Polarization theory of motivations, emotions and
... deepening of hyperpolarization of cells and beginning of hyperpolarization inhibition together with reduction of nervous tissue metabolism. It is clear that on the whole the character of polarization processes after injection of narcotic preparation was opposite to that one observed at ischemia. It ...
... deepening of hyperpolarization of cells and beginning of hyperpolarization inhibition together with reduction of nervous tissue metabolism. It is clear that on the whole the character of polarization processes after injection of narcotic preparation was opposite to that one observed at ischemia. It ...
Protein Synthesis:
... Free ribosomes occur in all cells. Free ribosomes usually produce proteins that are used in the cytosol or in the organelle they occur in. Membrane bound ribosomes When certain proteins are synthesized by a ribosome, it can become "membrane-bound", associated with the membrane of the nucleus and the ...
... Free ribosomes occur in all cells. Free ribosomes usually produce proteins that are used in the cytosol or in the organelle they occur in. Membrane bound ribosomes When certain proteins are synthesized by a ribosome, it can become "membrane-bound", associated with the membrane of the nucleus and the ...
RL 19 - School of Informatics
... brain, providing feelings of enjoyment and reinforcement to motivate a person to perform certain activities. It is released (particularly in areas such as the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex) by rewarding experiences such as food, sex, drugs, and neutral stimuli that become associated with t ...
... brain, providing feelings of enjoyment and reinforcement to motivate a person to perform certain activities. It is released (particularly in areas such as the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex) by rewarding experiences such as food, sex, drugs, and neutral stimuli that become associated with t ...
1 - LWW.com
... (DiI) (Molecular Probes, Leiden, The Netherlands) and True Blue (TB) (Molecular probes, Leiden, The Netherlands) were used 1. 3 months postoperatively, The left MN trunk was re-exposed, cut at the elbow level, and placed into a ...
... (DiI) (Molecular Probes, Leiden, The Netherlands) and True Blue (TB) (Molecular probes, Leiden, The Netherlands) were used 1. 3 months postoperatively, The left MN trunk was re-exposed, cut at the elbow level, and placed into a ...
Nervous Systems
... opening voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. – Ca2+ ions diffuse into presynaptic neuron ...
... opening voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. – Ca2+ ions diffuse into presynaptic neuron ...
Ch. 48 - Ltcconline.net
... b. slower onset but last longer 2. eg. when norepinephrine binds to its receptor, a G protein is activated, which ultimately opens many channels (review ch. 11) D. Neurotransmitters - each bind to own receptor - some bind to different receptors which produce very different effects in postsynaptic ce ...
... b. slower onset but last longer 2. eg. when norepinephrine binds to its receptor, a G protein is activated, which ultimately opens many channels (review ch. 11) D. Neurotransmitters - each bind to own receptor - some bind to different receptors which produce very different effects in postsynaptic ce ...
56 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
... The vestibulocerebellum Function: The control of the equilibrium and postural movements. Especially important in controlling the balance between agonist and antagonist M. contractions of the spine, hips, and shoulders during rapid changes in body positions. ...
... The vestibulocerebellum Function: The control of the equilibrium and postural movements. Especially important in controlling the balance between agonist and antagonist M. contractions of the spine, hips, and shoulders during rapid changes in body positions. ...
Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional
... • Sparsening has many advantages, especially if it occurs in a structure that is implicated in learning (such as the MB). • As well as reducing overlaps, sparse representations could facilitate storage (fewer synapses need to be modified), pattern matching (fewer elements need to be compared) and p ...
... • Sparsening has many advantages, especially if it occurs in a structure that is implicated in learning (such as the MB). • As well as reducing overlaps, sparse representations could facilitate storage (fewer synapses need to be modified), pattern matching (fewer elements need to be compared) and p ...
Neurology
... Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS. The nervous system consists of two types of cells. Nerve cells are called neurons. The typical neuron is an elongated cell that consists of a cell body, containing the nucleus. Various support cells are associated with the neurons, most typi ...
... Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS. The nervous system consists of two types of cells. Nerve cells are called neurons. The typical neuron is an elongated cell that consists of a cell body, containing the nucleus. Various support cells are associated with the neurons, most typi ...
Chapter_013
... Subtypes of cholinergic and adrenergic receptors • Subtypes of cholinergic receptors ...
... Subtypes of cholinergic and adrenergic receptors • Subtypes of cholinergic receptors ...
Teacher Guide
... pre-synaptic neuron – the neuron releasing the neurotransmitter receptors – special molecules on dendrites that taste each specific neurotransmitter. both neurotransmitter and receptor have to fit together like a lock and key synapse – a gap between two neurons forming the site of information transf ...
... pre-synaptic neuron – the neuron releasing the neurotransmitter receptors – special molecules on dendrites that taste each specific neurotransmitter. both neurotransmitter and receptor have to fit together like a lock and key synapse – a gap between two neurons forming the site of information transf ...
Dissecting appetite
... eating might be harmful — or when we have an emotional experience or suffer food poisoning. All this research — figuring out the appetite ...
... eating might be harmful — or when we have an emotional experience or suffer food poisoning. All this research — figuring out the appetite ...
The Interoceptive, or Visceral, Sensations
... nteroceptive sensations are general visceral sensations that arise from the internal organs. The special visceral sensations (smell and taste) are discussed with the cranial nerves. General visceral afferent fibers are found in cranial nerves VII, IX, and X and in the thoracolumbar and sacral autono ...
... nteroceptive sensations are general visceral sensations that arise from the internal organs. The special visceral sensations (smell and taste) are discussed with the cranial nerves. General visceral afferent fibers are found in cranial nerves VII, IX, and X and in the thoracolumbar and sacral autono ...
LIMBIC SYSTEM
... paroxysmal disorders as seen in this patient. In this chapter we will learn about this important and diverse neural system and the consequences of limbic system damage or dysfunction. ...
... paroxysmal disorders as seen in this patient. In this chapter we will learn about this important and diverse neural system and the consequences of limbic system damage or dysfunction. ...
BrainMechanismsofUnconsciousInference2010
... neurons primarily via ‘spikes’ or action potentials. ...
... neurons primarily via ‘spikes’ or action potentials. ...
Hemoglobin
... can have normal life span. Or: Homozygotes (Hb SS): mutation occurs in both β-globin chain with apparent anemia and its symptoms 2- Hb C disease: Like HbS, Hb C is a mutant Hb in which glutamic acid in 6th position of β-chain is replaced by lysine. RBCs will be large oblong and hexagonal. The hetero ...
... can have normal life span. Or: Homozygotes (Hb SS): mutation occurs in both β-globin chain with apparent anemia and its symptoms 2- Hb C disease: Like HbS, Hb C is a mutant Hb in which glutamic acid in 6th position of β-chain is replaced by lysine. RBCs will be large oblong and hexagonal. The hetero ...
Biopsychology – Paper 2
... that is they move impulses towards the CNS . This type of neuron receives information or stimuli from sensory receptors found in various locations in the body, for example the eyes, ears, tongue, skin. This information enters sensory neurons through the dendrites and passes it to the cell body – the ...
... that is they move impulses towards the CNS . This type of neuron receives information or stimuli from sensory receptors found in various locations in the body, for example the eyes, ears, tongue, skin. This information enters sensory neurons through the dendrites and passes it to the cell body – the ...
Neuroscience
... netrin-1, promote apoptosis. This pro-apoptotic activity requires initial caspase cleavage of the receptor's intracellular domain. Netrin-1 is therefore a pro-survival factor acting by blocking cell death induced by its unbound receptors. Netrin-1 protects neurons from death during development and f ...
... netrin-1, promote apoptosis. This pro-apoptotic activity requires initial caspase cleavage of the receptor's intracellular domain. Netrin-1 is therefore a pro-survival factor acting by blocking cell death induced by its unbound receptors. Netrin-1 protects neurons from death during development and f ...
Central Nervous System
... Central Nervous System Hypothalamus – serves as a link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. ...
... Central Nervous System Hypothalamus – serves as a link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. ...
Chapter 16
... Gustatory Pathway 12. Indicate which cranial nerves conduct taste impulses from separate regions of ...
... Gustatory Pathway 12. Indicate which cranial nerves conduct taste impulses from separate regions of ...
... Certain factors of brain dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease are known, but much about the disease is unknown. The known factors include the onset and progress of dementia in patients and the presence of the plaques and tangles in their brains, which may be detected at autopsy. But specific causes re ...
Slide ()
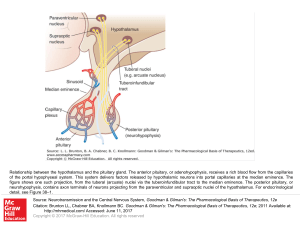
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.