Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... and mouse hippocampus respond as place cells: that is, they fire bursts of action potentials when the animal passes through a specific part of its environment. Hippocampal place cells interact extensively with head direction cells, whose activity acts as an inertial compass, and with grid cells in t ...
... and mouse hippocampus respond as place cells: that is, they fire bursts of action potentials when the animal passes through a specific part of its environment. Hippocampal place cells interact extensively with head direction cells, whose activity acts as an inertial compass, and with grid cells in t ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
Reflex Arc - Cloudfront.net
... How does the nervous system work? SENSE – Sensory neurons: sense stimuli (things you react to, like pain, heat, pressure, etc.) in your environment COMPREHEND – Interneurons: connect sensory neurons to motor neurons; located in the brain/spinal cord RESPOND – Motor neurons: make your muscles ...
... How does the nervous system work? SENSE – Sensory neurons: sense stimuli (things you react to, like pain, heat, pressure, etc.) in your environment COMPREHEND – Interneurons: connect sensory neurons to motor neurons; located in the brain/spinal cord RESPOND – Motor neurons: make your muscles ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting potential (-70 mV); this means fewer positive ions are inside the cell (K+) than outside (Na+). As long as the inside remains more negative than the outside the neuron remains ...
... 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting potential (-70 mV); this means fewer positive ions are inside the cell (K+) than outside (Na+). As long as the inside remains more negative than the outside the neuron remains ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Cerebellar loop – tells the motor cortex how to carry out the planned activity ...
... Cerebellar loop – tells the motor cortex how to carry out the planned activity ...
Powerpoint - Center Grove Community School
... Not present on all cells When present, increases the speed of neural signals down the axon ...
... Not present on all cells When present, increases the speed of neural signals down the axon ...
Design of Intelligent Machines Heidi 2005
... “Cortical columns are formed by the binding together of many minicolumns by common input and short range horizontal connections. … The number of minicolumns per column varies … between 50 and 80. Long range intracortical projections link columns with similar functional properties.” (p. 3) ...
... “Cortical columns are formed by the binding together of many minicolumns by common input and short range horizontal connections. … The number of minicolumns per column varies … between 50 and 80. Long range intracortical projections link columns with similar functional properties.” (p. 3) ...
NervousSystem2
... carries impulses (the excitatory state) to all of its synapses. If it is an excitatory interneuron, every one of these synapses will be excitatory. If it is an inhibitory interneuron, every one of these synapses will be inhibitory. If it is an efferent neuron to striated muscle, each of its neuroeff ...
... carries impulses (the excitatory state) to all of its synapses. If it is an excitatory interneuron, every one of these synapses will be excitatory. If it is an inhibitory interneuron, every one of these synapses will be inhibitory. If it is an efferent neuron to striated muscle, each of its neuroeff ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... Chemical synapses are not as fast as electrical but are the most common type of synapse. A chemical, called a ______________________, is released from the sending neuron and travels across the ___________________(a gap between the neurons) to the receiving neuron. Advantages of the chemical synapse: ...
... Chemical synapses are not as fast as electrical but are the most common type of synapse. A chemical, called a ______________________, is released from the sending neuron and travels across the ___________________(a gap between the neurons) to the receiving neuron. Advantages of the chemical synapse: ...
Your Nervous System
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
METABOLIC-REDOX ADAPTATIONS OF NEURONS AND
... oxidative metabolism for survival, whereas astrocytes resist to almost complete inhibition of mitochondrial respiration. A key factor in this process is PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3), an enzyme that promotes glycolysis by activating its regulatory enzyme PFK1 (6-phos ...
... oxidative metabolism for survival, whereas astrocytes resist to almost complete inhibition of mitochondrial respiration. A key factor in this process is PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3), an enzyme that promotes glycolysis by activating its regulatory enzyme PFK1 (6-phos ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 24.Sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? autonomic &somatic 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.CNS 27.The neuron is the basic functional unit of the nervous syst ...
... 24.Sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? autonomic &somatic 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.CNS 27.The neuron is the basic functional unit of the nervous syst ...
Neurotransmitters
... positive and negative ions causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons. ...
... positive and negative ions causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons. ...
Neurons: Our Building Blocks
... -Neurons do not actually touch each other to pass on information. The gap between neurons is called the synapse. -The synapse acts as an electrical insulator, preventing an electrical charge from racing to the next cell. -To pass across the synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft, an electrical message must ...
... -Neurons do not actually touch each other to pass on information. The gap between neurons is called the synapse. -The synapse acts as an electrical insulator, preventing an electrical charge from racing to the next cell. -To pass across the synaptic gap, or synaptic cleft, an electrical message must ...
nervous system
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
Answers to Questions — neurons
... 3. Hyponatremia occurs when people have very low amounts of sodium in their body. How might the nervous system be affected if the person had this condition? Sodium is important in generating action potentials, thus low amounts of sodium would make it so neurons are less able to transmit signals. In ...
... 3. Hyponatremia occurs when people have very low amounts of sodium in their body. How might the nervous system be affected if the person had this condition? Sodium is important in generating action potentials, thus low amounts of sodium would make it so neurons are less able to transmit signals. In ...
Slide ()
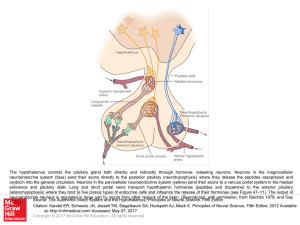
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... This link is called a synapse. The extent to which the signal from one neuron is passed on to the next depends on many factors, e.g. the amount of neurotransmittor available, the number and arrangement of receptors, amount of neurotransmittor reabsorbed, etc. ...
... This link is called a synapse. The extent to which the signal from one neuron is passed on to the next depends on many factors, e.g. the amount of neurotransmittor available, the number and arrangement of receptors, amount of neurotransmittor reabsorbed, etc. ...
Notes - The Nervous System
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... (Spindle on slack) the spindle would not be providing proprioceptive input. • To avoid this problem both the smaller gamma motor neurons( Ў ) and the larger alpha motor neuron are both innervated simultaneously. • Gamma motor neurons originate in the brain stem. Regulate the resting muscle tone. Dyn ...
... (Spindle on slack) the spindle would not be providing proprioceptive input. • To avoid this problem both the smaller gamma motor neurons( Ў ) and the larger alpha motor neuron are both innervated simultaneously. • Gamma motor neurons originate in the brain stem. Regulate the resting muscle tone. Dyn ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... B. synapse on muscles in the eye, neck, and head C. synapse on local circuit neurons and/or lower motor neurons <––– D. affect motor patterns only indirectly via their inputs to the basal ganglia. E. None of the above 2. A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of A. all of the motor neuro ...
... B. synapse on muscles in the eye, neck, and head C. synapse on local circuit neurons and/or lower motor neurons <––– D. affect motor patterns only indirectly via their inputs to the basal ganglia. E. None of the above 2. A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of A. all of the motor neuro ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM: NEURAL TISSUE
... PNS Glial Cells • Schwann cells – Myelin • All peripheral nerves are myelinated ...
... PNS Glial Cells • Schwann cells – Myelin • All peripheral nerves are myelinated ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.