Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... following in your description: hyperpolarization, depolarization, threshold, and refractory period. 7. Describe how the nodes of Ranvier speed up transmission of a nerve signal. 8. In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. Discuss how this affects nervous sy ...
... following in your description: hyperpolarization, depolarization, threshold, and refractory period. 7. Describe how the nodes of Ranvier speed up transmission of a nerve signal. 8. In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. Discuss how this affects nervous sy ...
BIOLOGY 3201
... 2. __?__ are three protective membranes surrounding the brain . 3. grey matter: brownish-grey nerve tissue consisting of mainly __?__ within the brain and spinal cord 4. Which part of the autonomic nervous system helps us respond to stress? 5. Which part of the peripheral nervous system do we have c ...
... 2. __?__ are three protective membranes surrounding the brain . 3. grey matter: brownish-grey nerve tissue consisting of mainly __?__ within the brain and spinal cord 4. Which part of the autonomic nervous system helps us respond to stress? 5. Which part of the peripheral nervous system do we have c ...
Action Potential Web Quest
... Play the game “Make A Mad Mad Mad Neuron” with Dr. Dedristein (use headphones if you have some) 4. My score was _____________ because _________________________________________ Part 2 – Other Cells in the Brain & Reward Pathway Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/neuroscience/braincells/ Ans ...
... Play the game “Make A Mad Mad Mad Neuron” with Dr. Dedristein (use headphones if you have some) 4. My score was _____________ because _________________________________________ Part 2 – Other Cells in the Brain & Reward Pathway Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/neuroscience/braincells/ Ans ...
Nociceptive system
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Topic iQuiz
... – spinal cord; 3 – motor neuron; 4 – muscle; 5 – sensory neurons. The correct sequence of events is … ...
... – spinal cord; 3 – motor neuron; 4 – muscle; 5 – sensory neurons. The correct sequence of events is … ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... is not controlled by mirror-neurons, but by coded electrochemical signals. This research is not new; the contemporary of Friedrich Nietzsche, the German neurologist Heinrich Lissauer, studied the retinas of eyes detail. Visual object agnosia and MRI scans have illuminated a paradox first illuminated ...
... is not controlled by mirror-neurons, but by coded electrochemical signals. This research is not new; the contemporary of Friedrich Nietzsche, the German neurologist Heinrich Lissauer, studied the retinas of eyes detail. Visual object agnosia and MRI scans have illuminated a paradox first illuminated ...
Chapter 2
... releases hormones or releasing factors which in turn cause pituitary gland to release its hormones ...
... releases hormones or releasing factors which in turn cause pituitary gland to release its hormones ...
2. Peripheral Nervous System
... 3) Repolarization – K+ moves outside, Na+ stays inside ◦ After inside flooded with NA+, K+ gates open and let K+ Out (while NA+ gates close) ...
... 3) Repolarization – K+ moves outside, Na+ stays inside ◦ After inside flooded with NA+, K+ gates open and let K+ Out (while NA+ gates close) ...
PNS Study Guide
... 1. What does your nervous system do for your body? 2. Describe the 3 steps of normal brain activity. Include the 3 steps and how they communicate to other parts of the nervous system. 3. What type of signals are impulses? Are they slow or rapid signals? 4. What are the 2 structural classifications o ...
... 1. What does your nervous system do for your body? 2. Describe the 3 steps of normal brain activity. Include the 3 steps and how they communicate to other parts of the nervous system. 3. What type of signals are impulses? Are they slow or rapid signals? 4. What are the 2 structural classifications o ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities can have profound ef ...
... After passing through the empty synaptic cleft the neurotransmitters attach or bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron These neurotransmitters can then make the receiving neuron either more or less likely to fire It is in this infinitesimally small space that irregularities can have profound ef ...
Nervous System = communication conduit b/w brain
... Myelin sheath has gaps (nodes of Ranvier) along axon Na+/K+ cannot diffuse through myelin but they can reach plasma membrane at these nodes This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels length of axon. Some neurons have myelin, some do not ...
... Myelin sheath has gaps (nodes of Ranvier) along axon Na+/K+ cannot diffuse through myelin but they can reach plasma membrane at these nodes This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels length of axon. Some neurons have myelin, some do not ...
4.BiologicalPsycholo..
... scale is exaggerated here. Such measurements require ultra-small electrodes, as described later in this chapter.) The inside of an axon at rest is about -60 to -70 millivolts, compared with the outside. Electrochemical changes in a neuron generate an action potential. When positively charged sodium ...
... scale is exaggerated here. Such measurements require ultra-small electrodes, as described later in this chapter.) The inside of an axon at rest is about -60 to -70 millivolts, compared with the outside. Electrochemical changes in a neuron generate an action potential. When positively charged sodium ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... o True Sodium ions are more numerous outside the cell and depolarize the neurons when they enter o False There are 5X more neurons than glial cells o Trace information from spines to the terminal boutons ▪ Information arrives at the spines/ dendrites. It is than summed at the soma and than sen ...
... o True Sodium ions are more numerous outside the cell and depolarize the neurons when they enter o False There are 5X more neurons than glial cells o Trace information from spines to the terminal boutons ▪ Information arrives at the spines/ dendrites. It is than summed at the soma and than sen ...
THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... Serotonin is a neurotransmitter and it has a connection with depression. It functions in humans through the regulation of intestinal movements, the regulation of mood and sleep, and cognitive functions including memory. Therefore, it affects humans and animals by having a role in their social behavi ...
... Serotonin is a neurotransmitter and it has a connection with depression. It functions in humans through the regulation of intestinal movements, the regulation of mood and sleep, and cognitive functions including memory. Therefore, it affects humans and animals by having a role in their social behavi ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it less likely. Particular NTs seem to effect particular behavior and emotions. Dopamine = affects learning, attention and emotion (alertness and movement); excess D activity i ...
... NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it less likely. Particular NTs seem to effect particular behavior and emotions. Dopamine = affects learning, attention and emotion (alertness and movement); excess D activity i ...
PPT
... Neural evidence: Mirror neurons • Gallese et al. (1996) found “mirror” neurons in the monkey motor cortex, activated when – an action was carried out – the same action (or a similar one) was seen. ...
... Neural evidence: Mirror neurons • Gallese et al. (1996) found “mirror” neurons in the monkey motor cortex, activated when – an action was carried out – the same action (or a similar one) was seen. ...
Motor Neurons
... • Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. – Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping’ the gaps in an axon). ...
... • Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between schwann cells. – Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping’ the gaps in an axon). ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... years of evolution. Because animals, and thus brains, evolved on this planet, they express also the selective biases imposed by the physics of our world and environment: light-dark cycles, natural images and sounds, to take only a few examples, are not randomly distributed; they have quite specific ...
... years of evolution. Because animals, and thus brains, evolved on this planet, they express also the selective biases imposed by the physics of our world and environment: light-dark cycles, natural images and sounds, to take only a few examples, are not randomly distributed; they have quite specific ...
C. elegans
... Motor neurons are in the ventral horn, & sensory neurons are in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord ...
... Motor neurons are in the ventral horn, & sensory neurons are in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord ...
Slide 1
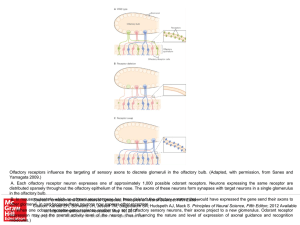
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
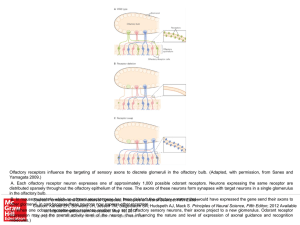
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... Our brains mediate everything we perceive, feel, decide, and do. This is accomplished by an incredibly densely packed network of hundreds of billions of neurons, which fall into perhaps hundreds of different classes, defined by their shape and the molecules they contain. Each computes in concert wit ...
... Our brains mediate everything we perceive, feel, decide, and do. This is accomplished by an incredibly densely packed network of hundreds of billions of neurons, which fall into perhaps hundreds of different classes, defined by their shape and the molecules they contain. Each computes in concert wit ...
Visual vs. Language-based Thinking
... effectiveness of dynamic compared to static visualizations. However, this remains an hypothesis to be tested, for which interdisciplinary research is required. Such research might also shed light on the relation between the mirror neuron system and working memory. We assume that visualizations depic ...
... effectiveness of dynamic compared to static visualizations. However, this remains an hypothesis to be tested, for which interdisciplinary research is required. Such research might also shed light on the relation between the mirror neuron system and working memory. We assume that visualizations depic ...