Review for Exam 2
... 8) The appearance of which element in a star’s core triggers a Type II supernova explosion? 9) What is a nova? What is a Type Ia supernova? ...
... 8) The appearance of which element in a star’s core triggers a Type II supernova explosion? 9) What is a nova? What is a Type Ia supernova? ...
Astro 18 – Section Week 2
... The deeper absorption line at 760nm is caused by our atmosphere's oxygen molecule. The two absorption lines at 720 and 890nm (from methane) appear on Saturn and Titan, but the rings do not have them ...
... The deeper absorption line at 760nm is caused by our atmosphere's oxygen molecule. The two absorption lines at 720 and 890nm (from methane) appear on Saturn and Titan, but the rings do not have them ...
Binocular Universe: Bikini Bottom
... Except this year. That's because these evenings Capricornus, which always impresses me more as the bottom half of a bikini than a "sea-goat (whatever that is) plays host to brilliant Jupiter. The king of the planets draws the attention of everyone from all quarters to the wet quarter, whether you're ...
... Except this year. That's because these evenings Capricornus, which always impresses me more as the bottom half of a bikini than a "sea-goat (whatever that is) plays host to brilliant Jupiter. The king of the planets draws the attention of everyone from all quarters to the wet quarter, whether you're ...
STARS In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
Stars Power Point
... • Low numbers are brightest, high are dimmest • Sun = -26.7 • Sirius = -1.45 (Brightest Star) ...
... • Low numbers are brightest, high are dimmest • Sun = -26.7 • Sirius = -1.45 (Brightest Star) ...
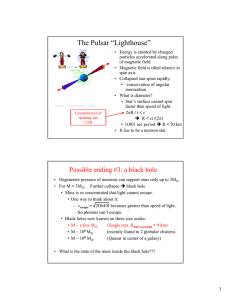
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... • Outer layers of star gradually contract onto core which becomes too massive to be held up by degenerate electron pressure • e- + p Î n • Sudden core collapse: 104 km Î 20 km • Then core rebounds • Outer layers fall in, then get hit by rebounding core. ...
... • Outer layers of star gradually contract onto core which becomes too massive to be held up by degenerate electron pressure • e- + p Î n • Sudden core collapse: 104 km Î 20 km • Then core rebounds • Outer layers fall in, then get hit by rebounding core. ...
April 1st
... • Not enough mass for fusion • Minimum mass of gas need for fusion is 0.08 solar masses (80 times the mass of Jupiter) ...
... • Not enough mass for fusion • Minimum mass of gas need for fusion is 0.08 solar masses (80 times the mass of Jupiter) ...
Jeopardy Questions
... A: X-ray observations of hot gas in galaxy clusters, gravitational lensing from galaxy clusters, flat rotation curves of spiral galaxies ...
... A: X-ray observations of hot gas in galaxy clusters, gravitational lensing from galaxy clusters, flat rotation curves of spiral galaxies ...
Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun:
... A: Hydrogen & Helium exist on these planets in liquid form 6-Which planet spins on its side (>90 degrees)? A: Uranus 7-How do you determine a planet’s day ? How do you determine a planet’s year? A: Day- the rotation around the axis Year- Revolution/Orbit around Sun 8-Which of the geocentric, helioce ...
... A: Hydrogen & Helium exist on these planets in liquid form 6-Which planet spins on its side (>90 degrees)? A: Uranus 7-How do you determine a planet’s day ? How do you determine a planet’s year? A: Day- the rotation around the axis Year- Revolution/Orbit around Sun 8-Which of the geocentric, helioce ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Astronomers use a Spectroscope to determine the composition of a Star ...
... • Astronomers use a Spectroscope to determine the composition of a Star ...
Characteristics of Stars
... 4. In relation to the brightness of other stars how bright is the Sun? What are the three characteristics astronomers use to classify stars? 5. What size is the Sun compared to other stars? What are very large stars called? How far would the supergiant Betelgeuse reach if it were to replace our Sun? ...
... 4. In relation to the brightness of other stars how bright is the Sun? What are the three characteristics astronomers use to classify stars? 5. What size is the Sun compared to other stars? What are very large stars called? How far would the supergiant Betelgeuse reach if it were to replace our Sun? ...
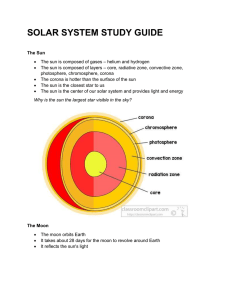
solar system study guide
... The sun is composed of gases – helium and hydrogen The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light ...
... The sun is composed of gases – helium and hydrogen The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light ...
Astronomy Day 2006: A short presentation on eclipsing binary stars
... Another reason that I am interested in these star systems is the potential for the discovery of extra-solar planets that theoretically can exist in stable orbit around the binary star pair. These might be seen through transit observations of very high inclination angle binary stars. After all, they ...
... Another reason that I am interested in these star systems is the potential for the discovery of extra-solar planets that theoretically can exist in stable orbit around the binary star pair. These might be seen through transit observations of very high inclination angle binary stars. After all, they ...
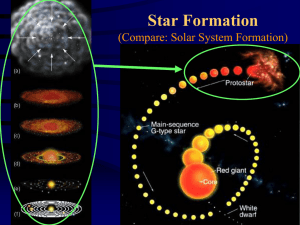
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
Chapter 19 I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B
... E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between objects. 3. The more mass an object has the greater its gravitational pull. a. The Sun has more mass than any ob ...
... E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition of gravity is the attractive force between objects. 3. The more mass an object has the greater its gravitational pull. a. The Sun has more mass than any ob ...
Terminology Used in Planetary Data
... can throw people into confusion. At times it can be like reading another language! So here is a brief summary of the commonly used terms and what they mean. The diagram will help you to better understand these descriptions! Orbits In our solar system, the planets orbit the Sun and each planet has mo ...
... can throw people into confusion. At times it can be like reading another language! So here is a brief summary of the commonly used terms and what they mean. The diagram will help you to better understand these descriptions! Orbits In our solar system, the planets orbit the Sun and each planet has mo ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... how bright it appears to be from Earth, not how bright it actually is. Absolute magnitude is how bright the star is at a standard distance from Earth. It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main ...
... how bright it appears to be from Earth, not how bright it actually is. Absolute magnitude is how bright the star is at a standard distance from Earth. It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main ...
12.4 Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun
... It can be seen from this H-R diagram that stars more massive than the Sun follow very different paths when leaving the Main Sequence: ...
... It can be seen from this H-R diagram that stars more massive than the Sun follow very different paths when leaving the Main Sequence: ...