3a handout
... III. Neurons and Neurotransmitters-Psychsim activity, Human Brain CD, Action potential video A. Explain the function of the Cell body, axon, dendrite, myelin sheath, and nodes of Ranvier ...
... III. Neurons and Neurotransmitters-Psychsim activity, Human Brain CD, Action potential video A. Explain the function of the Cell body, axon, dendrite, myelin sheath, and nodes of Ranvier ...
BIO 132
... modulatory systems in the brain: Noradrenergic Cholinergic Dopaminergic Serotonergic ...
... modulatory systems in the brain: Noradrenergic Cholinergic Dopaminergic Serotonergic ...
Anat 1: Ch 17 (SS99)
... Preganglionic neurons (cell bodies) located in brain stem & sacral segments of spinal cord Ganglionic neurons (cell bodies) in ganglia near target organs: Intramural ganglia Effects of parasympathetic division ? ...
... Preganglionic neurons (cell bodies) located in brain stem & sacral segments of spinal cord Ganglionic neurons (cell bodies) in ganglia near target organs: Intramural ganglia Effects of parasympathetic division ? ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... of cranial nerves and spinal cord segments S2 through S4 • For this reason this division is called the Craniosacral Division (or Craniosacral outflow) ...
... of cranial nerves and spinal cord segments S2 through S4 • For this reason this division is called the Craniosacral Division (or Craniosacral outflow) ...
nervous system
... b.) Motor neurons: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands c.) Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them 3. Neuron Parts and Function a.) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm; location of cellular metabolic activi ...
... b.) Motor neurons: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands c.) Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them 3. Neuron Parts and Function a.) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm; location of cellular metabolic activi ...
File
... Transmit impulses from CNS to the muscles in order to produce movement (voluntary or involuntary) ...
... Transmit impulses from CNS to the muscles in order to produce movement (voluntary or involuntary) ...
Neural-Ville
... neurotransmitter are sent into the tiny space between nerve cells, called the synaptic gap. ...
... neurotransmitter are sent into the tiny space between nerve cells, called the synaptic gap. ...
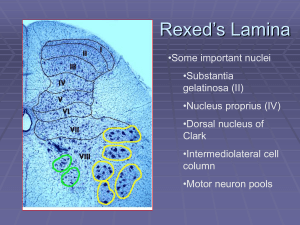
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
Neurons
... the cell membrane If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. ...
... the cell membrane If resting potential rises above threshold, an action potential starts to travel from the cell body down the axon Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. ...
Sensory Neuron Processing
... ANS and Somatic Motor Control Dr. Gary Mumaugh – Bethel University ...
... ANS and Somatic Motor Control Dr. Gary Mumaugh – Bethel University ...
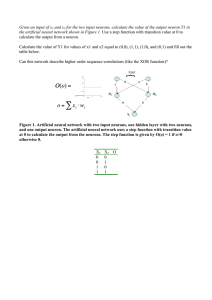
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
Nervous System
... Function: To sense changes in their surroundings and respond by transmitting nerve impulses along cellular processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integ ...
... Function: To sense changes in their surroundings and respond by transmitting nerve impulses along cellular processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integ ...
Nervous System Structure
... touch) react to a stimulus and generate nerve impulses in the sensory neurons near them. The sensory neurons carry the impulse to the spinal cord and then to the brain where interneurons interpret the sensory information The interneurons send out impulses to motor neurons which elicit a response by ...
... touch) react to a stimulus and generate nerve impulses in the sensory neurons near them. The sensory neurons carry the impulse to the spinal cord and then to the brain where interneurons interpret the sensory information The interneurons send out impulses to motor neurons which elicit a response by ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... If you are unsure about the precise mode of action of neurotransmission and neuromodulation, you might like to consult Chapter 3, where these terms are explained. Neurotransmitter would be employed where ballistic action is called for as in the brain rapidly instigating a response or in inhibiting a ...
... If you are unsure about the precise mode of action of neurotransmission and neuromodulation, you might like to consult Chapter 3, where these terms are explained. Neurotransmitter would be employed where ballistic action is called for as in the brain rapidly instigating a response or in inhibiting a ...
PPT
... machine diagnosis, real-time particle identification, visual quality inspection systems, beer testing, welding quality analysis, paper quality prediction, computer chip quality analysis, analysis of grinding operations, chemical product design analysis, machine maintenance analysis, project bidding, ...
... machine diagnosis, real-time particle identification, visual quality inspection systems, beer testing, welding quality analysis, paper quality prediction, computer chip quality analysis, analysis of grinding operations, chemical product design analysis, machine maintenance analysis, project bidding, ...
Introduction
... •Einstein’s own words about his thinking process,”…words do not seem to play any role” but there is “associative play” of “more or less clear images” of the “visual and muscular type”. Witelson et al (1999) ...
... •Einstein’s own words about his thinking process,”…words do not seem to play any role” but there is “associative play” of “more or less clear images” of the “visual and muscular type”. Witelson et al (1999) ...
The nervous system
... memory loss, and a variety of other symptoms. Its incidence is age related, rising from 10% at age 65 to 35% at age 85. The disease is progressive, with patients losing the ability to live alone and take care of themselves. There are also personality changes, almost always for the worse. It is diffi ...
... memory loss, and a variety of other symptoms. Its incidence is age related, rising from 10% at age 65 to 35% at age 85. The disease is progressive, with patients losing the ability to live alone and take care of themselves. There are also personality changes, almost always for the worse. It is diffi ...
The Nervous System
... Gray Matter: Darker CNS tissues made up of neurons’ cell bodies & dendrites White Matter: Paler CNS tissues comprised of myelin-sheathed nerve fibers ...
... Gray Matter: Darker CNS tissues made up of neurons’ cell bodies & dendrites White Matter: Paler CNS tissues comprised of myelin-sheathed nerve fibers ...
Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: Neurons by
... Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: ◊ Neurons by far the most common ◊ They possess an axon and a number of dendrites ∼ Bipolar: ◊ Neurons with a centrally placed cell body ◊ 1 axon extends away from cell body ◊ 1 dendrite extends from axon ◊ Occur in afferent pathways of the visual, ...
... Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: ◊ Neurons by far the most common ◊ They possess an axon and a number of dendrites ∼ Bipolar: ◊ Neurons with a centrally placed cell body ◊ 1 axon extends away from cell body ◊ 1 dendrite extends from axon ◊ Occur in afferent pathways of the visual, ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.