Endocrine and nervous system
... Sensory neurons to the brain cells called Interneurons. • The brain will then send an impulse through motor neurons to the necessary muscle or organs, telling it to contract. ...
... Sensory neurons to the brain cells called Interneurons. • The brain will then send an impulse through motor neurons to the necessary muscle or organs, telling it to contract. ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... Reflexes are involuntary coordinated patterns of muscle contraction and relaxation elicited by peripheral stimuli. Charles Sherrington introduced the concept of a reflex arc (neural pathway from receptor to effector). He also suggested that reflexes may be elementary units of behavior. ...
... Reflexes are involuntary coordinated patterns of muscle contraction and relaxation elicited by peripheral stimuli. Charles Sherrington introduced the concept of a reflex arc (neural pathway from receptor to effector). He also suggested that reflexes may be elementary units of behavior. ...
The Neuron
... 4) Axon terminals contain tiny, oval sacs (synaptic vesicles) which contain chemicals known as neurotransmitters. 5) These neurotransmitters cross the synaptic space *Synaptic vesicles and neurotransmitters are other two parts needed for a synapse. ...
... 4) Axon terminals contain tiny, oval sacs (synaptic vesicles) which contain chemicals known as neurotransmitters. 5) These neurotransmitters cross the synaptic space *Synaptic vesicles and neurotransmitters are other two parts needed for a synapse. ...
neurons
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
Review 3 ____ 1. The cells that provide structural support and
... 10. Leonard's mother became dehydrated during a recent illness, and the levels of sodium in her body were significantly reduced. If enough sodium was lost you might expect that a. her nervous system would become highly activated and action potentials would be generated continuously b. fewer action p ...
... 10. Leonard's mother became dehydrated during a recent illness, and the levels of sodium in her body were significantly reduced. If enough sodium was lost you might expect that a. her nervous system would become highly activated and action potentials would be generated continuously b. fewer action p ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... in CNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = nuclei in PNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = ganglia processes: two types; axons and dendrites Dendrites shorter branching receptor regions contain all organelles (except nucleus) as in cell body large surface area for reception of sign ...
... in CNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = nuclei in PNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = ganglia processes: two types; axons and dendrites Dendrites shorter branching receptor regions contain all organelles (except nucleus) as in cell body large surface area for reception of sign ...
PHD COURSE NEUROMORPHIC TACTILE SENSING MARCH 25
... Abstract: Tactile sensory information is gained as our skin interacts with objects of the external world. The skin is endowed with an incredibly rich set of sensors, which transduce mechanical strains in the skin into patterns of neural spikes in the nerve fibers that convey the primary sensory info ...
... Abstract: Tactile sensory information is gained as our skin interacts with objects of the external world. The skin is endowed with an incredibly rich set of sensors, which transduce mechanical strains in the skin into patterns of neural spikes in the nerve fibers that convey the primary sensory info ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The myelin sheath in peripheral nerves normally runs along the axon punctuated by unsheathed nodes of Ranvier which contain a high density of voltage-gated ...
... The myelin sheath in peripheral nerves normally runs along the axon punctuated by unsheathed nodes of Ranvier which contain a high density of voltage-gated ...
Nervous System
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
Nervous System
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
Nerve Impulses - manorlakesscience
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... There are about 1000 billion Each can be connected to over 10s of 1000s of other neurons ...
... There are about 1000 billion Each can be connected to over 10s of 1000s of other neurons ...
Data/hora: 28/03/2017 12:03:40 Provedor de dados: 17 País: United
... Resumo: The neuron, when considered as a signal processing device, itsinputs are the frequency of pulses received at the synapses, and its output is the frequency of action potentials generated- in essence, a neuron is a pulse frequency signal processing device. In comparison, electrical devices use ...
... Resumo: The neuron, when considered as a signal processing device, itsinputs are the frequency of pulses received at the synapses, and its output is the frequency of action potentials generated- in essence, a neuron is a pulse frequency signal processing device. In comparison, electrical devices use ...
Nervous System PPT - Effingham County Schools
... Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs - they are numbered according to where they are located. • Emerge from cord through foramen of vertebrae. • Each nerve level attaches to a body section – Dermatone - patches of skin that correspond to each nerve. ...
... Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs - they are numbered according to where they are located. • Emerge from cord through foramen of vertebrae. • Each nerve level attaches to a body section – Dermatone - patches of skin that correspond to each nerve. ...
Parts of the Neuron 45
... that separates one neuron from another. Dendrites are treelike structures that project from the soma. Dendrites have receptor sites, or docking stations, that enable them to receive neurotransmitters released by neighboring neurons (Häusser, Spruston, & Stuart, 2000). Through its dendrites, each neu ...
... that separates one neuron from another. Dendrites are treelike structures that project from the soma. Dendrites have receptor sites, or docking stations, that enable them to receive neurotransmitters released by neighboring neurons (Häusser, Spruston, & Stuart, 2000). Through its dendrites, each neu ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... Afferent (towards the central nervous system: CNS) Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...
... Afferent (towards the central nervous system: CNS) Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...
Nervous Systems (ch. 48 & 49) Sum13
... 1. All sensory, motor, and interneurons neurons 2. Sensory neuron dendrites & cell bodies AND motor neuron axons 3. Interneurons only 4. Motor neuron dendrites and interneuron axons ...
... 1. All sensory, motor, and interneurons neurons 2. Sensory neuron dendrites & cell bodies AND motor neuron axons 3. Interneurons only 4. Motor neuron dendrites and interneuron axons ...
BN20 cortical motor control
... Neuron most active Preferred direction but active at 45 from preferred How is direction determined? Populations of M1 neurons Net activity of neurons with different preferred directions vectors ~ ...
... Neuron most active Preferred direction but active at 45 from preferred How is direction determined? Populations of M1 neurons Net activity of neurons with different preferred directions vectors ~ ...
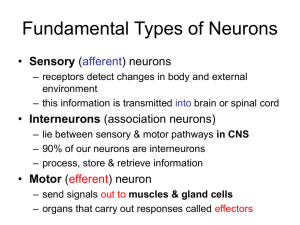
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
... environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
nerve slide show
... • Stimuli: An external or internal change. • Sensory Input: Information about stimuli that is gathered by the nervous system. • Integration: Sensory input is collected and evaluated or interpreted by the nervous system • CNS: Central Nervous System, command center consisting of the brain and spinal ...
... • Stimuli: An external or internal change. • Sensory Input: Information about stimuli that is gathered by the nervous system. • Integration: Sensory input is collected and evaluated or interpreted by the nervous system • CNS: Central Nervous System, command center consisting of the brain and spinal ...
Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System
... • Chronic, potentially debilitating disease that affects the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. • Myelin sheath is destroyed- It hardens to a tissue called the scleroses • Transmitted nerve impulses are short-circuited • Affected person loses control of his/her mu ...
... • Chronic, potentially debilitating disease that affects the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. • Myelin sheath is destroyed- It hardens to a tissue called the scleroses • Transmitted nerve impulses are short-circuited • Affected person loses control of his/her mu ...
www.sakshieducation.com
... A) Ions moving across the cell membrane B) Small neuroglial cells that act as batteries for the neuron itself ...
... A) Ions moving across the cell membrane B) Small neuroglial cells that act as batteries for the neuron itself ...
A2.2.2.SecretSignals - jj-sct
... to send messages in a hurry, allowing a race car driver to react while driving at intense speeds or a tennis player to return the lightning-fast serve of an opponent. We have looked at the structure of a neuron and we know that the nerve cell can generate and send an electrical signal. This signal t ...
... to send messages in a hurry, allowing a race car driver to react while driving at intense speeds or a tennis player to return the lightning-fast serve of an opponent. We have looked at the structure of a neuron and we know that the nerve cell can generate and send an electrical signal. This signal t ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.