Chapter Four
... outside of the membrane is positively charged (and the inside is negatively charged) because the axon contains ions. When the axon is resting, its ion channels are closed, so ions cannot move in or out of the axon. An action potential is caused by the opening of some ion channels in the membrane at ...
... outside of the membrane is positively charged (and the inside is negatively charged) because the axon contains ions. When the axon is resting, its ion channels are closed, so ions cannot move in or out of the axon. An action potential is caused by the opening of some ion channels in the membrane at ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/nervous system tea
... Specialized cells that myelinate the axons of neurons found in the PNS. (Honors) 11. What is a Synapse? Junction or point of close contact between neurons. 12. What are Nodes of Ranvier? Spaces in the myelin sheath between schwann cells. 13. What are Ganglia? (Honors) Collection(clumps) of nerve cel ...
... Specialized cells that myelinate the axons of neurons found in the PNS. (Honors) 11. What is a Synapse? Junction or point of close contact between neurons. 12. What are Nodes of Ranvier? Spaces in the myelin sheath between schwann cells. 13. What are Ganglia? (Honors) Collection(clumps) of nerve cel ...
Scoring Rubric
... The nervous system is a critical system that sends signals throughout the body to coordinate movements and actions. It allows communication throughout your body and contains the brain, spinal cord and a large network of nerves. In total, your nervous system is made of 85 billion nerve cells called n ...
... The nervous system is a critical system that sends signals throughout the body to coordinate movements and actions. It allows communication throughout your body and contains the brain, spinal cord and a large network of nerves. In total, your nervous system is made of 85 billion nerve cells called n ...
How your brain and nervous system work
... • Recall that the gap between neurones is called a synapse. • Describe how an impulse triggers the release of a transmitter substance in a synapse and how it diffuses across to bind with receptor molecules in the membrane of the next neurone causing the impulse to continue. ...
... • Recall that the gap between neurones is called a synapse. • Describe how an impulse triggers the release of a transmitter substance in a synapse and how it diffuses across to bind with receptor molecules in the membrane of the next neurone causing the impulse to continue. ...
Physiology2 - Sheet#2 - Dr.Loai Alzgoul
... Physiology of sensory system : Sensation is transmitted from the PNS by the peripheral nerves to the spinal cord then up to the cortex. There are many spinal nerves, and each pair is connected to a vertebra (C2, C3, C4, L1, L2 … etc). When each spinal nerve enters the spinal cord it divides into: ...
... Physiology of sensory system : Sensation is transmitted from the PNS by the peripheral nerves to the spinal cord then up to the cortex. There are many spinal nerves, and each pair is connected to a vertebra (C2, C3, C4, L1, L2 … etc). When each spinal nerve enters the spinal cord it divides into: ...
BOX 5.2 GOLDMAN-HODGKIN-KATZ EQUATION An equation
... The relative contribution of each ion is determined by its concentration differences across the membrane and the relative permeability (pK, pNa, pCl) of the membrane to each type of ion. If a membrane is permeable to only one ion, then the Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz equation reduces to the Nernst equation ...
... The relative contribution of each ion is determined by its concentration differences across the membrane and the relative permeability (pK, pNa, pCl) of the membrane to each type of ion. If a membrane is permeable to only one ion, then the Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz equation reduces to the Nernst equation ...
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY Zsolt Liposits and Imre Kalló 2016
... centers. Descending pathways are also described, which bring information from supraspinal centers. One has gained sufficient knowledge, if understands and can explain the followings: 1) The development of the central nervous system from a tube-like structure, the wall of which host initially stem ce ...
... centers. Descending pathways are also described, which bring information from supraspinal centers. One has gained sufficient knowledge, if understands and can explain the followings: 1) The development of the central nervous system from a tube-like structure, the wall of which host initially stem ce ...
The Nervous System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... • Dendrites: receive stimuli or impulses from other nuerons and transmit info to soma. • Sensory components feel things like heat and cold • Very short and branched • Axons: Conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body to another neuron. Have single, long body with branches at end. • Secondary cel ...
... • Dendrites: receive stimuli or impulses from other nuerons and transmit info to soma. • Sensory components feel things like heat and cold • Very short and branched • Axons: Conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body to another neuron. Have single, long body with branches at end. • Secondary cel ...
Neuron is the basic working unit of the nervous system, specialized
... gland is composed of two lobes and secretes several different hormones that regulate the activity of other endocrine organs throughout the body. PONS ‐ A part of the hindbrain that, with other brain structures, controls respiration and regulates heart rhythms. The pons is a major route by which ...
... gland is composed of two lobes and secretes several different hormones that regulate the activity of other endocrine organs throughout the body. PONS ‐ A part of the hindbrain that, with other brain structures, controls respiration and regulates heart rhythms. The pons is a major route by which ...
The Nervous System
... • Dendrites: receive stimuli or impulses from other nuerons and transmit info to soma. • Sensory components feel things like heat and cold • Very short and branched • Axons: Conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body to another neuron. Have single, long body with branches at end. • Secondary cel ...
... • Dendrites: receive stimuli or impulses from other nuerons and transmit info to soma. • Sensory components feel things like heat and cold • Very short and branched • Axons: Conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body to another neuron. Have single, long body with branches at end. • Secondary cel ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Twelve
... This part, I love. Mater, of course is mother. The names of the layers of protection demonstrate each facet of the mother’s personality. On the outside you have the Dura mater which is the strong mother. A double thickness wraps around the outside of the brain and then a single thickness around the ...
... This part, I love. Mater, of course is mother. The names of the layers of protection demonstrate each facet of the mother’s personality. On the outside you have the Dura mater which is the strong mother. A double thickness wraps around the outside of the brain and then a single thickness around the ...
Sensory Pathways
... of Lissauer (posterolateral funiculus) by way of the lat. div. of dorsal root and terminates in the dorsal grey horn. Thinly myelinated (Ad) fibers (for fast sharp pain) and unmyelinated ...
... of Lissauer (posterolateral funiculus) by way of the lat. div. of dorsal root and terminates in the dorsal grey horn. Thinly myelinated (Ad) fibers (for fast sharp pain) and unmyelinated ...
Notes Chapter 50 Nervous and Sensory Systems
... Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves each consist of a dorsal root containing sensory neurons and a ventral root containing motor neurons. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) links the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The PNS is composed of a sensory division and a motor division. ...
... Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves each consist of a dorsal root containing sensory neurons and a ventral root containing motor neurons. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) links the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The PNS is composed of a sensory division and a motor division. ...
to get the file
... Electrotonic Signal Propagation: The potential decays along a dendrite (or axon) according to the distance from the current injection site. At every location the temporal response follows an exponential but with ever decreasing amplitude. If plotting only the maxima against the distance then you wi ...
... Electrotonic Signal Propagation: The potential decays along a dendrite (or axon) according to the distance from the current injection site. At every location the temporal response follows an exponential but with ever decreasing amplitude. If plotting only the maxima against the distance then you wi ...
“Using light to dissect and direct cellular organization and dynamics”
... engineered a system to control the transport and positioning of intracellular components with light. This allows us to directly explore the functional consequences of organelle mislocalization. In addition, we have engineered novel probes for the super-resolution imaging of microtubules, the intrace ...
... engineered a system to control the transport and positioning of intracellular components with light. This allows us to directly explore the functional consequences of organelle mislocalization. In addition, we have engineered novel probes for the super-resolution imaging of microtubules, the intrace ...
Clinicals - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... NGF. Oligodendrocytes don’t form guide tubes like Schwann cell in PNS. Gliosis causes glial scar that acts as a barrier to growth. ...
... NGF. Oligodendrocytes don’t form guide tubes like Schwann cell in PNS. Gliosis causes glial scar that acts as a barrier to growth. ...
4Central Nervous System (CNS)
... Associated with ____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Brain – Cerebellum Second largest part of the human brain _____________________________________________ to produce coordinated movements so tha ...
... Associated with ____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Brain – Cerebellum Second largest part of the human brain _____________________________________________ to produce coordinated movements so tha ...
to Psychology 3
... - although neurons are diverse in form, the typical neuron posseses (1) a soma - or cell body which contains the nucleus and other standard organelles, (2) dendrites - branch-like structures connected to the soma which receive signals, (3) an axon - "a long, thin fiber that transmits signals away fr ...
... - although neurons are diverse in form, the typical neuron posseses (1) a soma - or cell body which contains the nucleus and other standard organelles, (2) dendrites - branch-like structures connected to the soma which receive signals, (3) an axon - "a long, thin fiber that transmits signals away fr ...
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
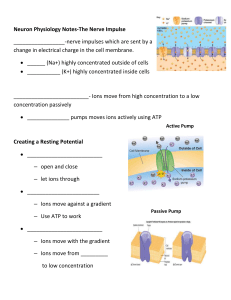
Neuron Physiology Notes
... potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) which causes “trigger zo ...
... potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) which causes “trigger zo ...
The Nervous System - Marshall Middle
... neuron usually has several dendrites. 3. Axon: a nerve fiber that carries messages away from the cell body. There is only one axon for each neuron. Some axons are surrounded by a fatty covering called a myelin sheath that protects the axon and allows impulses to travel faster along the axon. 4. Syna ...
... neuron usually has several dendrites. 3. Axon: a nerve fiber that carries messages away from the cell body. There is only one axon for each neuron. Some axons are surrounded by a fatty covering called a myelin sheath that protects the axon and allows impulses to travel faster along the axon. 4. Syna ...
Exam 5 - Spring13 - Take home
... 13. In the popular press, you may hear the statement that “M.S. is a disease that attacks the nerves.” Is this a true statement? Briefly explain. 14. If you had a brain tumor that affected the cerebral cortex and the neurosurgeon said she was going to operate based on textbook descriptions of the lo ...
... 13. In the popular press, you may hear the statement that “M.S. is a disease that attacks the nerves.” Is this a true statement? Briefly explain. 14. If you had a brain tumor that affected the cerebral cortex and the neurosurgeon said she was going to operate based on textbook descriptions of the lo ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... DENDRITE - A treelike extension of the neuron cell body. The dendrite is the primary site for receiving and integrating information from other neurons. DOPAMINE - A catecholamine neurotransmitter known to have varied functions depending on where it acts. Dopamine-containing neurons in the substantia ...
... DENDRITE - A treelike extension of the neuron cell body. The dendrite is the primary site for receiving and integrating information from other neurons. DOPAMINE - A catecholamine neurotransmitter known to have varied functions depending on where it acts. Dopamine-containing neurons in the substantia ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.