chapter10
... Degenerate stellar remnant (C,O core) Extremely dense: 1 teaspoon of white dwarf material: mass ≈ 16 tons!!! Chunk of white dwarf material the size of a beach ball would outweigh an ocean liner! ...
... Degenerate stellar remnant (C,O core) Extremely dense: 1 teaspoon of white dwarf material: mass ≈ 16 tons!!! Chunk of white dwarf material the size of a beach ball would outweigh an ocean liner! ...
Document
... f. Universal Gravitation i. Equation ii. Inverse Square Law g. Acceleration due to Gravity on a Planet (g) i. Acceleration due to gravity away from the surface(g/) h. Orbital Velocity i. Escape Velocity j. Satellites i. Equations (3) k. Newton’s Version of Kepler’s 3rd Law l. Microgravity m. Einstei ...
... f. Universal Gravitation i. Equation ii. Inverse Square Law g. Acceleration due to Gravity on a Planet (g) i. Acceleration due to gravity away from the surface(g/) h. Orbital Velocity i. Escape Velocity j. Satellites i. Equations (3) k. Newton’s Version of Kepler’s 3rd Law l. Microgravity m. Einstei ...
The Solar System
... • Gas Giants: (Jupiter & Saturn) – Thick H/He atmosphere, liquid hydrogen mantle, ice core ...
... • Gas Giants: (Jupiter & Saturn) – Thick H/He atmosphere, liquid hydrogen mantle, ice core ...
Document
... What is the biggest surprise about extrasolar planetary systems? a. Most of the systems only have one planet. b. Many systems have several planets larger than Jupiter. c. Many systems have very large planets orbiting close to the star. d. Most of the planets do not fit into the categories of terrest ...
... What is the biggest surprise about extrasolar planetary systems? a. Most of the systems only have one planet. b. Many systems have several planets larger than Jupiter. c. Many systems have very large planets orbiting close to the star. d. Most of the planets do not fit into the categories of terrest ...
S E N S ` 2 0 0 6
... basic questions arising when somebody think about the origin of Solar system and other planetary systems. But there is not yet any theory confirmed all circumstances. How one planet begins its life? Is it originate from the gas and dust between stars? Or it’s life begins from star’s pieces after som ...
... basic questions arising when somebody think about the origin of Solar system and other planetary systems. But there is not yet any theory confirmed all circumstances. How one planet begins its life? Is it originate from the gas and dust between stars? Or it’s life begins from star’s pieces after som ...
Document
... solar masses, what is the dividing line, that is, the lowest mass for a high-mass star? a) 2, b) 4, c) 8, d) 12, e) 20 27. What is the primary composition of a white dwarf? a) hydrogen, b) helium, c) carbon, d) oxygen, e) silicon 28. What are black dwarfs? a) the lowest mass main sequence stars b) t ...
... solar masses, what is the dividing line, that is, the lowest mass for a high-mass star? a) 2, b) 4, c) 8, d) 12, e) 20 27. What is the primary composition of a white dwarf? a) hydrogen, b) helium, c) carbon, d) oxygen, e) silicon 28. What are black dwarfs? a) the lowest mass main sequence stars b) t ...
STARS- hot glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by
... B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Nebula (cloud of dust and gas) collapses under its own gravity B) Friction in core causes temperature to reach 10,000,000 c C) fusion begins and a star is born 4] How stars are found A) Loner-by itself (our sun) B) Binary ...
... B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Nebula (cloud of dust and gas) collapses under its own gravity B) Friction in core causes temperature to reach 10,000,000 c C) fusion begins and a star is born 4] How stars are found A) Loner-by itself (our sun) B) Binary ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... line in the diagram) and this is called the Main Sequence. Stars that lie in this area are called main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these ...
... line in the diagram) and this is called the Main Sequence. Stars that lie in this area are called main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these ...
characteristics of stars
... RED GIANT - a star near the end of its life, that becomes larger and redder as it runs out of its hydrogen fuel. RED SUPERGIANT - a star with mass 10 times or more larger than the sun near the end of its life that becomes larger and redder as it runs out of hydrogen. WHITE DWARF - a small star with ...
... RED GIANT - a star near the end of its life, that becomes larger and redder as it runs out of its hydrogen fuel. RED SUPERGIANT - a star with mass 10 times or more larger than the sun near the end of its life that becomes larger and redder as it runs out of hydrogen. WHITE DWARF - a small star with ...
Wasp-17b: An Ultra-Low Density Planet in a Probable Retrograde
... Angular momentum of star and planets derive from parent molecular cloud ⇒ Close alignment between the stellar spin and the planetary orbit axis is expected ...
... Angular momentum of star and planets derive from parent molecular cloud ⇒ Close alignment between the stellar spin and the planetary orbit axis is expected ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... times less light than the Sun does. A star with an absolute magnitude of 0 (that’s 5 magnitudes smaller than the Sun) emits about 2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5 (or 100) times as much light as the Sun. Remember: smaller magnitudes mean more light. ...
... times less light than the Sun does. A star with an absolute magnitude of 0 (that’s 5 magnitudes smaller than the Sun) emits about 2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5x2.5 (or 100) times as much light as the Sun. Remember: smaller magnitudes mean more light. ...
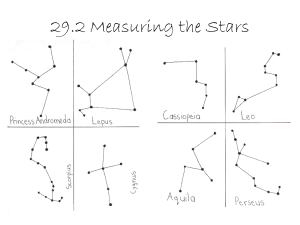
Constellations
... and planets based on the premise that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. ...
... and planets based on the premise that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. ...
Lesson 4d Models of the Solar System
... Venus has phases (like the moon) and appears to change size Jupiter has objects orbiting it (moons) There are dark spots on the sun The sun rotates and the spots on the ...
... Venus has phases (like the moon) and appears to change size Jupiter has objects orbiting it (moons) There are dark spots on the sun The sun rotates and the spots on the ...
Stars Powerpoint
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left be ...
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left be ...
Document
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
Intro to Astronomy
... Hundreds of robotic spacecraft have been launched for many missions around our solar system. Most of these do not return to the Earth. Typically, spacecraft will use the gravity of the Earth or other planets to send them farther out into space. The method is called “gravity assist” or “sling-shot”. ...
... Hundreds of robotic spacecraft have been launched for many missions around our solar system. Most of these do not return to the Earth. Typically, spacecraft will use the gravity of the Earth or other planets to send them farther out into space. The method is called “gravity assist” or “sling-shot”. ...
Gravitational redshifts
... synthetic line profiles) are shorter than laboratory values due to convective blueshift. Curves before and after mid-transit (µ = 0.21, 0.59, 0.87) are not exact mirror images due to intrinsic stellar line asymmetries. This simulation from a CO5BOLD model predicts the behavior of an Fe I line ( 620 ...
... synthetic line profiles) are shorter than laboratory values due to convective blueshift. Curves before and after mid-transit (µ = 0.21, 0.59, 0.87) are not exact mirror images due to intrinsic stellar line asymmetries. This simulation from a CO5BOLD model predicts the behavior of an Fe I line ( 620 ...