Planets of Our Solar System
... • No atmosphere due to – low gravitational pull (it’s the smallest planet) – high daytime temperatures ...
... • No atmosphere due to – low gravitational pull (it’s the smallest planet) – high daytime temperatures ...
Chapter 16: The Origin of the Solar System RQ 16
... solids. At these inner orbits, material with lower boiling points (lighter elements) could not be collected, since it still was in its gaseous state. This way the inner planets selectively were made out of heavy elements and thus have now high densities. At greater distance from the center, matter l ...
... solids. At these inner orbits, material with lower boiling points (lighter elements) could not be collected, since it still was in its gaseous state. This way the inner planets selectively were made out of heavy elements and thus have now high densities. At greater distance from the center, matter l ...
Solar.System
... discovery in 1930, and nothing of similar size was discovered for several decades. • Now other large objects have been discovered in Kuiper belt, including Eris. • The International Astronomical Union (IAU) now classifies Pluto and Eris as dwarf planets. • Dwarf planets have not cleared most other o ...
... discovery in 1930, and nothing of similar size was discovered for several decades. • Now other large objects have been discovered in Kuiper belt, including Eris. • The International Astronomical Union (IAU) now classifies Pluto and Eris as dwarf planets. • Dwarf planets have not cleared most other o ...
Table of Facts - Portfolio using Bloom`s Revised Taxonomy
... Saturn has two prominent rings - A and B and, one faint ring (C) which can be seen from Earth Saturn has 53 named satellites If Saturn’s rings were compressed into one it would be no more than 100 km in width Saturn's outermost ring (F), is a complex structure made up of several smaller rings along ...
... Saturn has two prominent rings - A and B and, one faint ring (C) which can be seen from Earth Saturn has 53 named satellites If Saturn’s rings were compressed into one it would be no more than 100 km in width Saturn's outermost ring (F), is a complex structure made up of several smaller rings along ...
Lecture 5 - Orbits, Sizes, Precession
... epicycle of Venus centered on a line between the Earth and the Sun • Then, Venus can never be the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth, so it can never have gibbous phases – no “full Venus”. ...
... epicycle of Venus centered on a line between the Earth and the Sun • Then, Venus can never be the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth, so it can never have gibbous phases – no “full Venus”. ...
The Sun: close-up of a spectral class G main sequence star
... The Sun: close-up of a spectral class G main sequence star ...
... The Sun: close-up of a spectral class G main sequence star ...
PH507 - University of Kent
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
Terrestrial planets
... Comets: a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust, which for some reason didn't get incorporated into planets when the solar system was formed. This makes them very interesting as samples of the early history of the solar system. ...
... Comets: a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust, which for some reason didn't get incorporated into planets when the solar system was formed. This makes them very interesting as samples of the early history of the solar system. ...
Solar System: 3rd Grade
... Have each group sign into www.tinkercad.com using one computer per group. Go over what a plane is in geometry and have discuss how to use a plane and what it is for. Have them discuss how big each square is in the plane. Ask how many millimeters are in a centimeter. Have each group start designing t ...
... Have each group sign into www.tinkercad.com using one computer per group. Go over what a plane is in geometry and have discuss how to use a plane and what it is for. Have them discuss how big each square is in the plane. Ask how many millimeters are in a centimeter. Have each group start designing t ...
Unit Test - Dnyansagar Coaching Classes, Ahmednagar
... i) Venus has 3 moons. ii) The Sun is the center of our solar system. iii) Uranus rotates from west to east. iv) Like the moon, Venus also has the phases. (D) Find odd man out. 1) Mercury, Venus, Mars, Sirius 2) Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn 3) Sun, Sirius, Pole Star, Venus 4) Mriga, Punarvasu, Ashl ...
... i) Venus has 3 moons. ii) The Sun is the center of our solar system. iii) Uranus rotates from west to east. iv) Like the moon, Venus also has the phases. (D) Find odd man out. 1) Mercury, Venus, Mars, Sirius 2) Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn 3) Sun, Sirius, Pole Star, Venus 4) Mriga, Punarvasu, Ashl ...
Orbits of the planets - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... constant speed around the Sun B) an illusion that takes place when a planet is at its maximum distance from the Sun C) when a planet slows down when at large distances from the Sun D) a dance move ...
... constant speed around the Sun B) an illusion that takes place when a planet is at its maximum distance from the Sun C) when a planet slows down when at large distances from the Sun D) a dance move ...
The Sky Above
... Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and has a temperature of 6,000°C (11,000°F). ...
... Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible layer is called the photosphere and has a temperature of 6,000°C (11,000°F). ...
View Presentation Slides
... Stars have “life cycles”. They are “born” and they “die” but are not alive like us. Stars like the Sun “die” by “puffing” off their outer layers of gas and dust. This process creates a beautiful variety of NEBULAE in the Milky Way GALAXY. ...
... Stars have “life cycles”. They are “born” and they “die” but are not alive like us. Stars like the Sun “die” by “puffing” off their outer layers of gas and dust. This process creates a beautiful variety of NEBULAE in the Milky Way GALAXY. ...
day 1 hand out - the sun
... The most important star for Earth is the one at the centre of our solar system: the sun. It provides the energy needed by plants and animals, and its gravitational pull keeps the Earth in a steady orbit. By studying the Sun, we also learn about other stars. Since the sun is so close to Earth, it is ...
... The most important star for Earth is the one at the centre of our solar system: the sun. It provides the energy needed by plants and animals, and its gravitational pull keeps the Earth in a steady orbit. By studying the Sun, we also learn about other stars. Since the sun is so close to Earth, it is ...
Regents Review Questions.Unit 2.Astronomy
... 15 Describe the relationship between the distance from the Sun and the period of revolution for these four planets. Astronomers have discovered more than 400 planets outside of our solar system. The first extrasolar planet was detected in 1995 orbiting a star known as 51 Pegasi, which is similar in ...
... 15 Describe the relationship between the distance from the Sun and the period of revolution for these four planets. Astronomers have discovered more than 400 planets outside of our solar system. The first extrasolar planet was detected in 1995 orbiting a star known as 51 Pegasi, which is similar in ...
Name_______________________Period_________Date
... The disk of dust and gas that formed the Sun and planets is known as the solar nebula. Dense concentration at center became the Sun. Temperature differed, Hotter at center and cooler at edges disk Due to temp differences different compounds were able to condense depending on distance from Su ...
... The disk of dust and gas that formed the Sun and planets is known as the solar nebula. Dense concentration at center became the Sun. Temperature differed, Hotter at center and cooler at edges disk Due to temp differences different compounds were able to condense depending on distance from Su ...
The Sun
... million tons of hydrogen – Converting ~ 4 million tons into energy – As hydrogen is consumed, helium is produced forming the solar core • Core is continually growing in size • ~ 100 billion years of fuel left • The sun will remain it’s currents size ~ 10 billion years before it grows in size and eve ...
... million tons of hydrogen – Converting ~ 4 million tons into energy – As hydrogen is consumed, helium is produced forming the solar core • Core is continually growing in size • ~ 100 billion years of fuel left • The sun will remain it’s currents size ~ 10 billion years before it grows in size and eve ...
Some Basic Facts to Know
... For electron to move from inner orbit to one further out, it must gain exactly the energy difference between the orbits Î Absorb photon with correct energy Electron falling to lower level Î can emit photon with energy ...
... For electron to move from inner orbit to one further out, it must gain exactly the energy difference between the orbits Î Absorb photon with correct energy Electron falling to lower level Î can emit photon with energy ...
Astronomy Quiz 2
... 9. The objects people refer to as shooting stars are often meteors burning up in Earth’s atmosphere. If a meteor does not burn up but strikes Earth, it is called a. An asteroid c. A meteoroid b. A meteorite d. A satellite 10. Rocky bodies that orbit between Mars and Jupiter are _______________. a. ...
... 9. The objects people refer to as shooting stars are often meteors burning up in Earth’s atmosphere. If a meteor does not burn up but strikes Earth, it is called a. An asteroid c. A meteoroid b. A meteorite d. A satellite 10. Rocky bodies that orbit between Mars and Jupiter are _______________. a. ...
Centre of Mass
... • For life to exist on a palnet, it must also be in the habitable zone. This is the region in the solar system which is neither too hot nor too cold, but just right. Astronomers believe that in other solar systems, too, such habitable zones exist and life is more probable in those planets which fall ...
... • For life to exist on a palnet, it must also be in the habitable zone. This is the region in the solar system which is neither too hot nor too cold, but just right. Astronomers believe that in other solar systems, too, such habitable zones exist and life is more probable in those planets which fall ...
Are Cool Stars Popular? Better Ask Sol
... Understanding how this activity affects planets in our solar system is important for determining if far away planet systems could support life. Yet, 70% of the observable universe is made up of red stars that are too dim to see with the naked eye, because they have cooler surfaces and are less than ...
... Understanding how this activity affects planets in our solar system is important for determining if far away planet systems could support life. Yet, 70% of the observable universe is made up of red stars that are too dim to see with the naked eye, because they have cooler surfaces and are less than ...
True or False: If the statement is true, write “True”, if it is “False” tell
... _____ The Earth’s axis always points in the same direction. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Mercury is the hottest planet with the highest average surface temperature. ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... _____ The Earth’s axis always points in the same direction. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Mercury is the hottest planet with the highest average surface temperature. ________________________________________________________________________ ...
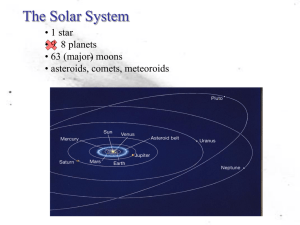
Solar System

The Solar System comprises the Sun and the planetary system that orbits it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets, with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies such as comets and asteroids. Of those that orbit the Sun indirectly, two are larger than the smallest planet.The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terrestrial planets, being primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets are giant planets, being substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are gas giants, being composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus and Neptune, are ice giants, being composed largely of substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, called ices, such as water, ammonia and methane. All planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a nearly flat disc called the ecliptic.The Solar System also contains smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, mostly contains objects composed, like the terrestrial planets, of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc, populations of trans-Neptunian objects composed mostly of ices, and beyond them a newly discovered population of sednoids. Within these populations are several dozen to possibly tens of thousands of objects large enough to have been rounded by their own gravity. Such objects are categorized as dwarf planets. Identified dwarf planets include the asteroid Ceres and the trans-Neptunian objects Pluto and Eris. In addition to these two regions, various other small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust, freely travel between regions. Six of the planets, at least three of the dwarf planets, and many of the smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellites, usually termed ""moons"" after the Moon. Each of the outer planets is encircled by planetary rings of dust and other small objects.The solar wind, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region in the interstellar medium known as the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of interstellar wind; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud, which is believed to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way.