distribution of leucine-3h during axoplasmic
... the hypothesis that microtubules are related to axonal transport . In small, vesicle-filled nerve terminals in the blastema, labeled material was restricted to a thin zone a short distance beneath the plasma membrane while the central region of the terminal was largely unlabeled . The peripheral pat ...
... the hypothesis that microtubules are related to axonal transport . In small, vesicle-filled nerve terminals in the blastema, labeled material was restricted to a thin zone a short distance beneath the plasma membrane while the central region of the terminal was largely unlabeled . The peripheral pat ...
Powerpoint
... The three smallest bones in the body, the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup, are in the middle ear. The hammer gets the vibrations from the eardrum, then sends them to the anvil. The anvil passes the vibrations to the stirrup. The stirrup passes the vibrations to the inner ear. ...
... The three smallest bones in the body, the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup, are in the middle ear. The hammer gets the vibrations from the eardrum, then sends them to the anvil. The anvil passes the vibrations to the stirrup. The stirrup passes the vibrations to the inner ear. ...
Ion Channels and Neuronal Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis
... changes are responsible for cerebellar ataxia in these mutants.15 To determine whether different subtypes of sodium channels are expressed in Purkinje cells in demyelinating disorders, Black et al6 first studied the taiep rat, a mutant in which myelin is formed normally but subsequently degenerates ...
... changes are responsible for cerebellar ataxia in these mutants.15 To determine whether different subtypes of sodium channels are expressed in Purkinje cells in demyelinating disorders, Black et al6 first studied the taiep rat, a mutant in which myelin is formed normally but subsequently degenerates ...
Concepts and functions - Pécsi Tudományegyetem
... The cell types that make up nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglia. Neurons come in many shapes and sizes. There are billions of them in a human brain. Basically they have a cell body that contains the nucleus surrounded by cytoplasmic elements for protein synthesis and energy production. There ar ...
... The cell types that make up nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglia. Neurons come in many shapes and sizes. There are billions of them in a human brain. Basically they have a cell body that contains the nucleus surrounded by cytoplasmic elements for protein synthesis and energy production. There ar ...
test1 - Scioly.org
... Which of the following does not match its function? Astrocytes: signaling changes to the neurons Microglia: cleaning out debris Oligodendrocytes: protections and insulation Ependymal cells: circulating cerebrospinal fluid ...
... Which of the following does not match its function? Astrocytes: signaling changes to the neurons Microglia: cleaning out debris Oligodendrocytes: protections and insulation Ependymal cells: circulating cerebrospinal fluid ...
Chapter 11 Nervous System parts 1 and 2
... Phagocytes that monitor the health of neurons by breaking down invading microorganisms and dead ...
... Phagocytes that monitor the health of neurons by breaking down invading microorganisms and dead ...
THALAMUS
... subsequently shifts these neurons to the single-spike mode of action potential generation. Similarly, activation of alfa1-adrenergic, 5-HT2 receptors, mGluR receptors has similar effect in the thalamic reticular neurons (McCormick, 1997). 2. In contrast, activation of muscarinic receptors in the tha ...
... subsequently shifts these neurons to the single-spike mode of action potential generation. Similarly, activation of alfa1-adrenergic, 5-HT2 receptors, mGluR receptors has similar effect in the thalamic reticular neurons (McCormick, 1997). 2. In contrast, activation of muscarinic receptors in the tha ...
Nervous System
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
Spinal Cord Anatomy - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... • Without stimulation, muscles atrophy. • When only UMN of primary motor cortex is damaged • spastic paralysis occurs - muscles affected by persistent spasms and exaggerated tendon reflexes • Muscles remain healthy longer but their movements are no longer subject to voluntary control. • Muscles comm ...
... • Without stimulation, muscles atrophy. • When only UMN of primary motor cortex is damaged • spastic paralysis occurs - muscles affected by persistent spasms and exaggerated tendon reflexes • Muscles remain healthy longer but their movements are no longer subject to voluntary control. • Muscles comm ...
CH 8 Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Chuck was not seriously injured, but when he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because A. sensory memory had not been converted to short-term memory. B. short-term memory had not been converted to sensory memory. C. he lost both sensory and short- ...
... Chuck was not seriously injured, but when he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because A. sensory memory had not been converted to short-term memory. B. short-term memory had not been converted to sensory memory. C. he lost both sensory and short- ...
Nervous system Sense cells and organs
... All animal except Porifera have some type of nervous system Nerve tissue: secondary tissue (as muscle tissues) Nerve cells or neurons evolved in conjunction with muscle: For animals to move in response to stimuli, they must coordinate their body movements through muscle contraction ...
... All animal except Porifera have some type of nervous system Nerve tissue: secondary tissue (as muscle tissues) Nerve cells or neurons evolved in conjunction with muscle: For animals to move in response to stimuli, they must coordinate their body movements through muscle contraction ...
Passive Conduction - Cable Theory
... Theoretical models describing propagation of synaptic potentials have evolved significantly over the past century. Synaptic potentials are the root of neural activity, electrical potential differences caused by fluxes of biological ions across the neural membrane. The first important breakthrough ca ...
... Theoretical models describing propagation of synaptic potentials have evolved significantly over the past century. Synaptic potentials are the root of neural activity, electrical potential differences caused by fluxes of biological ions across the neural membrane. The first important breakthrough ca ...
Spinal Cord - Lamont High
... Spinal Cord Contains 2 types of nerve tissue---gray and white matter ...
... Spinal Cord Contains 2 types of nerve tissue---gray and white matter ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... A lot of what we do as computational neuroscientists is turn experimental observations into equations. The goal here is to understand how networks or single neurons work. We should always keep in mind that: a) this is less than ideal, b) we’re really after the big picture: how the brain works. ...
... A lot of what we do as computational neuroscientists is turn experimental observations into equations. The goal here is to understand how networks or single neurons work. We should always keep in mind that: a) this is less than ideal, b) we’re really after the big picture: how the brain works. ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
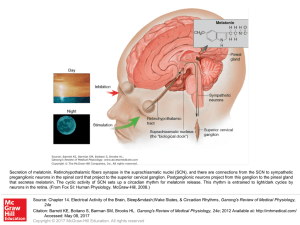
... Secretion of melatonin. Retinohypothalamic fibers synapse in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and there are connections from the SCN to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord that project to the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic neurons project from this ganglion to the pinea ...
... Secretion of melatonin. Retinohypothalamic fibers synapse in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and there are connections from the SCN to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord that project to the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic neurons project from this ganglion to the pinea ...
A horizontal spinal cord slice preparation for studying descending
... synaptic transmission in spinal neurons have concentrated on inputs from two sources; those from primary afferents and local circuit neurons. This focus is due largely to practical considerations. For example, peripheral inputs can be readily activated by stimulation of dorsal roots that often remai ...
... synaptic transmission in spinal neurons have concentrated on inputs from two sources; those from primary afferents and local circuit neurons. This focus is due largely to practical considerations. For example, peripheral inputs can be readily activated by stimulation of dorsal roots that often remai ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... the dendrites, axon, or cell body of the postsynaptic neuron. This binding of neurotransmitters creates a depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron stimulating an action potential and allowing the message to move on. ...
... the dendrites, axon, or cell body of the postsynaptic neuron. This binding of neurotransmitters creates a depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron stimulating an action potential and allowing the message to move on. ...
The Nervous System
... •This gland is a big player in puberty, ultimately producing sperm in males and eggs in females • This little gland also plays a role with lots of other hormones, like ones that control the amount of sugars and water in your body. And it ...
... •This gland is a big player in puberty, ultimately producing sperm in males and eggs in females • This little gland also plays a role with lots of other hormones, like ones that control the amount of sugars and water in your body. And it ...
7-6_TheGenOfSpecResp_MajorosMyrtill
... The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic, postural reflex that among the others works against the gravity force. First of all it is important to mention that muscles are attached to tendons which hold them to the bone. At the attachment of the muscles to tendons there is a muscle spindle which is very s ...
... The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic, postural reflex that among the others works against the gravity force. First of all it is important to mention that muscles are attached to tendons which hold them to the bone. At the attachment of the muscles to tendons there is a muscle spindle which is very s ...
Nervous System - Napa Valley College
... won’t open. The level of the action potential is always the same. The direction is always one way down the axon. The sodium channels are inactivated for awhile after the action ...
... won’t open. The level of the action potential is always the same. The direction is always one way down the axon. The sodium channels are inactivated for awhile after the action ...
Slide ()
... excitatory input from the ipsilateral cochlear nucleus (CN) and inhibitory input from the contralateral cochlear nucleus. A coronal section through the brain stem of a cat illustrates the anatomical connections. Small spherical bushy cells and stellate cells in the ipsilateral ventral cochlear nucle ...
... excitatory input from the ipsilateral cochlear nucleus (CN) and inhibitory input from the contralateral cochlear nucleus. A coronal section through the brain stem of a cat illustrates the anatomical connections. Small spherical bushy cells and stellate cells in the ipsilateral ventral cochlear nucle ...
Slide 1
... propagate in unmyelinated axons through the depolarization of adjacent regions of membrane. In the illustrated axon, region 2 is undergoing depolarization during the generation of the action potential, whereas region 3 has already generated the action potential and is now hyperpolarized. The action ...
... propagate in unmyelinated axons through the depolarization of adjacent regions of membrane. In the illustrated axon, region 2 is undergoing depolarization during the generation of the action potential, whereas region 3 has already generated the action potential and is now hyperpolarized. The action ...
notes as
... synapse it causes vesicles of transmitter chemical to be released – There are several kinds of transmitter • The transmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that all ...
... synapse it causes vesicles of transmitter chemical to be released – There are several kinds of transmitter • The transmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that all ...
Laboratory 9: Pons to Midbrain MCB 163 Fall 2005 Slide #108 1
... superficial layer receives projections from retinal ganglion cells. Evidence for local circuits within this layer include behaviors such as the orienting response to auditory stimuli, and saccadic responses to visual stimuli. A main sense of cortical input to the superior colliculus is the frontal e ...
... superficial layer receives projections from retinal ganglion cells. Evidence for local circuits within this layer include behaviors such as the orienting response to auditory stimuli, and saccadic responses to visual stimuli. A main sense of cortical input to the superior colliculus is the frontal e ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.