* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comets - Astronomy @ Walton High School
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Halley's Comet wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
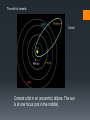
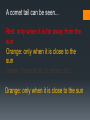
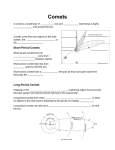
West McNaught Lovejoy Bennet Hyakutake Discuss with the person next to you. What do you think this lesson will be about? Hale-Bopp Halley’s http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mZG2nyUXiY Comet •A comet is a relatively small solar system body that orbits the Sun. When close enough to the Sun they display a visible coma (a fuzzy outline or atmosphere due to solar radiation) and sometimes a tail. Asteroid •Asteroids are small solar system bodies that orbit the Sun. Made of rock and metal, they can also contain organic compounds. Asteroids are similar to comets but do not have a visible coma (fuzzy outline and tail) like comets do. Meteoroid •A meteoroid is a small rock or particle of debris in our solar system. They range in size from dust to around 10 metres in diameter (larger objects are usually referred to as asteroids). Meteor A meteoroid that burns up as it passes through the Earth’s atmosphere is known as a meteor. If you’ve ever looked up at the sky at night and seen a streak of light or ‘shooting star’ what you are actually seeing is a meteor. Meteorite •A meteoroid that survives falling through the Earth’s atmosphere and colliding with the Earth’s surface is known as a meteorite. Comets Learning Outcomes • To distinguish between the orbits of planets and those of comets. • To describe the likely origins of short-period and long-period comets. • To describe the structure of a typical comet and account for its tails. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsTE6pV 4wpU Your task is to create a model of a comet using the materials provided. It should clearly show the main features of the comet. Learning Outcomes • To distinguish between the orbits of planets and those of comets. • To describe the likely origins of short-period and long-period comets. • To describe the structure of a typical comet and account for its tails. Complete the sheet on comets. You may use the internet to help you. The orbit of comets: Comet Comets orbit in an (eccentric) ellipse. The sun is at one focus (not in the middle). A comet has two tails. A dust tail and a gas (or ion) tail. Learning Outcomes • To distinguish between the orbits of planets and those of comets. • To describe the likely origins of short-period and long-period comets. • To describe the structure of a typical comet and account for its tails. Write a short story to summarise what you have done this lesson. What have you learnt, how did you learn about it, what did you do? Long period comets are thought to originate in the... Red: Kuiper Belt Orange: Asteroid Belt Green: Oort Cloud Green: Oort Cloud Comets orbit in: Red: an eccentric ellipse. Orange: a hyperbola. Green: a circle Red: an eccentric ellipse. The gas (ion) tail of a comet points... Red: towards the sun Orange: in the opposite direction to the direction the comet is moving in. Green: away from the sun. Green: away from the sun. Short period comets are thought to originate in the... Red: Kuiper Belt Orange: Asteroid Belt Green: Oort Cloud Red: Kuiper Belt The nucleus of a comet is surrounded by its... Red: tail Orange: coma Green: arm Orange: coma A comet tail can be seen... Red: only when it is far away from the sun Orange: only when it is close to the sun Green: throughout its entire orbit Orange: only when it is close to the sun