General classification of peripheral nervous system
... at the base of the brain and at the brain stem. They serve specific peripheral structures. The examples of cranial nerves are: Nerves ...
... at the base of the brain and at the brain stem. They serve specific peripheral structures. The examples of cranial nerves are: Nerves ...
Research Article Suspension of Mitotic Activity in Dentate Gyrus of
... G1 and S phases, with G2 being the least sensitive [3]. However, research into the process by which hypothermia affects the cell cycle has been largely neglected. This is despite the fact that work on the response of mammalian cells to lower than optimal temperatures, first published in the mid 20th ...
... G1 and S phases, with G2 being the least sensitive [3]. However, research into the process by which hypothermia affects the cell cycle has been largely neglected. This is despite the fact that work on the response of mammalian cells to lower than optimal temperatures, first published in the mid 20th ...
Slide ()
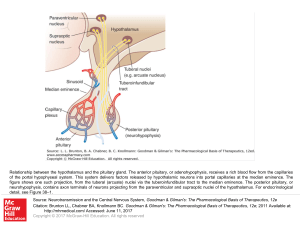
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
Somatotropic axis
... – Incorporation of sulfur into the epiphyseal cartilage • Sulfation factor • Indirect action of GH (delayed response) ...
... – Incorporation of sulfur into the epiphyseal cartilage • Sulfation factor • Indirect action of GH (delayed response) ...
Sense of Touch and Feeling
... neurons and where they go, this is what determines how we evaluate the signal. The interesting part is that each individual’s somatotopic map is different and determined by that persons own experience in life. This is in result determines how each person may react differently to the same stimulus. ...
... neurons and where they go, this is what determines how we evaluate the signal. The interesting part is that each individual’s somatotopic map is different and determined by that persons own experience in life. This is in result determines how each person may react differently to the same stimulus. ...
ap® biology 2008 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... Question 1 Overview This question tested knowledge of protein form and function from the basic to the applied level. Students were asked to describe the bonds involved with protein structure and apply their knowledge of protein structure to specific functions, such as muscle contraction, cell signal ...
... Question 1 Overview This question tested knowledge of protein form and function from the basic to the applied level. Students were asked to describe the bonds involved with protein structure and apply their knowledge of protein structure to specific functions, such as muscle contraction, cell signal ...
An international registry for neurodegeneration with brain iron
... treatment targets, but the development of diseasemodifying medications is often hampered by the fragmentation of efforts and the low number of available patients. The integration of scattered resources is, therefore, crucial for the success of future scientific accomplishments. Here we report the in ...
... treatment targets, but the development of diseasemodifying medications is often hampered by the fragmentation of efforts and the low number of available patients. The integration of scattered resources is, therefore, crucial for the success of future scientific accomplishments. Here we report the in ...
Expression of ml-m4 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Proteins in
... Nilsson et al., 1992; Callahan et al., 1993). Also, degeneration of basal forebrain cholinergic systems may contribute to memory loss and other cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease (Coyle et al., 1983). Indeed, the potential for cholinergic replacement therapies in dementia (McKinney and Coyle, ...
... Nilsson et al., 1992; Callahan et al., 1993). Also, degeneration of basal forebrain cholinergic systems may contribute to memory loss and other cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease (Coyle et al., 1983). Indeed, the potential for cholinergic replacement therapies in dementia (McKinney and Coyle, ...
Nervous System
... system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors ...
... system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors ...
DECISION MAKING AND THE BRAIN: NEUROLOGISTS` VIEW
... From the non-dualistic perspective decision making is a brain process. Basic knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the central nervous system is crucial for comprehension of the neurological substrate of decision making. The nervous system is divided anatomically into central nervous system and ...
... From the non-dualistic perspective decision making is a brain process. Basic knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the central nervous system is crucial for comprehension of the neurological substrate of decision making. The nervous system is divided anatomically into central nervous system and ...
NeuralNets
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
Chapter 11 Marieb
... postsynaptic potentials. This increases the likelihood of postsynaptic cell action potential. The mechanism is that increased calcium levels in the axon terminal increase the release of neurotransmitter. Synaptic potentiation is involved in learning…the efficacy of neural pathway is improved. It has ...
... postsynaptic potentials. This increases the likelihood of postsynaptic cell action potential. The mechanism is that increased calcium levels in the axon terminal increase the release of neurotransmitter. Synaptic potentiation is involved in learning…the efficacy of neural pathway is improved. It has ...
Ch 3 Vision - Texas A&M University
... Excitatory and inhibitory connections • What neurons transmit is electricity. • Some neurons send positive (excitatory) signals (+) increase the firing rate of the target neuron. • some neurons send negative (inhibitory) signals (-) depress the firing rate of the target neuron. ch 3 ...
... Excitatory and inhibitory connections • What neurons transmit is electricity. • Some neurons send positive (excitatory) signals (+) increase the firing rate of the target neuron. • some neurons send negative (inhibitory) signals (-) depress the firing rate of the target neuron. ch 3 ...
TOXIC TORTS - Rural Law with Peter Long
... readily accepts are due to cigarettes. The synergistic effect of chemicals when combined can be overwhelming, and little research has been conducted on this aspect of toxicity. The lawyer may be faced with a situation in which the readily identifiable chemical in a particular case may not have been ...
... readily accepts are due to cigarettes. The synergistic effect of chemicals when combined can be overwhelming, and little research has been conducted on this aspect of toxicity. The lawyer may be faced with a situation in which the readily identifiable chemical in a particular case may not have been ...
Chap 14b Powerpoint
... Beta (14–30 Hz) waves are present with sensory input and mental activity when the nervous system is active. Theta (4–7 Hz) waves indicate emotional stress or a brain ...
... Beta (14–30 Hz) waves are present with sensory input and mental activity when the nervous system is active. Theta (4–7 Hz) waves indicate emotional stress or a brain ...
Medullary control of nociceptive transmission
... regulation of motivation, emotions and various autonomic functions. Neuropathic pain: pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system. NK1 receptors: receptors for ligation of substance P, one of the main neurotransmitters released by primary afferent nociceptive fi ...
... regulation of motivation, emotions and various autonomic functions. Neuropathic pain: pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system. NK1 receptors: receptors for ligation of substance P, one of the main neurotransmitters released by primary afferent nociceptive fi ...
Cervical Facet Hypertrophy Symptoms of Facet Disease
... your body. These wear down over time, with obesity, and with trauma (ex: MVA). Sometimes you have facet disease without any other cause just due to your genetics. Facet joints glide and allow movement in order to provide flexibility, stability, and support to the spine Enlargement of facet joint ...
... your body. These wear down over time, with obesity, and with trauma (ex: MVA). Sometimes you have facet disease without any other cause just due to your genetics. Facet joints glide and allow movement in order to provide flexibility, stability, and support to the spine Enlargement of facet joint ...
12 - FacultyWeb
... • Composed of myelinated and unmyeinated nerve fibers • Fibers allow communication between different parts of the spinal cord and between the cord and brain ...
... • Composed of myelinated and unmyeinated nerve fibers • Fibers allow communication between different parts of the spinal cord and between the cord and brain ...
Odor and nutrition - ernährungs umschau
... circular adenosine mono phosphate, intracellular chemical messenger (second messenger) which is formed from ATP after activation of an adenylyl cyclase enzyme ...
... circular adenosine mono phosphate, intracellular chemical messenger (second messenger) which is formed from ATP after activation of an adenylyl cyclase enzyme ...
B Type
... Which of the following is not a major clinical feature of dementia with Lewy bodies? A. progressive cognitive decline B. fluctuating cognition with variations in attention C. parkinsonism in the early stage D. incontinence E. visual hallucination ...
... Which of the following is not a major clinical feature of dementia with Lewy bodies? A. progressive cognitive decline B. fluctuating cognition with variations in attention C. parkinsonism in the early stage D. incontinence E. visual hallucination ...
Rhetorical Mimic: Using Empathy to Persuade
... help us make decisions, and to help us learn from the experiences of others instead of being dependent on our own trials and errors” (Loc 3198). In other words, we learn how to respond to situations by what Keysers calls “sharing circuits”—we become “’infected’ by the emotions of other individuals” ...
... help us make decisions, and to help us learn from the experiences of others instead of being dependent on our own trials and errors” (Loc 3198). In other words, we learn how to respond to situations by what Keysers calls “sharing circuits”—we become “’infected’ by the emotions of other individuals” ...
Electric Cures - Bioelectronic Medicine could create an `off switch` for
... behavior of the targeted cells, changing their function. It turns out that many drugs work in a similar manner. The pharmaceutical industry invests billions of dollars to design, synthesize and develop new chemicals as experimental drugs that, like neurotransmitters, are nothing more than molecule ...
... behavior of the targeted cells, changing their function. It turns out that many drugs work in a similar manner. The pharmaceutical industry invests billions of dollars to design, synthesize and develop new chemicals as experimental drugs that, like neurotransmitters, are nothing more than molecule ...
The Nervous System
... 9. Which of the above require ATP? 10. Which of the above creates the difference in concentration of Na and K ions between the inside and the outside of the neuron. 11. Which of the above is most responsible for the difference in charge between inside and outside of a neuron at ...
... 9. Which of the above require ATP? 10. Which of the above creates the difference in concentration of Na and K ions between the inside and the outside of the neuron. 11. Which of the above is most responsible for the difference in charge between inside and outside of a neuron at ...
Slide 1
... Low-affinity/high-specificity binding Broad binding diversity Ability to form large interaction surfaces ...
... Low-affinity/high-specificity binding Broad binding diversity Ability to form large interaction surfaces ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.