FREE Sample Here
... like the twisted branches of a tree, receive messages from other neurons. On the opposite side of the cell body is a long, slim, tube-like extension called an axon. The axon carries messages received by the dendrites to other neurons. Axons end in small bulges called terminal buttons, which send mes ...
... like the twisted branches of a tree, receive messages from other neurons. On the opposite side of the cell body is a long, slim, tube-like extension called an axon. The axon carries messages received by the dendrites to other neurons. Axons end in small bulges called terminal buttons, which send mes ...
The Study of the Nervous System in Psychology
... like the twisted branches of a tree, receive messages from other neurons. On the opposite side of the cell body is a long, slim, tube-like extension called an axon. The axon carries messages received by the dendrites to other neurons. Axons end in small bulges called terminal buttons, which send mes ...
... like the twisted branches of a tree, receive messages from other neurons. On the opposite side of the cell body is a long, slim, tube-like extension called an axon. The axon carries messages received by the dendrites to other neurons. Axons end in small bulges called terminal buttons, which send mes ...
Intelligent agents capable of developing memory of their environment
... [Husbands et al., 1994]). The network was defined in a 2-D space, where a collection of artificial neurons are distributed with growing and branching axons. The genetic code inside them specifies the intructions for axonal growth and branching in neurons. Connections between neurons are made when an ...
... [Husbands et al., 1994]). The network was defined in a 2-D space, where a collection of artificial neurons are distributed with growing and branching axons. The genetic code inside them specifies the intructions for axonal growth and branching in neurons. Connections between neurons are made when an ...
Synaptic Specificity in Frog Sympathetic Ganglia During
... elicited directly by a depolarizing current pulse (Purves, 1975). Some neurons appeared to receive both a B fiber and a C fiber input, with synaptic potentials of each having similar size and waveform. In such cases, the possibility that branches of one axon were present in both preganglionic roots ...
... elicited directly by a depolarizing current pulse (Purves, 1975). Some neurons appeared to receive both a B fiber and a C fiber input, with synaptic potentials of each having similar size and waveform. In such cases, the possibility that branches of one axon were present in both preganglionic roots ...
Resonate-and-fire neurons
... channels, there could be thousands of different conductance-based mechanisms for excitability and spiking, and, hence, thousands of biophysically accurate models of spiking neurons. Most such models can be studied using dynamical systems theory. For example, a rest state corresponds to an equilibriu ...
... channels, there could be thousands of different conductance-based mechanisms for excitability and spiking, and, hence, thousands of biophysically accurate models of spiking neurons. Most such models can be studied using dynamical systems theory. For example, a rest state corresponds to an equilibriu ...
pdf 2.5M
... conditions of the population. One can observe multiple steady states, including global quiescence and global saturation, as well as a variety of oscillatory regimes for the electrical activity of the neurons. Although a single neuron, under the present model, does not oscillate, a coupled population ...
... conditions of the population. One can observe multiple steady states, including global quiescence and global saturation, as well as a variety of oscillatory regimes for the electrical activity of the neurons. Although a single neuron, under the present model, does not oscillate, a coupled population ...
Molecular Underpinnings of Motor Pattern Generation: Differential
... The results were similar to those obtained with the initial anti-Shaker antibody described in Results (data not shown). Quantitation of anti-Shal staining intensit y. Staining intensity was semiquantitatively measured with the N IH Image program on a Macintosh computer (Apple Computers, Cupertino, C ...
... The results were similar to those obtained with the initial anti-Shaker antibody described in Results (data not shown). Quantitation of anti-Shal staining intensit y. Staining intensity was semiquantitatively measured with the N IH Image program on a Macintosh computer (Apple Computers, Cupertino, C ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS
... neurones while those carrying impulses away from CNS are called efferent neurones. ...
... neurones while those carrying impulses away from CNS are called efferent neurones. ...
07. Pons Internal Features 0102010-10-01 05:141.9
... • The efferent motor fibers of the nucleus run ventrally and leave the brain stem as the abducens nerve between the pons and the pyramid of the medulla • The internuclear neurons have axons that travel in the contralateral medial longitudinal fasciculus to the division of the oculomotor nucleus that ...
... • The efferent motor fibers of the nucleus run ventrally and leave the brain stem as the abducens nerve between the pons and the pyramid of the medulla • The internuclear neurons have axons that travel in the contralateral medial longitudinal fasciculus to the division of the oculomotor nucleus that ...
To Be or Not to Be … an Inhibitory Neurotransmitter
... “I’ve heard of dendrites and axons and stuff, but it never made much sense to me. Aren’t axons and dendrites just like wires that connect to each other using chemical signals?” Jessica answers: A. they use Morse code--where do you think that came from? B. cells have tiny metal wires going throughout ...
... “I’ve heard of dendrites and axons and stuff, but it never made much sense to me. Aren’t axons and dendrites just like wires that connect to each other using chemical signals?” Jessica answers: A. they use Morse code--where do you think that came from? B. cells have tiny metal wires going throughout ...
NEUROTRANSMISSION
... The exchange of information from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of another is called neurotransmission. Neurotransmission takes place through the release of chemicals into the space between the axon of the first neuron and the dendrites of the second neuron. These chemicals are called neuro ...
... The exchange of information from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of another is called neurotransmission. Neurotransmission takes place through the release of chemicals into the space between the axon of the first neuron and the dendrites of the second neuron. These chemicals are called neuro ...
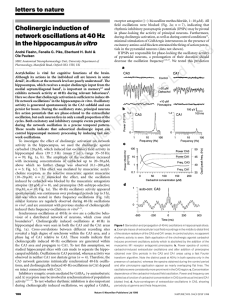
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... could be involved in the generation of the oscillations, and propagation to CA1 may depend on the excitatory Schaffer collateral input onto CA1 neurons. During 40-Hz oscillations in the hippocampus in vivo, individual pyramidal neurons do not fire action potentials at every cycle6. To analyse the fr ...
... could be involved in the generation of the oscillations, and propagation to CA1 may depend on the excitatory Schaffer collateral input onto CA1 neurons. During 40-Hz oscillations in the hippocampus in vivo, individual pyramidal neurons do not fire action potentials at every cycle6. To analyse the fr ...
Parietal cortex neurons of the monkey related to the visual guidance
... Microelectrode penetrations were made mainly in the posterior bank of the intraparietal sulcus. Eye movements were recorded using the magnetic search coil technique (Robinson 1963; Judge et al. 1980), monitored with an oscilloscope and sampled by the A/D converter every 10 ms (Fig. 1 EM). We used vi ...
... Microelectrode penetrations were made mainly in the posterior bank of the intraparietal sulcus. Eye movements were recorded using the magnetic search coil technique (Robinson 1963; Judge et al. 1980), monitored with an oscilloscope and sampled by the A/D converter every 10 ms (Fig. 1 EM). We used vi ...
The Nervous System
... Neuron Structure • A neuron is a specialized nerve cell that transfers messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. ...
... Neuron Structure • A neuron is a specialized nerve cell that transfers messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. ...
BIOL 105 S 2011 MTX 2 QA 110512.1
... 3) The three general functions of the nervous system are A) sensory, motor, and predictive. B) sensory, motor, and manipulative. C) sensory, motor, and integrative. D) reflexive, predictive, and motor. E) emotion, memory, and movement. Answer: C 6) The part of the peripheral nervous system that brin ...
... 3) The three general functions of the nervous system are A) sensory, motor, and predictive. B) sensory, motor, and manipulative. C) sensory, motor, and integrative. D) reflexive, predictive, and motor. E) emotion, memory, and movement. Answer: C 6) The part of the peripheral nervous system that brin ...
BIOL241 Lab tips Labs17-22
... Activity 3 is to learn the anatomy of the 12 cranial nerves, which can be studied from models or links. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP11504 The MAJOR part of Lab 19 is the SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION. Detailed info for this can be found in the Lab 19 handout. Tips for Lab 21- An ...
... Activity 3 is to learn the anatomy of the 12 cranial nerves, which can be studied from models or links. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP11504 The MAJOR part of Lab 19 is the SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION. Detailed info for this can be found in the Lab 19 handout. Tips for Lab 21- An ...
Chapter 12 - Las Positas College
... Tissue Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Tissue Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
LYRICA (pregabalin) eLearning System
... The somatic (or voluntary) nervous system allows interaction with the external environment. Its functions — such as movement of skeletal muscles — are under an individual's control. These nervous system divisions are schematically illustrated in Figure 1C. Figure 1C: Voluntary and Involuntary Nervou ...
... The somatic (or voluntary) nervous system allows interaction with the external environment. Its functions — such as movement of skeletal muscles — are under an individual's control. These nervous system divisions are schematically illustrated in Figure 1C. Figure 1C: Voluntary and Involuntary Nervou ...
Neurotransmitter Function
... The action potential is a local (usually dendritic) event Potential is propagated across the membrane (120meters/second). Parts of the axon covered by the myelin sheath cannot produce action potentials. The potential can jump along the length of the axon by Nodes of Ranvier via passive condu ...
... The action potential is a local (usually dendritic) event Potential is propagated across the membrane (120meters/second). Parts of the axon covered by the myelin sheath cannot produce action potentials. The potential can jump along the length of the axon by Nodes of Ranvier via passive condu ...
Identification of Mechanoafferent Neurons in Terrestrial Snail
... cutaneus secundus; Fig. 2A). In addition, the Pl4 neuron had a second axon branch that projected into the cerebral ganglion through the pleurocerebral connective (n ⫽ 5, Fig. 2B). In two cases, axons from the pleural sensory neurons were traced to the skin. ...
... cutaneus secundus; Fig. 2A). In addition, the Pl4 neuron had a second axon branch that projected into the cerebral ganglion through the pleurocerebral connective (n ⫽ 5, Fig. 2B). In two cases, axons from the pleural sensory neurons were traced to the skin. ...
F-Spondin Is Required for Accurate Pathfinding of Commissural
... (D) Immunolocalization of F-spondin protein with the R5 Ab (same section as in [C]). The protein is localized in the basal membrane that underlies the floor plate, around the notochord and in the basal membrane that ensheaths the peripheral nerve. Scale bar, 50 mm. (E) E14 rat ventral spinal cord im ...
... (D) Immunolocalization of F-spondin protein with the R5 Ab (same section as in [C]). The protein is localized in the basal membrane that underlies the floor plate, around the notochord and in the basal membrane that ensheaths the peripheral nerve. Scale bar, 50 mm. (E) E14 rat ventral spinal cord im ...
Dendritic Signal Integration
... now serves as the foundation for modern computer modeling of neurons with dendritic trees. Such models are now being used to provide insight into how charge spreads in elaborately branching dendritic trees containing many different types of ion channels. Another way that dendrites influence EPSPs is ...
... now serves as the foundation for modern computer modeling of neurons with dendritic trees. Such models are now being used to provide insight into how charge spreads in elaborately branching dendritic trees containing many different types of ion channels. Another way that dendrites influence EPSPs is ...
nerve part 1
... Axonal Transport • Transport of materials in the axons can be done by 2 mechansims; ...
... Axonal Transport • Transport of materials in the axons can be done by 2 mechansims; ...
ling411-11-Columns - OWL-Space
... II, III – pyramidal neurons of these layers project to other cortical areas IV – spiny stellate cells, receive activation from thalamus and transmit it to other neurons of same column V, VI – pyramidal neurons of these layers project to subcortical areas Various kinds of inhibitory neurons a ...
... II, III – pyramidal neurons of these layers project to other cortical areas IV – spiny stellate cells, receive activation from thalamus and transmit it to other neurons of same column V, VI – pyramidal neurons of these layers project to subcortical areas Various kinds of inhibitory neurons a ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.