The first cool rocky/icy exoplanet
... host star. But because these planets had to be large to cause an observable Doppler shift, the planetary systems revealed were unlike the solar system; astronomers were faced with massive gas giants in close orbits around their host star. By January 2006, about 170 extrasolar planets were known, of ...
... host star. But because these planets had to be large to cause an observable Doppler shift, the planetary systems revealed were unlike the solar system; astronomers were faced with massive gas giants in close orbits around their host star. By January 2006, about 170 extrasolar planets were known, of ...
slides - Indico
... Metal-Poor Stars ? • Extremely metal-poor (MP) stars have recorded the heavy element abundances produced in the first generations of stars in the Universe • The shape of the low-metallicity tail of the Metallicity Distribution Function will (eventually) show structure that reveals the characteristic ...
... Metal-Poor Stars ? • Extremely metal-poor (MP) stars have recorded the heavy element abundances produced in the first generations of stars in the Universe • The shape of the low-metallicity tail of the Metallicity Distribution Function will (eventually) show structure that reveals the characteristic ...
How the universe works – Answer Key Star dust is the building
... Star dust is the building blocks of life. Every atom in your body was produced inside the fiery core of the sun. All life begins with stars. In our galaxy there are over 100 billion stars and in the universe there are over 100 billion galaxies. There are more stars than there are grains of sand on e ...
... Star dust is the building blocks of life. Every atom in your body was produced inside the fiery core of the sun. All life begins with stars. In our galaxy there are over 100 billion stars and in the universe there are over 100 billion galaxies. There are more stars than there are grains of sand on e ...
Some space objects are visible to the human eye.
... A constellation is a group of stars that form a pattern in the sky. In the constellation Cygnus, for example, a group of bright stars form the shape of a flying swan. Any other objects in that area of the sky, such as galaxies, are said to be located in Cygnus, even if they are not parts of the swan ...
... A constellation is a group of stars that form a pattern in the sky. In the constellation Cygnus, for example, a group of bright stars form the shape of a flying swan. Any other objects in that area of the sky, such as galaxies, are said to be located in Cygnus, even if they are not parts of the swan ...
The Brightness of Stars
... a certain color range The filters are simply colored glass that goes over the mirror or lens of a telescope Astronomers say Vega has an MV of 0, which means Vega has an absolute magnitude of 0 in the V (for visible--no filters) color band ...
... a certain color range The filters are simply colored glass that goes over the mirror or lens of a telescope Astronomers say Vega has an MV of 0, which means Vega has an absolute magnitude of 0 in the V (for visible--no filters) color band ...
Chapter 14. Stellar Structure and Evolution
... When a star first forms it is chemically homogeneous and composed mostly of Hydrogen. The temperature and density must be highest at its core to provide the pressure needed to support the full weight of the star. Naturally, it is deep in the core, then, that conditions first become suitable for ther ...
... When a star first forms it is chemically homogeneous and composed mostly of Hydrogen. The temperature and density must be highest at its core to provide the pressure needed to support the full weight of the star. Naturally, it is deep in the core, then, that conditions first become suitable for ther ...
Introduction
... cross-correlation function was firstly applied to astronomy by Simkin (1974). The spectrograph behavior has also to be kept under control, to achieve the required precisions, and a radial-velocity reference serves to accomplish this. There are currently two different techniques to establish this ref ...
... cross-correlation function was firstly applied to astronomy by Simkin (1974). The spectrograph behavior has also to be kept under control, to achieve the required precisions, and a radial-velocity reference serves to accomplish this. There are currently two different techniques to establish this ref ...
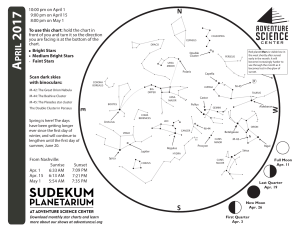
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... Maiden. Neither of these constellations has any other bright stars. Even under dark skies away from city lights, it’s hard to imagine these mythological figures just by connecting the dots. Not too far from Spica is the bright planet Jupiter. If you have binoculars, you may be able to see the giant p ...
... Maiden. Neither of these constellations has any other bright stars. Even under dark skies away from city lights, it’s hard to imagine these mythological figures just by connecting the dots. Not too far from Spica is the bright planet Jupiter. If you have binoculars, you may be able to see the giant p ...
summary - guideposts
... The next four outward are Jovian planets that are large and low density. All four of the Jovian worlds have ring systems and large families of moons. Jupiter’s Galilean satellites were discovered by Galileo. The terrestrial planets have no visible rings and few moons. Studies of craters on the moon ...
... The next four outward are Jovian planets that are large and low density. All four of the Jovian worlds have ring systems and large families of moons. Jupiter’s Galilean satellites were discovered by Galileo. The terrestrial planets have no visible rings and few moons. Studies of craters on the moon ...
Astronomy 112: Physics of Stars Problem set 2: Due April 29 1. Time
... 7. Polytropes: A neutron star is roughly describable as a polytrope of index 1. The radius of a typical neutron star of mass 1.4 solar masses is 10 km. What is its central density? The density of the atomic nucleus is 2.4 x 10**14 g cm−3 . Compare the value you computed to this number. Neutron stars ...
... 7. Polytropes: A neutron star is roughly describable as a polytrope of index 1. The radius of a typical neutron star of mass 1.4 solar masses is 10 km. What is its central density? The density of the atomic nucleus is 2.4 x 10**14 g cm−3 . Compare the value you computed to this number. Neutron stars ...
observingnebulaeclusters-1
... within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (C.R. O'Dell, Rice University) provides a more ...
... within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (C.R. O'Dell, Rice University) provides a more ...
star
... The Lives of Stars Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can take a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then try ...
... The Lives of Stars Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can take a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then try ...
For Chapter 16 on November 26, 2012
... • The Kuiper Belt extends just beyond the orbit of Neptune and into the space of Eris. • Consists of comet and cometary material and other small objects – Trans Neptunian Objects • Many astronomers put the edge of the solar system to be at about 100 AU. • Voyager 1, launched in 1977, and in 2004 rea ...
... • The Kuiper Belt extends just beyond the orbit of Neptune and into the space of Eris. • Consists of comet and cometary material and other small objects – Trans Neptunian Objects • Many astronomers put the edge of the solar system to be at about 100 AU. • Voyager 1, launched in 1977, and in 2004 rea ...
PSC101-lecture12
... • Among these clouds the Hubble Space Telescope observed lumps and knots that appear to be new stars and planets being formed. ...
... • Among these clouds the Hubble Space Telescope observed lumps and knots that appear to be new stars and planets being formed. ...
2008F-ExtraSolarPlanets-Smith
... varied the mass of the planet to range from 1/300th the mass of Jupiter to ten times the mass of Jupiter. The data shows that fainter stars can be seen with planets of smaller mass. Analyzing this information using the center of mass and Kepler’s Law shows why this is true. As the mass of the planet ...
... varied the mass of the planet to range from 1/300th the mass of Jupiter to ten times the mass of Jupiter. The data shows that fainter stars can be seen with planets of smaller mass. Analyzing this information using the center of mass and Kepler’s Law shows why this is true. As the mass of the planet ...
Search for Life in the Universe
... – Semi-major axis: minimum:median:maximum = 0.02:1.0:5.9 AU – Solar system: Mercury:Earth:Jupiter = 0.4:1.0:5.2 AU ...
... – Semi-major axis: minimum:median:maximum = 0.02:1.0:5.9 AU – Solar system: Mercury:Earth:Jupiter = 0.4:1.0:5.2 AU ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19)
... slight dependence on other things, like its total metal abundance). Note: the “main sequence” is the location in the H-R diagram of all stars of different ...
... slight dependence on other things, like its total metal abundance). Note: the “main sequence” is the location in the H-R diagram of all stars of different ...
What theories account for the origin of the solar system?
... A. A Review of the Origin of Matter B. The Chemical Composition of the Solar Nebula C. The Condensation of Solids D. The Formation of Planetesimals E. The Growth of Protoplanets F. Is There a Jovian Problem? G. Explaining the Characteristics of the Solar System H. Clearing the Nebula IV. Planets Orb ...
... A. A Review of the Origin of Matter B. The Chemical Composition of the Solar Nebula C. The Condensation of Solids D. The Formation of Planetesimals E. The Growth of Protoplanets F. Is There a Jovian Problem? G. Explaining the Characteristics of the Solar System H. Clearing the Nebula IV. Planets Orb ...
answers2006_07_BC
... The Milky Way is a typical large spiral galaxy. Explain: how you can deduce simply from observations of the night sky (at a suitably dark site) that the Milky Way is a disc galaxy and that the Sun is located fairly close to the plane of the disc; ...
... The Milky Way is a typical large spiral galaxy. Explain: how you can deduce simply from observations of the night sky (at a suitably dark site) that the Milky Way is a disc galaxy and that the Sun is located fairly close to the plane of the disc; ...
Notes for Unit 5
... -note that when you look at an object in space, you are not seeing it as it presently looks. An example is the sun: it takes light about 8 minutes to travel from the sun to the earth, so when you see the sun (of course you would never look at the sun directly!!), you are seeing it as it appeared 8 m ...
... -note that when you look at an object in space, you are not seeing it as it presently looks. An example is the sun: it takes light about 8 minutes to travel from the sun to the earth, so when you see the sun (of course you would never look at the sun directly!!), you are seeing it as it appeared 8 m ...
The Solar System and its Place in the Galaxy
... encounters with giant molecular clouds in the galactic disk. Thus, older stars can be accelerated to higher mean velocities, as noted earlier. The reason(s) for the Sun's low velocity are not known. Velocity-altering encounters with giant molecular clouds occur with a typical frequency of once every ...
... encounters with giant molecular clouds in the galactic disk. Thus, older stars can be accelerated to higher mean velocities, as noted earlier. The reason(s) for the Sun's low velocity are not known. Velocity-altering encounters with giant molecular clouds occur with a typical frequency of once every ...