Kristen Turiano
... The Oort cloud is a nearly spherical collection of icy bodies about 1,000 times farther away from the sun than Pluto's orbit Gravitational interactions with passing stars can cause icy bodies in the Oort cloud to enter the inner solar system and become active comets. Comets lose ice and dust each ti ...
... The Oort cloud is a nearly spherical collection of icy bodies about 1,000 times farther away from the sun than Pluto's orbit Gravitational interactions with passing stars can cause icy bodies in the Oort cloud to enter the inner solar system and become active comets. Comets lose ice and dust each ti ...
Name________________________________________
... __________________. The name “comet” means “___________________________ star” in Greek. Most comets have two tails, a gas tail and a dust tail. Both tails usually point ____________________ from the sun due to the force of ______________________________ from the sun. A comet’s tail can be more than ...
... __________________. The name “comet” means “___________________________ star” in Greek. Most comets have two tails, a gas tail and a dust tail. Both tails usually point ____________________ from the sun due to the force of ______________________________ from the sun. A comet’s tail can be more than ...
Solar System Bodies PPT
... gas to somewhat liquid materials on what would be the “surface” Possible that the center is solid if differentiation is happening just as it did on Earth. ...
... gas to somewhat liquid materials on what would be the “surface” Possible that the center is solid if differentiation is happening just as it did on Earth. ...
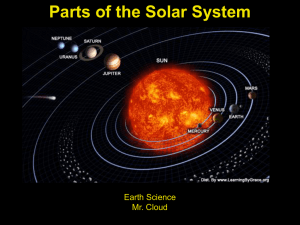
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the celestial objects
... Haumea, Makemake and Eris are recognised to be large enough to have been sorounded by their own gravity, and are thus termed dwarf planets. The hypothetical Oort cloud, which acts as the source for long-period comets, may also exsit at a distance roughly a thousand times beyond these regions. Within ...
... Haumea, Makemake and Eris are recognised to be large enough to have been sorounded by their own gravity, and are thus termed dwarf planets. The hypothetical Oort cloud, which acts as the source for long-period comets, may also exsit at a distance roughly a thousand times beyond these regions. Within ...
OORT CLOUD EXPLORER - DYNAMIC OCCULTATION
... Oort cloud is exceedingly difficult, owing to the D−4 flux dependence. At this time there is very little, perhaps zero, direct observational measurement of this structure. The object 90377 (Senda) is a candidate for membership, but with a semi-major axis of less than 1000AU this object is certainly ...
... Oort cloud is exceedingly difficult, owing to the D−4 flux dependence. At this time there is very little, perhaps zero, direct observational measurement of this structure. The object 90377 (Senda) is a candidate for membership, but with a semi-major axis of less than 1000AU this object is certainly ...
File
... Nebular Hypothesis • A young solar nebula collapses under the force of gravity • The nebula flattens and becomes warmer near its center causing nuclear fusion to begin. • Remnants from the formation of the sun begin to coalesce and form planetesimals • Matter with higher density remains in close pr ...
... Nebular Hypothesis • A young solar nebula collapses under the force of gravity • The nebula flattens and becomes warmer near its center causing nuclear fusion to begin. • Remnants from the formation of the sun begin to coalesce and form planetesimals • Matter with higher density remains in close pr ...
Ch. 3 Sec. 5 Notes
... *As the ice turns the head into gas, it leaves a tail trailing behind it made of gas and dust *Comet means "long-haired star" in Greek *A comet's tail can be more than 100 million km long and stretch across most of the sky Origin of Comets *Most comets are found in one of two regions: 1. Kuiper belt ...
... *As the ice turns the head into gas, it leaves a tail trailing behind it made of gas and dust *Comet means "long-haired star" in Greek *A comet's tail can be more than 100 million km long and stretch across most of the sky Origin of Comets *Most comets are found in one of two regions: 1. Kuiper belt ...
Slide 1
... • Fragments of rock made of material similar to the material that formed the planets. – More than 50,000 asteroids have been found in our solar system. ...
... • Fragments of rock made of material similar to the material that formed the planets. – More than 50,000 asteroids have been found in our solar system. ...
Worksheet 1
... d. small icy bodies in the extreme outer parts of the Solar System that are disturbed into orbits that bring them closer to the Sun e. luminous clouds in the Earth’s upper atmosphere created when a small asteroid is captured by the Earth’s gravitational force 27. The asteroid belt lies between the o ...
... d. small icy bodies in the extreme outer parts of the Solar System that are disturbed into orbits that bring them closer to the Sun e. luminous clouds in the Earth’s upper atmosphere created when a small asteroid is captured by the Earth’s gravitational force 27. The asteroid belt lies between the o ...
Minor Objects in the Solar System
... o Chunks of rocks (rocky leftover planetisimals) that can be pretty big (some are a couple km across) o Most travel on the asteroid belt o The asteroid belt was created when the Solar System was created o Jupiter’s gravity prevented a bunch of rocks from getting together to form a planet which is no ...
... o Chunks of rocks (rocky leftover planetisimals) that can be pretty big (some are a couple km across) o Most travel on the asteroid belt o The asteroid belt was created when the Solar System was created o Jupiter’s gravity prevented a bunch of rocks from getting together to form a planet which is no ...
Monday – October 29th - East Hanover Township School District
... 2 Structure of a Comet • Nucleus – 10 km “Dirty Snowball” ...
... 2 Structure of a Comet • Nucleus – 10 km “Dirty Snowball” ...
Chapter 6 Our Solar System and Its Origin
... energy. The dense materials collides with each other, causing the gas to heat up. Once the temperature and density gets high enough for nuclear fusion to start, a star is born. Spinning Smoothing of the random motions Conservation of angular momentum causes the in-falling material to spin faster and ...
... energy. The dense materials collides with each other, causing the gas to heat up. Once the temperature and density gets high enough for nuclear fusion to start, a star is born. Spinning Smoothing of the random motions Conservation of angular momentum causes the in-falling material to spin faster and ...
Chapter 6 Our Solar System and Its Origin
... energy. The dense materials collides with each other, causing the gas to heat up. Once the temperature and density gets high enough for nuclear fusion to start, a star is born. Spinning Smoothing of the random motions Conservation of angular momentum causes the in-falling material to spin faster a ...
... energy. The dense materials collides with each other, causing the gas to heat up. Once the temperature and density gets high enough for nuclear fusion to start, a star is born. Spinning Smoothing of the random motions Conservation of angular momentum causes the in-falling material to spin faster a ...
Astronomy Unit – Part 3: The Planets Terrestrial Planet – the four
... Astronomy Unit – Part 3: The Planets Terrestrial Planet – the four small, dense, rocky planets that orbit closest to the sun Astronomical Unit (AU) – the average distance between the sun and the Earth, or 150 million km. Prograde Rotation – counterclockwise spin of a planet. Retrograde Rotation – th ...
... Astronomy Unit – Part 3: The Planets Terrestrial Planet – the four small, dense, rocky planets that orbit closest to the sun Astronomical Unit (AU) – the average distance between the sun and the Earth, or 150 million km. Prograde Rotation – counterclockwise spin of a planet. Retrograde Rotation – th ...
... produced by fragmentation of the larger ones, are more numerous.The rocks normally remain in circular, stable orbits, but collisions, along with the gravitational influence of Jupiter, can throw them into narrow, unstable orbits. Then the asteroids may enter the inner solar system, where they pose a ...
... produced by fragmentation of the larger ones, are more numerous.The rocks normally remain in circular, stable orbits, but collisions, along with the gravitational influence of Jupiter, can throw them into narrow, unstable orbits. Then the asteroids may enter the inner solar system, where they pose a ...
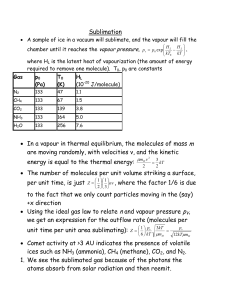
Sublimation • In a vapour in thermal equilibrium, the molecules of
... ¾ Must be only occaisionally ejected from the Oort cloud or Kuiper belt. ¾ Ejected from Oort cloud by gravitational perturbations from passing, nearby stars, or tidal action of the Milky Way disk. ¾ To account for the number of comets seen, Oort cloud must contain about 1012 comet nuclei! • Comets w ...
... ¾ Must be only occaisionally ejected from the Oort cloud or Kuiper belt. ¾ Ejected from Oort cloud by gravitational perturbations from passing, nearby stars, or tidal action of the Milky Way disk. ¾ To account for the number of comets seen, Oort cloud must contain about 1012 comet nuclei! • Comets w ...
It`s time for the human race to enter the solar system
... No description of our solar system would be complete without the most numerous objects in the solar system: asteroids and comets. Asteroids are small rocky bodies that orbit the Sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, primarily in the asteroid belt. Their orbits generally lie close to the plane ...
... No description of our solar system would be complete without the most numerous objects in the solar system: asteroids and comets. Asteroids are small rocky bodies that orbit the Sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, primarily in the asteroid belt. Their orbits generally lie close to the plane ...
Clues to the Origin of the Solar System
... across. At this time the objects are referred to as planetesimals. ! outer gas cooler than the inner gas !metal stuff can condense (freeze) at high temperatures while volatile stuff condenses at lower temps !at Jupiter temperature cool enough to freeze water further out ammonia and methane freezing ...
... across. At this time the objects are referred to as planetesimals. ! outer gas cooler than the inner gas !metal stuff can condense (freeze) at high temperatures while volatile stuff condenses at lower temps !at Jupiter temperature cool enough to freeze water further out ammonia and methane freezing ...
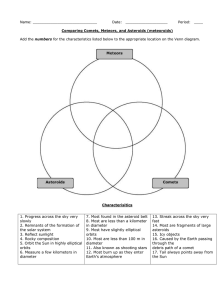
Microsoft Word - students_diffe
... 8. Most are less than a kilometer in diameter 9. Most have slightly elliptical orbits 10. Most are less than 100 m in diameter 11. Also known as shooting stars 12. Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere ...
... 8. Most are less than a kilometer in diameter 9. Most have slightly elliptical orbits 10. Most are less than 100 m in diameter 11. Also known as shooting stars 12. Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere ...
FORMATION OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... get larger by their gravitational pull attracting more matter creating PLANETS accreation ...
... get larger by their gravitational pull attracting more matter creating PLANETS accreation ...
Oort cloud

The Oort cloud (/ˈɔrt/ or /ˈʊərt/) or Öpik–Oort cloud, named after Dutch astronomer Jan Oort and Estonian astronomer Ernst Öpik, is a theoretical spherical cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals believed to surround the Sun at a distance of up to around 100,000 AU (2 ly). This places it at almost half of the distance to Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun, and in interstellar space. The Kuiper belt and the scattered disc, the other two reservoirs of trans-Neptunian objects, are less than one thousandth as far from the Sun as the Oort cloud. The outer limit of the Oort cloud defines the cosmographical boundary of the Solar System and the region of the Sun's gravitational dominance.The Oort cloud is thought to comprise two regions: a spherical outer Oort cloud and a disc-shaped inner Oort cloud, or Hills cloud. Objects in the Oort cloud are largely composed of ices, such as water, ammonia, and methane.Astronomers conjecture that the matter composing the Oort cloud formed closer to the Sun and was scattered far into space by the gravitational effects of the giant planets early in the Solar System's evolution. Although no confirmed direct observations of the Oort cloud have been made, it may be the source of all long-period and Halley-type comets entering the inner Solar System, and many of the centaurs and Jupiter-family comets as well. The outer Oort cloud is only loosely bound to the Solar System, and thus is easily affected by the gravitational pull both of passing stars and of the Milky Way itself. These forces occasionally dislodge comets from their orbits within the cloud and send them towards the inner Solar System. Based on their orbits, most of the short-period comets may come from the scattered disc, but some may still have originated from the Oort cloud.