The Planet with Three Suns
... Imagine a world where each season lasts over 100 years and you have three shadows at once. Now meet HD 131399ab, a newly discovered exo-planet with these exact quirks! (An exo-planet is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. T ...
... Imagine a world where each season lasts over 100 years and you have three shadows at once. Now meet HD 131399ab, a newly discovered exo-planet with these exact quirks! (An exo-planet is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. T ...
Earth Science Chapter Two: What Makes Up the Solar System
... 14. What makes Saturn easy to identify? 15. Why does Uranus appear to roll like a ball? 16. Which planet is considered Neptune’s twin planet? Lesson Seven: Other Objects in the Solar System 1. What is another name for rocky objects that orbit the sun? 2. Which object is round, orbits the sun, and i ...
... 14. What makes Saturn easy to identify? 15. Why does Uranus appear to roll like a ball? 16. Which planet is considered Neptune’s twin planet? Lesson Seven: Other Objects in the Solar System 1. What is another name for rocky objects that orbit the sun? 2. Which object is round, orbits the sun, and i ...
Instructor Notes
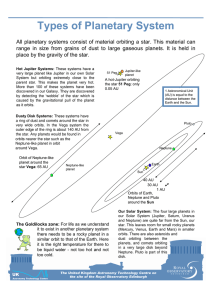
... system consisted of 4 Jovian (Jupiter‐like) planets and Pluto. An asteroid belt separated the inner and outer solar systems, and there were comets somewhere past the planets of the outer solar system ...
... system consisted of 4 Jovian (Jupiter‐like) planets and Pluto. An asteroid belt separated the inner and outer solar systems, and there were comets somewhere past the planets of the outer solar system ...
How has the model of the solar system changed over time?
... Kepler became convinced the ellipse was the shape of planet orbits, not the circle. This idea went against the 2,000 years of belief! Kepler had a hard time convincing other scientists of his time that planet orbits are not circles. Even the great scientist, Galileo, disagreed with Kepler. ...
... Kepler became convinced the ellipse was the shape of planet orbits, not the circle. This idea went against the 2,000 years of belief! Kepler had a hard time convincing other scientists of his time that planet orbits are not circles. Even the great scientist, Galileo, disagreed with Kepler. ...
Solar System
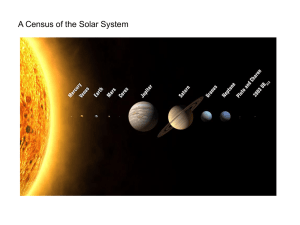
... – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – closest to the sun – composed primarily of rock and ...
... – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – closest to the sun – composed primarily of rock and ...
Solar System Overview-Sec.1
... – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – closest to the sun – composed primarily of rock and ...
... – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – closest to the sun – composed primarily of rock and ...
The solar system
... The solar system • The solar system includes the Sun, eight major planets, and their moons. • A large number of smaller objects are also part of the solar system, including dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteors. ...
... The solar system • The solar system includes the Sun, eight major planets, and their moons. • A large number of smaller objects are also part of the solar system, including dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteors. ...
The Solar System
... scientific observations and allows us to predict the movement of the planets is called the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go around it. We say that the planets are in orbit around the Sun. ...
... scientific observations and allows us to predict the movement of the planets is called the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go around it. We say that the planets are in orbit around the Sun. ...
Chapter 7 Solar System study guide
... Solar flares – explosion/ribbon of fire Solar prominences – ribbon of fire/gases – last days or months Fusion of H and He makes energy Sun has the most gravity Lesson two Inner Planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars Outer Planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Pluto – dwarf planet Planets r ...
... Solar flares – explosion/ribbon of fire Solar prominences – ribbon of fire/gases – last days or months Fusion of H and He makes energy Sun has the most gravity Lesson two Inner Planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars Outer Planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Pluto – dwarf planet Planets r ...
Extrasolar planets
... Period = 3.5 days => orbital distance of 0.05 AU Like the planet around 51Peg, the planet was found to be large and orbiting tightly around the star – these are also known as “hot Jupiters”. Mass = 0.62MJ ...
... Period = 3.5 days => orbital distance of 0.05 AU Like the planet around 51Peg, the planet was found to be large and orbiting tightly around the star – these are also known as “hot Jupiters”. Mass = 0.62MJ ...
Document
... Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The outer planets are the planets after the asteroid belt. ...
... Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The outer planets are the planets after the asteroid belt. ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun and Stars
... 17. How is distance measured in the universe? __________________________________________ 18. In which galaxy do we live? __________________________________What kind of galaxy is it? ___________ At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered ...
... 17. How is distance measured in the universe? __________________________________________ 18. In which galaxy do we live? __________________________________What kind of galaxy is it? ___________ At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered ...
Solar System - Spring Branch ISD
... The four large planets beyond the asteroid ___________ belt are Jupiter called gas giants. These planets are _______, Neptune These planets ________, Saturn _________, Uranus and ________. are gaseous in nature, composed of mostly hydrogen and helium ____________________. ...
... The four large planets beyond the asteroid ___________ belt are Jupiter called gas giants. These planets are _______, Neptune These planets ________, Saturn _________, Uranus and ________. are gaseous in nature, composed of mostly hydrogen and helium ____________________. ...
b. Compare the similarities and differences of planets to the stars in
... Compared to the stars, the planets in our solar system are _________________. a. much smaller b. closer to Earth c. the same distance apart d. farther away from Earth Answer: a Unlike the Sun, the planets in our solar system __________________. a. radiate light b. produce heat c. have elliptical orb ...
... Compared to the stars, the planets in our solar system are _________________. a. much smaller b. closer to Earth c. the same distance apart d. farther away from Earth Answer: a Unlike the Sun, the planets in our solar system __________________. a. radiate light b. produce heat c. have elliptical orb ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 5 - 9th Edition 2. Pluto is most
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
Introduction to the Solar System
... The distance between stars (and galaxies) is HUGE so we measure it in light years. Light Years is the distance light will travel in a year **very important**: a light year is not a time, but a distance! ...
... The distance between stars (and galaxies) is HUGE so we measure it in light years. Light Years is the distance light will travel in a year **very important**: a light year is not a time, but a distance! ...
5-SolarSystem
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E di ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E di ...
Monday – October 29th - East Hanover Township School District
... 2) Both must be large enough that their own gravity pulls them into the shapes of spheres; this rules out numerous smaller bodies like most asteroids, many of which have irregular shapes. 3) Planets clear smaller objects out of their orbits by sucking the small bodies into themselves or flinging the ...
... 2) Both must be large enough that their own gravity pulls them into the shapes of spheres; this rules out numerous smaller bodies like most asteroids, many of which have irregular shapes. 3) Planets clear smaller objects out of their orbits by sucking the small bodies into themselves or flinging the ...
How do the planets stay in orbit around the sun?
... cloud of gas and dust which spun around a newly forming star, our sun, at its center. The planets all formed from this spinning diskshaped cloud, and continued this rotating course around the sun after they were formed. The gravity of the sun keeps the planets in their orbits. They stay in their orb ...
... cloud of gas and dust which spun around a newly forming star, our sun, at its center. The planets all formed from this spinning diskshaped cloud, and continued this rotating course around the sun after they were formed. The gravity of the sun keeps the planets in their orbits. They stay in their orb ...
Planet

A planet (from Ancient Greek ἀστήρ πλανήτης (astēr planētēs), or πλάνης ἀστήρ (plánēs astēr), meaning ""wandering star"") is an astronomical object orbiting a star, brown dwarf, or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science, mythology, and religion. Several planets in the Solar System can be seen with the naked eye. These were regarded by many early cultures as divine, or as emissaries of deities. As scientific knowledge advanced, human perception of the planets changed, incorporating a number of disparate objects. In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially adopted a resolution defining planets within the Solar System. This definition is controversial because it excludes many objects of planetary mass based on where or what they orbit. Although eight of the planetary bodies discovered before 1950 remain ""planets"" under the modern definition, some celestial bodies, such as Ceres, Pallas, Juno, Vesta (each an object in the solar asteroid belt), and Pluto (the first trans-Neptunian object discovered), that were once considered planets by the scientific community are no longer viewed as such.The planets were thought by Ptolemy to orbit Earth in deferent and epicycle motions. Although the idea that the planets orbited the Sun had been suggested many times, it was not until the 17th century that this view was supported by evidence from the first telescopic astronomical observations, performed by Galileo Galilei. By careful analysis of the observation data, Johannes Kepler found the planets' orbits were not circular but elliptical. As observational tools improved, astronomers saw that, like Earth, the planets rotated around tilted axes, and some shared such features as ice caps and seasons. Since the dawn of the Space Age, close observation by space probes has found that Earth and the other planets share characteristics such as volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology.Planets are generally divided into two main types: large low-density giant planets, and smaller rocky terrestrials. Under IAU definitions, there are eight planets in the Solar System. In order of increasing distance from the Sun, they are the four terrestrials, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, then the four giant planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Six of the planets are orbited by one or more natural satellites.More than a thousand planets around other stars (""extrasolar planets"" or ""exoplanets"") have been discovered in the Milky Way: as of 1 October 2015, 1968 known extrasolar planets in 1248 planetary systems (including 490 multiple planetary systems), ranging in size from just above the size of the Moon to gas giants about twice as large as Jupiter. On December 20, 2011, the Kepler Space Telescope team reported the discovery of the first Earth-sized extrasolar planets, Kepler-20e and Kepler-20f, orbiting a Sun-like star, Kepler-20. A 2012 study, analyzing gravitational microlensing data, estimates an average of at least 1.6 bound planets for every star in the Milky Way.Around one in five Sun-like stars is thought to have an Earth-sized planet in its habitable zone.