Linking Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Current
... uncertainties and the quality of the evidence Biodiversity is the variability within and among species, as well as the variability at other levels of organization, such as between ecosystems and landscapes. The variability across elements within levels of organization can be measured as richness (th ...
... uncertainties and the quality of the evidence Biodiversity is the variability within and among species, as well as the variability at other levels of organization, such as between ecosystems and landscapes. The variability across elements within levels of organization can be measured as richness (th ...
Review of the Impact of Invasive Alien Species on Species Protected
... lower taxon occurring outside of its natural range (past or present) and dispersal potential (i.e. outside the range it occupies naturally or could not occupy without direct or indirect introduction or care by humans) and includes any part, gametes or propagule of such species that might survive and ...
... lower taxon occurring outside of its natural range (past or present) and dispersal potential (i.e. outside the range it occupies naturally or could not occupy without direct or indirect introduction or care by humans) and includes any part, gametes or propagule of such species that might survive and ...
CSubscript>4Subscript>?Superscript>
... Differences in maximum quantum yield (the initial slope of the absorbed light response curve) have been closely correlated with differences in photosynthetic performance as a function of temperature (Ehleringer 1978; Ehleringer and Pearcy 1983). C3 plants have a greater maximum quantum yield than C4 ...
... Differences in maximum quantum yield (the initial slope of the absorbed light response curve) have been closely correlated with differences in photosynthetic performance as a function of temperature (Ehleringer 1978; Ehleringer and Pearcy 1983). C3 plants have a greater maximum quantum yield than C4 ...
wildlife matters - Australian Wildlife Conservancy
... threatened mammal species have made very modest gains during the last 10 years. The other 59 species have declined or, at best, maintained their parlous position. This is an extremely poor return on investment and demonstrates beyond any doubt that a new model for conservation is required. AWC’s con ...
... threatened mammal species have made very modest gains during the last 10 years. The other 59 species have declined or, at best, maintained their parlous position. This is an extremely poor return on investment and demonstrates beyond any doubt that a new model for conservation is required. AWC’s con ...
Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering
... 1. One of the most pervasive concepts in the study of community assembly is the metaphor of the environmental filter, which refers to abiotic factors that prevent the establishment or persistence of species in a particular location. The metaphor has its origins in the study of community change durin ...
... 1. One of the most pervasive concepts in the study of community assembly is the metaphor of the environmental filter, which refers to abiotic factors that prevent the establishment or persistence of species in a particular location. The metaphor has its origins in the study of community change durin ...
Is Taxonomic Diversity Enough? The Role of Phylogenetic
... The results of the above statistical analysis do not offer strong evidence in support of the importance of functional diversity in community response to environmental stressors. There were slight, but consistent, trends across diversities indices that are important to consider. The relationships be ...
... The results of the above statistical analysis do not offer strong evidence in support of the importance of functional diversity in community response to environmental stressors. There were slight, but consistent, trends across diversities indices that are important to consider. The relationships be ...
Chapter 2 Diatoms in the pelagic and benthic environment
... in the Western Ghats and extends up to 70 km before meeting the Arabian Sea. The width and depth of the mouth is approximately 5.5 km and 5 - 6 m respectively. This area is strongly influenced by the southwest monsoon and the changes associated with its onset have marked effects on the phytoplankton ...
... in the Western Ghats and extends up to 70 km before meeting the Arabian Sea. The width and depth of the mouth is approximately 5.5 km and 5 - 6 m respectively. This area is strongly influenced by the southwest monsoon and the changes associated with its onset have marked effects on the phytoplankton ...
Purple Loosestrife - Biological Control of Invasive Plants in the
... No native or accidentally introduced herbivores with the potential for control of L. salicaria were found in North America (Hight, 1990). More recently, several native pathogens have been evaluated for their potential as biological control agents (Nyvall, 1995; Nyvall and Hu, 1997). Surveys in Europ ...
... No native or accidentally introduced herbivores with the potential for control of L. salicaria were found in North America (Hight, 1990). More recently, several native pathogens have been evaluated for their potential as biological control agents (Nyvall, 1995; Nyvall and Hu, 1997). Surveys in Europ ...
lesson 1: explore the ecosystem
... Mountain forest ecosystem as an example. This can be modified for your local ecosystem using the blank template. c. Show your students each of the six cards and explain that they will be playing a card game similar to “War.” • Each player will start with an equal number of ...
... Mountain forest ecosystem as an example. This can be modified for your local ecosystem using the blank template. c. Show your students each of the six cards and explain that they will be playing a card game similar to “War.” • Each player will start with an equal number of ...
File
... Refer to the illustration above. Explain how DDT and other toxic substances can become concentrated in organisms and how the substance is transferred up through a food chain. Write your answer in the space below. ANS: If there is a toxic substance such as DDT in an organism’s food, it will pass thro ...
... Refer to the illustration above. Explain how DDT and other toxic substances can become concentrated in organisms and how the substance is transferred up through a food chain. Write your answer in the space below. ANS: If there is a toxic substance such as DDT in an organism’s food, it will pass thro ...
Selection of a marker gene to construct a reference library
... and 26% belonged to Carex spp. In contrast, almost all sequences of bean goose belonged to Carex spp. (99%). Using the same samples, microhistology provided consistent food composition with metabarcoding results for greater white-fronted goose, while 13% of Poaceae was recovered for bean goose. In a ...
... and 26% belonged to Carex spp. In contrast, almost all sequences of bean goose belonged to Carex spp. (99%). Using the same samples, microhistology provided consistent food composition with metabarcoding results for greater white-fronted goose, while 13% of Poaceae was recovered for bean goose. In a ...
Chapter 53 communities
... – If there are one or more significant difference in their niches EXPERIMENT Ecologist Joseph Connell studied two barnacle speciesBalanus balanoides and Chthamalus stellatus that have a stratified distribution on rocks along the coast of Scotland. ...
... – If there are one or more significant difference in their niches EXPERIMENT Ecologist Joseph Connell studied two barnacle speciesBalanus balanoides and Chthamalus stellatus that have a stratified distribution on rocks along the coast of Scotland. ...
4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change
... Between about 18,000 and 11,500 years ago the climate and environments of North America were changing rapidly. Temperatures were warming. Rainfall patterns were changing. The glaciers were melting. The seasonal difference in temperatures was increasing. These climate changes were causing fundamental ...
... Between about 18,000 and 11,500 years ago the climate and environments of North America were changing rapidly. Temperatures were warming. Rainfall patterns were changing. The glaciers were melting. The seasonal difference in temperatures was increasing. These climate changes were causing fundamental ...
On the evolutionary ecology of species` ranges - People
... environment. Thomas et al. (2001) have recently demonstrated that the evolution of increased dispersal rates and habitat breadth are both involved in accelerated responses of several butterfly and cricket species to warming trends in Britain. Once the invasion stalls, three factors that favour conti ...
... environment. Thomas et al. (2001) have recently demonstrated that the evolution of increased dispersal rates and habitat breadth are both involved in accelerated responses of several butterfly and cricket species to warming trends in Britain. Once the invasion stalls, three factors that favour conti ...
video slide - Course-Not
... – If there are one or more significant difference in their niches EXPERIMENT Ecologist Joseph Connell studied two barnacle speciesBalanus balanoides and Chthamalus stellatus that have a stratified distribution on rocks along the coast of Scotland. ...
... – If there are one or more significant difference in their niches EXPERIMENT Ecologist Joseph Connell studied two barnacle speciesBalanus balanoides and Chthamalus stellatus that have a stratified distribution on rocks along the coast of Scotland. ...
Ch. 41 Text
... occupied by that species A species’ realized niche is the niche actually occupied by that species As a result of competition, a species’ fundamental niche may differ from its realized niche For example, the presence of one barnacle species limits the realized niche of another species ...
... occupied by that species A species’ realized niche is the niche actually occupied by that species As a result of competition, a species’ fundamental niche may differ from its realized niche For example, the presence of one barnacle species limits the realized niche of another species ...
Rangeland Weed Management - KSRE Bookstore
... Mowing generally is not effective in controlling perennial forbs, although repeated mowings will reduce their vigor and limit their spread. Herbicides Applications of 2,4-D and other herbicides have reduced forb populations on many grasslands. Removing all forbs from rangeland with indiscriminate sp ...
... Mowing generally is not effective in controlling perennial forbs, although repeated mowings will reduce their vigor and limit their spread. Herbicides Applications of 2,4-D and other herbicides have reduced forb populations on many grasslands. Removing all forbs from rangeland with indiscriminate sp ...
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PRODUCTIVITY AND SPECIES
... The notion that productivity (rate of conversion of resources to biomass per unit area per unit time) affects species richness can be traced to at least the mid-1960s (45, 106, 113, 153). Nonetheless, the causal mechanisms behind the patterns between productivity and species diversity, as well as th ...
... The notion that productivity (rate of conversion of resources to biomass per unit area per unit time) affects species richness can be traced to at least the mid-1960s (45, 106, 113, 153). Nonetheless, the causal mechanisms behind the patterns between productivity and species diversity, as well as th ...
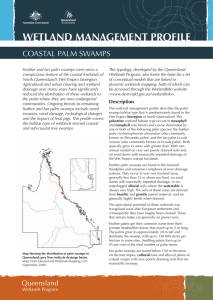
Coastal palm swamps
... the Wet Tropics coastal lowlands. Feather palm swamps are found in the lowland floodplain and estuarine complexes of river drainage systems. They occur in very wet lowland areas, generally less than 15 m above sea level, on sand dunes with seasonally impeded drainage, or on waterlogged alluvial soil ...
... the Wet Tropics coastal lowlands. Feather palm swamps are found in the lowland floodplain and estuarine complexes of river drainage systems. They occur in very wet lowland areas, generally less than 15 m above sea level, on sand dunes with seasonally impeded drainage, or on waterlogged alluvial soil ...
Species Interactions
... occupied by that species A species’ realized niche is the niche actually occupied by that species As a result of competition, a species’ fundamental niche may differ from its realized niche For example, the presence of one barnacle species limits the realized niche of another species ...
... occupied by that species A species’ realized niche is the niche actually occupied by that species As a result of competition, a species’ fundamental niche may differ from its realized niche For example, the presence of one barnacle species limits the realized niche of another species ...
Impacts of environmental variability in open populations and
... times be greatly magnified by temporal variation in the local environment. As we shall see, temporal variation can substantially enhance the ‘‘mass effect.’’ This consequence of temporal variation can in turn constrain species richness, by making it more difficult for species specialized to particular ...
... times be greatly magnified by temporal variation in the local environment. As we shall see, temporal variation can substantially enhance the ‘‘mass effect.’’ This consequence of temporal variation can in turn constrain species richness, by making it more difficult for species specialized to particular ...
Extending the stressgradient hypothesis is competition among
... abiotic factors and/or the availability of resources can determine the strength and direction of interactions among species within a trophic level (Dunson and Travis 1990, Chesson and Huntly 1997, Pringle et al. 2007). However, most research has focused on the importance of competition alone, withou ...
... abiotic factors and/or the availability of resources can determine the strength and direction of interactions among species within a trophic level (Dunson and Travis 1990, Chesson and Huntly 1997, Pringle et al. 2007). However, most research has focused on the importance of competition alone, withou ...
Macroecological and macroevolutionary patterns of
... contained within the other monophyletic angiosperm lineages. Numbers of species sampled are found within the bars. (Online version in colour.) plant species receive little-to-no damage with 40% of species receiving less than 5% damage, and only a small number of species are heavily damaged (less tha ...
... contained within the other monophyletic angiosperm lineages. Numbers of species sampled are found within the bars. (Online version in colour.) plant species receive little-to-no damage with 40% of species receiving less than 5% damage, and only a small number of species are heavily damaged (less tha ...
Macroecological and macroevolutionary patterns of leaf herbivory
... contained within the other monophyletic angiosperm lineages. Numbers of species sampled are found within the bars. (Online version in colour.) plant species receive little-to-no damage with 40% of species receiving less than 5% damage, and only a small number of species are heavily damaged (less tha ...
... contained within the other monophyletic angiosperm lineages. Numbers of species sampled are found within the bars. (Online version in colour.) plant species receive little-to-no damage with 40% of species receiving less than 5% damage, and only a small number of species are heavily damaged (less tha ...
Bifrenaria

Bifrenaria, abbreviated Bif. in horticultural trade, is a genus of plant in family Orchidaceae. It contains 20 species found in Panama, Trinidad and South America. There are no known uses for them, but their abundant, and at first glance artificial, flowers, make them favorites of orchid growers.The genus can be split in two clearly distinct groups: one of highly robust plants with large flowers, that encompass the first species to be classified under the genus Bifrenaria; other of more delicate plants with smaller flowers occasionally classified as Stenocoryne or Adipe. There are two additional species that are normally classified as Bifrenaria, but which molecular analysis indicate to belong to different orchid groups entirely. One is Bifrenaria grandis which is endemic to Bolívia and which is now placed in Lacaena, and Bifrenaria steyermarkii, an inhabitant of the northern Amazon Forest, which does not have an alternative classification.