primers (supplementary material Table S1) were designed to express the GFP in frame with the nls, and stop codons were added to term ...
... were mixed to produce the GFP-loxP-nls sequence, a second loxP site added at the 3⬘ by PCR, and the resulting GFP-loxP-nls-loxP cassette cloned in the p6NST90 plasmid. Primers (supplementary material Table S1) were designed to express the GFP in frame with the nls, and stop codons were added to term ...
Deep sequencing of transcriptomes from the nervous systems of two
... From these transcripts, genes associated with neural function were identified and manually curated to produce a characterization of multiple gene families important for nervous system function. This included genes for 34 distinct ion channel types, 17 biogenic amine and 5 GABA receptors, 28 major tr ...
... From these transcripts, genes associated with neural function were identified and manually curated to produce a characterization of multiple gene families important for nervous system function. This included genes for 34 distinct ion channel types, 17 biogenic amine and 5 GABA receptors, 28 major tr ...
Anatomy, pigmentation, ventral and dorsal subpopulations of
... Received 16 March 1990 and in revised form 14 August ...
... Received 16 March 1990 and in revised form 14 August ...
Behavioral Challenges in the Classroom
... How could gross and fine motor delays affect behavior? If you can not kick the ball, you do not play If you cannot ride a bike, you are left out If you cannot write your name, you look different If you cannot tie your shoe you look different ...
... How could gross and fine motor delays affect behavior? If you can not kick the ball, you do not play If you cannot ride a bike, you are left out If you cannot write your name, you look different If you cannot tie your shoe you look different ...
23mri2
... in the molecule interact with external magnetic field. They have magnetic moments 1860 times larger than protons and may screen a bit the external field as their orbitals are modified by the external field. ...
... in the molecule interact with external magnetic field. They have magnetic moments 1860 times larger than protons and may screen a bit the external field as their orbitals are modified by the external field. ...
Ch 25 - Molecular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
What is the Nervous System?
... The neuron is covered with the Myelin Sheath or Schwann Cells. These are white segmented covering around axons and dendrites of many peripheral neurons. The covering is continuous along the axons or dendrites except at the point of termination and at the nodes of Ranvier. The neurilemma is the layer ...
... The neuron is covered with the Myelin Sheath or Schwann Cells. These are white segmented covering around axons and dendrites of many peripheral neurons. The covering is continuous along the axons or dendrites except at the point of termination and at the nodes of Ranvier. The neurilemma is the layer ...
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... in the CA1 area7, cholinergically induced oscillations require ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors. In both CA3 and CA1 the oscillatory activity was completely abolished by the non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist 6-nitro-7-sulphamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline-2,3-dione (NBQX, 20 mM; n ¼ 5; Fig. 2c, ...
... in the CA1 area7, cholinergically induced oscillations require ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors. In both CA3 and CA1 the oscillatory activity was completely abolished by the non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist 6-nitro-7-sulphamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline-2,3-dione (NBQX, 20 mM; n ¼ 5; Fig. 2c, ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.